游戏规则
该游戏的规则与实际的玩法应该有点差异,因为我没有去细查21点的确切玩法,只是根据印象中进行了一系列的定义,具体如下:
1.玩家为人类玩家与电脑玩家,共2个玩家。电脑为庄家。
2.先给人类玩家与电脑玩家分别发两张牌作为底牌。
3.判断双方底牌是否为blackjack,如果一方为blackjack则直接判胜利,并在总分中记上一分。如果双方均为blackjack,则判双方平局,均不得分
4.如果没有出现blackjack的情况,人类玩家根据牌面决定是否要牌,若要牌则得到牌堆的一张牌,并再次判断。如果人类牌面的点数超过21点,则直接判负。
5.如果人类玩家停止要牌,且未因为超过21点而判负,则电脑要牌(电脑的要牌基于一个算法,后期如果更新,这个算法要基于对胜率的估算),电脑停止要牌后,判断与人类的输赢情况。赢者加一分。
6.人类玩家决定是否继续下一轮,如果继续,则从剩余牌堆中继续发牌开始上述过程。如果不继续,则计算总分,判断谁胜出。
7.如果牌堆的牌已经不够玩一轮的话,自动判断游戏结束。人类可以选择是否重新再玩。
程序功能
要实现上面游戏的规则,程序的功能进行划分如下,不同的功能用不同的函数来实现,以达到代码的复用。
1.牌堆:在发牌的过程中,牌堆中会去除已经发出的牌
2.发牌:要牌的时候,需要从牌堆随机抽取一张牌
3.计分:能对手中的牌的分数进行计算,其中需要考虑靠A的特殊性
4.胜负判断:当结束要牌的时候,能通过分数判断胜负
5.要牌与否:一个让你判断是否继续要牌的功能
6.游戏结束判断:让你决定是否提前结束游戏,如果不提前结束,则在牌堆中牌的数量比较少的时候,自动结束游戏
7.一局游戏的过程

//角色类
class Role:
def __init__(self):
"""初始化方法"""
# 定义列表,用来保存当前角色手中的牌,初始牌为空,保存的类型为Card对象
self.cards = []
# 向控制台打印手中所有的牌
def show_card(self, style=0, show=True):
lastpos = len(self.cards) - 1
if style == 1:
msg = '你拥有的牌:'
else:
msg = '庄家的牌:'
cardSow = ''
for i, card in enumerate(self.cards):
if show:
if i < lastpos:
cardSow = cardSow + (card.card_tpye + card.card_text) + ','
else:
cardSow = cardSow + (card.card_tpye + card.card_text)
else:
if i < lastpos:
cardSow = cardSow + (card.card_tpye + card.card_text) + ','
else:
cardSow = cardSow + ' ?\n'
print(msg + cardSow, sep='', end='')
# 打印当前角色手中所有牌之后,在进行换行。
print()
def get_value(self):
"""获取当前角色牌的点数(分为最小值和最大值)
"""
Score = 0
Have_Ace = False
for card in self.cards:
Score += card.card_value
for i in self.cards:
if i.card_text == 'A':
Have_Ace = True
break
else:
continue
if Have_Ace:
if Score + 10 <= 21:
Score = Score + 10
return Score
def clear_card(self):
# 清空牌,重新开始
self.cards = []

//牌类
class Card:
def __init__(self, card_tpye, card_text, card_value):
"""初始化方法
Parameters
---------
card_type:str
牌的类型:(红桃,黑桃,梅花,方片)
card_text:str
牌面显示的文本(A,K,Q,J)
card_value:int
牌面的真实值(例如A为1点或11点,K为10点)
"""
self.card_tpye = card_tpye
self.card_text = card_text
self.card_value = card_value

//牌管理类
class CardManager:
"""管理一整副扑克牌,并且能够进行发牌"""
def __init__(self):
"""初始化方法"""
# 用来保存一整副52张扑克牌
self.cards = []
# 定义所有牌的花色类型
all_card_type = "♥♠♣♦"
all_card_text = ["A", "K", "Q", "J", "10", "9", "8", "7", "6", "5", "4", "3", "2"]
all_card_value = [11, 10, 10, 10, 10, 9, 8, 7, 6, 5, 4, 3, 2]
# 对牌面类型、牌面值、牌面文本嵌套循环
for card_type in all_card_type:
for index, card_text in enumerate(all_card_text):
card = Card(card_type, card_text, all_card_value[index])
self.cards.append(card)
# 洗牌
random.shuffle(self.cards)
def getCard(self):
return self.cards
