一、代码使用样例
通过CountDownLatch实现:"主线程"等待"5个子线程"全部都完成"指定的工作(休眠1000ms)"之后,再继续运行。
import java.util.concurrent.CountDownLatch;
public class CountDownLatchTest {
private static CountDownLatch latch = new CountDownLatch(5);
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("Main Thread start....");
System.out.println();
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
new InnerThread().start();
}
try {
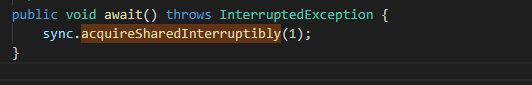
latch.await();
System.out.println();
System.out.println("Main Thread latch.getCount = " + latch.getCount());
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
System.out.println("Exception happened in latch await: " + e);
}
System.out.println("Main Thread end....");
}
static class InnerThread extends Thread {
public void run() {
synchronized (InnerThread.class) {
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " sleep 1000 ms.");
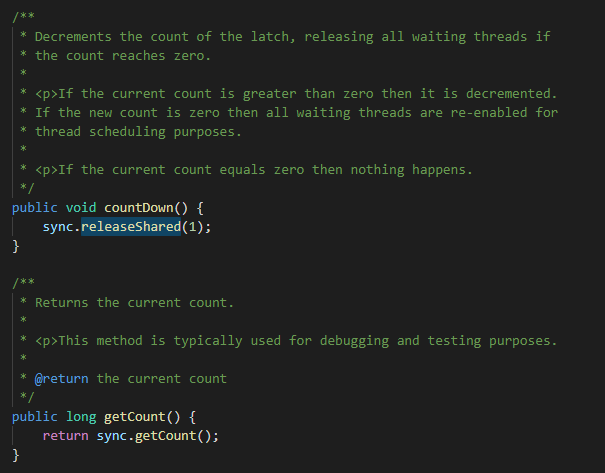
// 将CountDownLatch的数值减1
latch.countDown();
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " count number: " + latch.getCount());
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
}
执行结果: 主线程等待,直至 latch 通过 countDown 减为0后,主线程才继续执行。
Main Thread start....
Thread-1 sleep 1000 ms.
Thread-1 count number: 4
Thread-4 sleep 1000 ms.
Thread-4 count number: 3
Thread-0 sleep 1000 ms.
Thread-0 count number: 2
Thread-3 sleep 1000 ms.
Thread-3 count number: 1
Thread-2 sleep 1000 ms.
Thread-2 count number: 0
Main Thread latch.getCount = 0
Main Thread end....
二、常用方法解读
// 构造一个用给定计数初始化的 CountDownLatch。 CountDownLatch(int count) // 使当前线程在锁存器倒计数至零之前一直等待,除非线程被中断。 void await() // 使当前线程在锁存器倒计数至零之前一直等待,除非线程被中断或超出了指定的等待时间。 boolean await(long timeout, TimeUnit unit) // 递减锁存器的计数,如果计数到达零,则释放所有等待的线程。 void countDown() // 返回当前计数。 long getCount() // 返回标识此锁存器及其状态的字符串。 String toString()
三、源码解读
可以看出countDownLatch内部实现通过继承自AQS的Sync对象来实现。
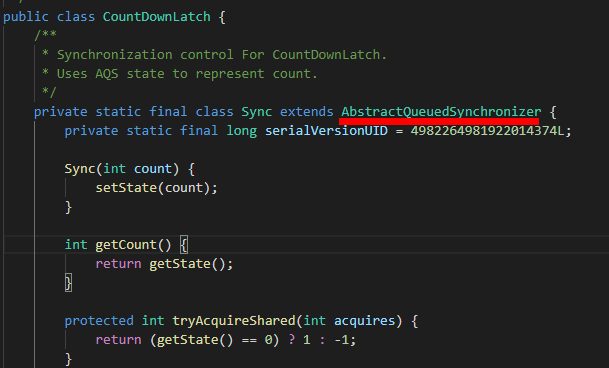
构造方法:
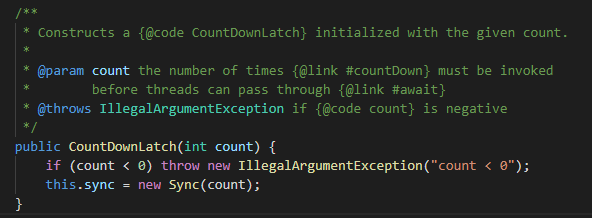
countDown等方法均与Sync类定义有关