1.重入锁(ReentrantLock)
重入锁使用java.util.concurrent.locks.ReentrantLock类来实现,具有与synchronized关键字相似的功能。
1 package com.company;
2
3 import java.util.concurrent.locks.ReentrantLock;
4
5 public class User implements Runnable {
6 private ReentrantLock lock = new ReentrantLock();
7 static int i = 0;
8 @Override
9 public void run() {
10 lock.lock();
11 for (int j = 0; j < 10000000; j++) {
12 i++;
13 }
14 System.out.println(i);
15 lock.unlock();
16 }
17
18 public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
19 //注意要使用同一个对象创建线程
20 User u = new User();
21 Thread t1 = new Thread(u);
22 Thread t2 = new Thread(u);
23 t1.start();
24 t2.start();
25 }
26 }
- 锁的时候响应中断
1 package com.company;
2
3 import java.util.concurrent.locks.ReentrantLock;
4
5 public class User implements Runnable {
6 private ReentrantLock lock1 = new ReentrantLock();
7 private ReentrantLock lock2 = new ReentrantLock();
8
9 @Override
10 public void run() {
11 //线程t1先持有lock1,休眠0.5秒尝试持有lock2
12 if(Thread.currentThread().getName().equals("t1")){
13 try {
14 lock1.lockInterruptibly();
15 Thread.sleep(500);
16 lock2.lockInterruptibly();
17 } catch (InterruptedException e) {
18 e.printStackTrace();
19 }
20 //线程t2先持有lock2,休眠0.5秒尝试持有lock1,但是lock1在被t1持有,导致死锁
21 //主线程休眠5秒后,中断线程t1,t1被中断,t2继续执行,执行完毕后退出。
22 }else{
23 try {
24 lock2.lockInterruptibly();
25 Thread.sleep(500);
26 lock1.lockInterruptibly();
27 } catch (InterruptedException e) {
28 e.printStackTrace();
29 }
30 }
31 if(lock1.isHeldByCurrentThread()){
32 lock1.unlock();
33 }
34 if(lock2.isHeldByCurrentThread()){
35 lock2.unlock();
36 }
37 }
38
39 public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
40 //注意要使用同一个对象创建线程
41 User u = new User();
42 Thread t1 = new Thread(u,"t1");
43 Thread t2 = new Thread(u,"t2");
44 t1.start();
45 t2.start();
46 Thread.sleep(5000);
47 t1.interrupt();
48 }
49 }
- 设定锁的等待时间
1 package com.company;
2
3 import org.omg.PortableServer.THREAD_POLICY_ID;
4
5 import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;
6 import java.util.concurrent.locks.ReentrantLock;
7
8 public class User implements Runnable {
9 private ReentrantLock lock = new ReentrantLock();
10
11 @Override
12 public void run() {
13 try {
14 if(lock.tryLock(5, TimeUnit.SECONDS)){
15 System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"成功获得锁");
16 Thread.sleep(6000);
17 }else{
18 System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"获得锁失败");
19 }
20 } catch (InterruptedException e) {
21 e.printStackTrace();
22 }
23 }
24
25 public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
26 //注意要使用同一个对象创建线程
27 User u = new User();
28 Thread t1 = new Thread(u,"t1");
29 Thread t2 = new Thread(u,"t2");
30 t1.start();
31 t2.start();
32 }
33 }
- 设定线程公平获得锁
公平锁需要维护有序队列,成本高。
1 package com.company;
2
3 import org.omg.PortableServer.THREAD_POLICY_ID;
4
5 import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;