# 发牌
def send_card(self, role, num=1):
"""给电脑或玩家发牌,
Parameters
------
role:Role
电脑或玩家
num:int
发牌的数量,默认1张
"""
for i in range(num):
card = self.cards.pop()
role.cards.append(card)

//游戏管理类
class GameManager:
def __init__(self):
# 创建扑克牌管理器类
self.cards = CardManager()
# 创建玩家角色
self.player = Role()
# 创建电脑角色
self.computer = Role()
self.total_score = np.array([0, 0]) # 总分的计分器
def start_game(self):
Round = 1
while len(self.cards.getCard()) > 10:
self.player.clear_card()
self.computer.clear_card()
input('开始, good luck...<<Enter>>\n')
print(f'第 {Round} 轮:')
print('.' * 60)
score = self.one_round()
self.total_score += score
print(f'总分数:{self.total_score[0]}:{self.total_score[1]}')
Round += 1
self.continue_or_quit()
def judgement(self, your_score, pc_score):
# 结束要牌的时候,计算双方的点数,判断输赢
if your_score > 21 and pc_score > 21:
print(f'平局,分数: {your_score}:{pc_score}')
return np.array([0, 0])
elif your_score > 21 and pc_score <= 21:
print(f'你输了,分数: {your_score}:{pc_score}')
return np.array([0, 1])
elif your_score <= 21 and pc_score > 21:
print(f'你赢了,分数: {your_score}:{pc_score}')
return np.array([1, 0])
elif your_score <= 21 and pc_score <= 21:
if your_score < pc_score:
print(f'你输了,分数: {your_score}:{pc_score}')
return np.array([0, 1])
elif your_score > pc_score:
print(f'你赢了,分数: {your_score}:{pc_score}')
return np.array([1, 0])
else:
print(f'平局,分数: {your_score}:{pc_score}')
return np.array([0, 0])
def one_round(self):
# 一个回合的游戏
self.cards.send_card(self.player, 2)
self.cards.send_card(self.computer, 2)
self.player.show_card(1)
self.computer.show_card(0, False)
score = np.array([self.player.get_value(), self.computer.get_value()])
if score[0] == 21 or score[1] == 21:
print('BlackJack 21点直接获胜')
return self.judgement(score[0], score[1])
else:
while score[0] <= 21:
Get_New_Poker = self.hit_or_stand()
# 要了一张牌
if Get_New_Poker:
self.player.show_card(1)
self.computer.show_card(0, False)
score[0] = self.player.get_value()
if score[0] > 21:
print('你超过21点')
self.computer.show_card(0)
print()
return self.judgement(score[0], score[1])
else:
continue
elif not Get_New_Poker:
# npc点数比玩家低,则要牌
while score[1] < score[0]:
self.cards.send_card(self.computer)
score[1] = self.computer.get_value()
self.player.show_card(1)
self.computer.show_card(0)
print()
return self.judgement(score[0], score[1])
else:
continue
def hit_or_stand(self):
# 玩家需要判断是否继续叫牌
AskPoker = input('是否叫牌? 【Y/N】>>:')
if AskPoker.upper() == 'Y':
print()
self.cards.send_card(self.player)
return True
elif AskPoker.upper() == 'N':
print('你没加牌.')