6 import java.util.concurrent.locks.ReentrantLock;
7
8 public class User implements Runnable {
9 //还有一个带有boolean参数的构造方法,为true时多个线程公平的获得锁
10 private ReentrantLock lock = new ReentrantLock(true);
11
12 @Override
13 public void run() {
14 while(true){
15 lock.lock();
16 try {
17 System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"获得锁");
18 Thread.sleep(100);
19 } catch (InterruptedException e) {
20 e.printStackTrace();
21 }
22 lock.unlock();
23 }
24 }
25
26 public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
27 //注意要使用同一个对象创建线程
28 User u = new User();
29 Thread t1 = new Thread(u,"t1");
30 Thread t2 = new Thread(u,"t2");
31 t1.start();
32 t2.start();
33 }
34 }
- 重入锁的wait和notify
重入锁的等待唤醒使用Condition类,等待使用await()方法,唤醒使用signal()方法,
1 package com.company;
2 import java.util.concurrent.locks.Condition;
3 import java.util.concurrent.locks.ReentrantLock;
4
5 public class User implements Runnable {
6 public static ReentrantLock lock = new ReentrantLock();
7 public static Condition condition = lock.newCondition();
8
9 @Override
10 public void run() {
11 try {
12 lock.lock();
13 condition.await();
14 System.out.println("唤醒了");
15 } catch (InterruptedException e) {
16 e.printStackTrace();
17 }
18 lock.unlock();
19 }
20
21 public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
22 //注意要使用同一个对象创建线程
23 User u = new User();
24 Thread t = new Thread(u);
25 t.start();
26 Thread.sleep(1000);
27 //condition只能用在lock块内
28 lock.lock();
29 condition.signal();
30 lock.unlock();
31 }
32 }
2.信号量(Semaphore)
synchronized关键字和重入锁同一时间只支持一个线程进入,信号量允许多个线程进入。
1 package com.company;
2 import java.util.concurrent.ExecutorService;
3 import java.util.concurrent.Executors;
4 import java.util.concurrent.Semaphore;
5
6 public class User implements Runnable {
7 final Semaphore semp = new Semaphore(5);
8
9 @Override
10 public void run() {
11 try {
12 semp.acquire();
13 Thread.sleep(1000);
14 System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"执行完了");
15 } catch (InterruptedException e) {
16 e.printStackTrace();
17 }
18 semp.release();
19
20 }
21
22 public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
23 //创建一个线程池,池里边有20个线程
24 ExecutorService executorService = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(20);
25 final User user= new User();
26 for (int i = 0; i < 20; i++) {
27 executorService.submit(user);
28 }
29 }
30 }
3.读写锁
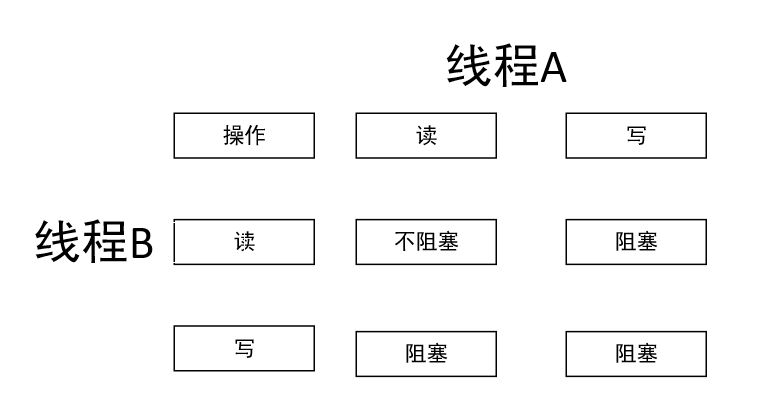
读写锁应用于读的次数远大于写的次数的场景,因为2个线程同时读并没有对资源修改,所以可以同时读,但是但凡一个线程有写操作,就会阻塞其他线程
1 package com.company;
2
3
4 import java.util.concurrent.CountDownLatch;
5 import java.util.concurrent.locks.Lock;
6 import java.util.concurrent.locks.ReadWriteLock;
7 import java.util.concurrent.locks.ReentrantLock;
8 import java.util.concurrent.locks.ReentrantReadWriteLock;
9
10 public class Main {
11
12 public void readSth(){
13 try {
14 Thread.sleep(1000);
15 } catch (InterruptedException e) {
16 e.printStackTrace();
17 }
18 }
19
20 public void writeSth(){
21 try {
22 Thread.sleep(2000);
23 } catch (InterruptedException e) {
24 e.printStackTrace();
25 }
26 }
27 //注意reader类和writer类需要持有同一个类的锁,这2个类持有同一个Main对象
28 public static class Reader implements Runnable{
29 private ReadWriteLock readWriteLock;
30 private Lock readlock;
31 private CountDownLatch latch;
32 private Main obj;
33
34 public Reader(ReadWriteLock readWriteLock,CountDownLatch latch,Main obj){
35 this.readWriteLock = readWriteLock;
36 this.readlock = readWriteLock.readLock();
37 this.latch = latch;
38 this.obj = obj;
39 }
40
41
42 @Override
43 public void run() {
44 readlock.lock();
45 obj.readSth();
46 readlock.unlock();
47 latch.countDown();
48 }
49 }
50
51 public static class Writer implements Runnable{
52 private ReadWriteLock readWriteLock;
53 private Lock writelock;
54 private CountDownLatch latch;
55 private Main obj;
56
57 public Writer(ReadWriteLock readWriteLock,CountDownLatch latch,Main obj){
58 this.readWriteLock = readWriteLock;
59 this.writelock = readWriteLock.writeLock();
60 this.latch = latch;
61 this.obj = obj;
62 }
63
64
65 @Override
66 public void run() {
67 writelock.lock();
68 obj.writeSth();
69 writelock.unlock();
70 latch.countDown();
71 }
72 }
73 public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
74 final long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
75 ReadWriteLock readWriteLock = new ReentrantReadWriteLock();
76 final CountDownLatch latch = new CountDownLatch(25);
77 Main m = new Main();
78 for (int i = 0; i < 20; i++) {
79 Thread t = new Thread(new Reader(readWriteLock,latch,m));
80 t.start();
81 }
82 for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
83 Thread t = new Thread(new Writer(readWriteLock,latch,m));
84 t.start();
85 }
86 latch.await();
87 final long end = System.currentTimeMillis();
88 final long cost = (end - start) /1000;
89 //执行时间11s
90 System.out.println(cost);
91 }
92 }
4.等待多个线程执行完的CountDownLatch
CountDownLatch可以让一个线程等待多个线程执行完后在执行。
1 package com.company;
2
3 import java.util.concurrent.CountDownLatch;
4
5 public class User implements Runnable {
6 private CountDownLatch c;
7
8 public User(CountDownLatch c){
9 this.c = c;
10 }
11
12 @Override
13 public void run() {
14 try {
15 Thread.sleep(2000);
16 } catch (InterruptedException e) {
17 e.printStackTrace();
18 }
19 c.countDown();
20
21 }
22
23 public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
24 long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
25 CountDownLatch c = new CountDownLatch(10);
26 for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
27 new Thread(new User(c)).start();
28 }
29 c.await();
30 long end = System.currentTimeMillis();
31 System.out.println((end-start)/1000+"秒后所有线程都执行完了");
32 }
33 }
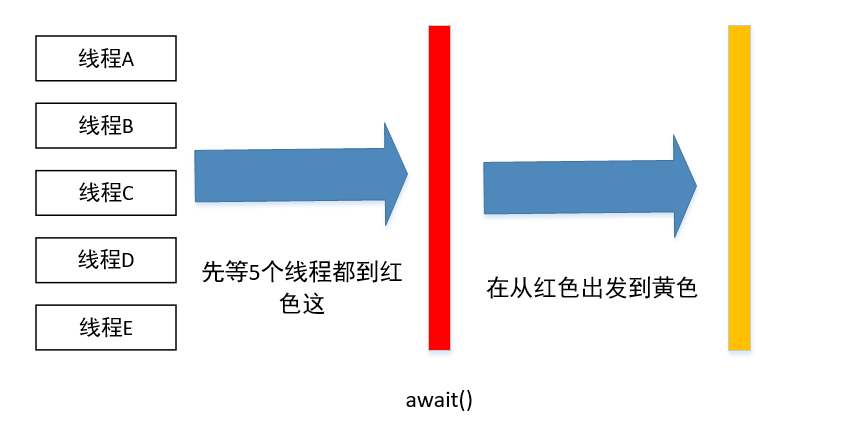
5.反复等待多个线程执行完的CyclicBarrier(?)