print()
return False
else:
print('输入错误 Y/y or N/n!>>')
return self.hit_or_stand()
def continue_or_quit(self):
# 在每一轮结束后,判断是否继续下一轮的游戏。当牌堆里面牌的数目不足的时候,自动停止游戏
NextRound = input('是否继续? 【Y/N】>>')
if NextRound.upper() == 'Y':
if len(self.cards.getCard()) < 10:
print('牌不够了')
input('Game Over')
exit(1)
else:
return True
elif NextRound.upper() == 'N':
input('Game Over')
exit(1)
else:
print('输入有误')
self.continue_or_quit()

//完整代码
import random
import numpy as np
from sys import exit
class Role:
def __init__(self):
"""初始化方法"""
# 定义列表,用来保存当前角色手中的牌,初始牌为空,保存的类型为Card对象
self.cards = []
# 向控制台打印手中所有的牌
def show_card(self, style=0, show=True):
lastpos = len(self.cards) - 1
if style == 1:
msg = '你拥有的牌:'
else:
msg = '庄家的牌:'
cardSow = ''
for i, card in enumerate(self.cards):
if show:
if i < lastpos:
cardSow = cardSow + (card.card_tpye + card.card_text) + ','
else:
cardSow = cardSow + (card.card_tpye + card.card_text)
else:
if i < lastpos:
cardSow = cardSow + (card.card_tpye + card.card_text) + ','
else:
cardSow = cardSow + ' ?\n'
print(msg + cardSow, sep='', end='')
# 打印当前角色手中所有牌之后,在进行换行。
print()
def get_value(self):
"""获取当前角色牌的点数(分为最小值和最大值)
"""
Score = 0
Have_Ace = False
for card in self.cards:
Score += card.card_value
for i in self.cards:
if i.card_text == 'A':
Have_Ace = True
break
else:
continue
if Have_Ace:
if Score + 10 <= 21:
Score = Score + 10
return Score
def clear_card(self):
# 清空牌,重新开始
self.cards = []
class Card:
def __init__(self, card_tpye, card_text, card_value):
"""初始化方法
Parameters
---------
card_type:str
牌的类型:(红桃,黑桃,梅花,方片)
card_text:str
牌面显示的文本(A,K,Q,J)
card_value:int
牌面的真实值(例如A为1点或11点,K为10点)
"""
self.card_tpye = card_tpye
self.card_text = card_text
self.card_value = card_value
class CardManager:
"""管理一整副扑克牌,并且能够进行发牌"""
def __init__(self):
"""初始化方法"""
# 用来保存一整副52张扑克牌
self.cards = []
# 定义所有牌的花色类型
all_card_type = "♥♠♣♦"
all_card_text = ["A", "K", "Q", "J", "10", "9", "8", "7", "6", "5", "4", "3", "2"]
all_card_value = [11, 10, 10, 10, 10, 9, 8, 7, 6, 5, 4, 3, 2]
# 对牌面类型、牌面值、牌面文本嵌套循环
for card_type in all_card_type:
for index, card_text in enumerate(all_card_text):
card = Card(card_type, card_text, all_card_value[index])
self.cards.append(card)
# 洗牌
random.shuffle(self.cards)
def getCard(self):
return self.cards
# 发牌
def send_card(self, role, num=1):
"""给电脑或玩家发牌,
Parameters
------
role:Role
电脑或玩家
num:int
发牌的数量,默认1张
"""
for i in range(num):
card = self.cards.pop()
role.cards.append(card)
"""
游戏管理类,检测用户输入,分数判断等
"""
class GameManager:
def __init__(self):
# 创建扑克牌管理器类
self.cards = CardManager()
# 创建玩家角色
self.player = Role()
# 创建电脑角色
self.computer = Role()
self.total_score = np.array([0, 0]) # 总分的计分器
def start_game(self):