1 package com.company;
2
3 import java.util.Random;
4 import java.util.concurrent.BrokenBarrierException;
5 import java.util.concurrent.CyclicBarrier;
6
7 public class CyclicBarrierDemo {
8 public static class Solider implements Runnable{
9 private String solider;
10 private final CyclicBarrier cyclic;
11
12 public Solider(String solider,CyclicBarrier cyclic) {
13 this.solider = solider;
14 this.cyclic = cyclic;
15 }
16
17 @Override
18 public void run() {
19 try {
20 //等士兵集合
21 cyclic.await();
22 doWork();
23 //等士兵完成任务
24 cyclic.await();
25 } catch (InterruptedException e) {
26 e.printStackTrace();
27 } catch (BrokenBarrierException e) {
28 e.printStackTrace();
29 }
30 }
31
32 void doWork() throws InterruptedException {
33 Thread.sleep(Math.abs(new Random().nextInt() % 10000));
34 System.out.println(solider+"任务完成");
35 }
36 }
37 //一批线程执行完了,最后执行什么
38 public static class BarrierRun implements Runnable{
39 boolean flag;
40 int N;
41
42 public BarrierRun(boolean flag,int N){
43 this.flag = flag;
44 this.N = N;
45 }
46 @Override
47 public void run() {
48 if(flag){
49 System.out.println("司令:"+N+"个士兵完成任务");
50 }else{
51 System.out.println("司令:"+N+"个士兵集合完毕");
52 flag = true;
53 }
54 }
55 }
56
57 public static void main(String[] args) {
58 final int N = 10;
59 boolean flag = false;
60 CyclicBarrier cyclicBarrier = new CyclicBarrier(N,new BarrierRun(flag,N));
61 System.out.println("集合队伍");
62 for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) {
63 System.out.println("士兵"+i+"报道");
64 new Thread(new Solider("士兵"+i,cyclicBarrier)).start();
65 }
66 }
67 }
6.线程阻塞(LockSupport)
LockSupport的park()方法可以阻塞当前线程。
LockSupport为每个线程准备一个许可,park()将许可变为不可用;unpark()将许可变为可用。
即使unpark()先执行,在碰到对应的park()也能继续执行。
1 package com.company;
2
3
4 import java.util.concurrent.locks.LockSupport;
5
6 public class User implements Runnable{
7 private static Object o = new Object();
8
9 @Override
10 public void run() {
11 synchronized (o){
12 System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName());
13 LockSupport.park();
14 }
15 }
16
17 public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
18 User u = new User();
19 Thread t1 = new Thread(u);
20 Thread t2 = new Thread(u);
21 t1.start();
22 t2.start();
23 24 LockSupport.unpark(t2);
25 t1.join();
26 t2.join();
27 }
28 }
park()还可以响应中断。
1 package com.company;
2
3
4 import java.util.concurrent.locks.LockSupport;
5
6 public class User implements Runnable{
7 private static Object o = new Object();
8
9 @Override
10 public void run() {
11 synchronized (o){
12 LockSupport.park();
13 if(Thread.interrupted()){
14 System.out.println("线程中断了");
15 }
16 }
17 }
18
19 public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
20 User u = new User();
21 Thread t1 = new Thread(u);
22 t1.start();
23 t1.interrupt();
24 }
25 }
7.限流算法
- 漏桶算法

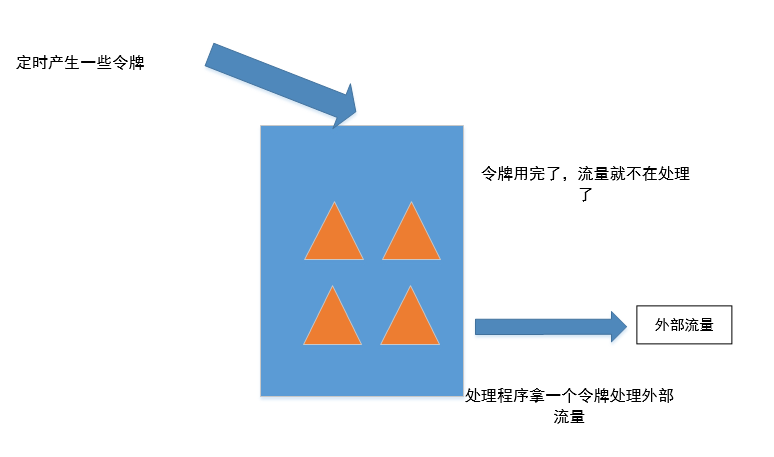
- 令牌桶算法(Guava的RateLimiter)
1 import com.google