Round = 1
while len(self.cards.getCard()) > 10:
self.player.clear_card()
self.computer.clear_card()
input('开始, good luck...<<Enter>>\n')
print(f'第 {Round} 轮:')
print('.' * 60)
score = self.one_round()
self.total_score += score
print(f'总分数:{self.total_score[0]}:{self.total_score[1]}')
Round += 1
self.continue_or_quit()
def judgement(self, your_score, pc_score):
# 结束要牌的时候,计算双方的点数,判断输赢
if your_score > 21 and pc_score > 21:
print(f'平局,分数: {your_score}:{pc_score}')
return np.array([0, 0])
elif your_score > 21 and pc_score <= 21:
print(f'你输了,分数: {your_score}:{pc_score}')
return np.array([0, 1])
elif your_score <= 21 and pc_score > 21:
print(f'你赢了,分数: {your_score}:{pc_score}')
return np.array([1, 0])
elif your_score <= 21 and pc_score <= 21:
if your_score < pc_score:
print(f'你输了,分数: {your_score}:{pc_score}')
return np.array([0, 1])
elif your_score > pc_score:
print(f'你赢了,分数: {your_score}:{pc_score}')
return np.array([1, 0])
else:
print(f'平局,分数: {your_score}:{pc_score}')
return np.array([0, 0])
def one_round(self):
# 一个回合的游戏
self.cards.send_card(self.player, 2)
self.cards.send_card(self.computer, 2)
self.player.show_card(1)
self.computer.show_card(0, False)
score = np.array([self.player.get_value(), self.computer.get_value()])
if score[0] == 21 or score[1] == 21:
print('BlackJack 21点直接获胜')
return self.judgement(score[0], score[1])
else:
while score[0] <= 21:
Get_New_Poker = self.hit_or_stand()
# 要了一张牌
if Get_New_Poker:
self.player.show_card(1)
self.computer.show_card(0, False)
score[0] = self.player.get_value()
if score[0] > 21:
print('你超过21点')
self.computer.show_card(0)
print()
return self.judgement(score[0], score[1])
else:
continue
elif not Get_New_Poker:
# npc点数比玩家低,则要牌
while score[1] < score[0]:
self.cards.send_card(self.computer)
score[1] = self.computer.get_value()
self.player.show_card(1)
self.computer.show_card(0)
print()
return self.judgement(score[0], score[1])
else:
continue
def hit_or_stand(self):
# 玩家需要判断是否继续叫牌
AskPoker = input('是否叫牌? 【Y/N】>>:')
if AskPoker.upper() == 'Y':
print()
self.cards.send_card(self.player)
return True
elif AskPoker.upper() == 'N':
print('你没加牌.')
print()
return False
else:
print('输入错误 Y/y or N/n!>>')
return self.hit_or_stand()
def continue_or_quit(self):
# 在每一轮结束后,判断是否继续下一轮的游戏。当牌堆里面牌的数目不足的时候,自动停止游戏
NextRound = input('是否继续? 【Y/N】>>')
if NextRound.upper() == 'Y':
if len(self.cards.getCard()) < 10:
print('牌不够了')
input('Game Over')
exit(1)
else:
return True
elif NextRound.upper() == 'N':
input('Game Over')
exit(1)
else:
print('输入有误')
self.continue_or_quit()
if __name__ == '__main__':
startGame = GameManager()
startGame.start_game()
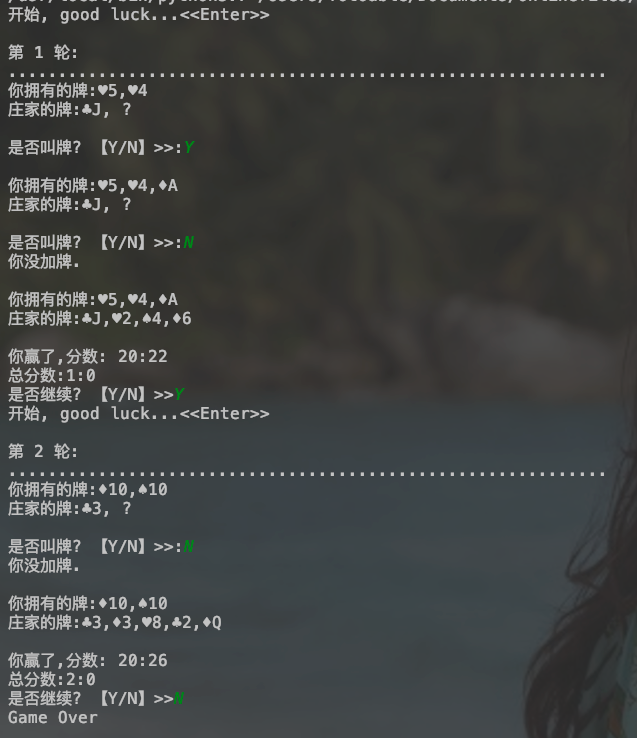
效果: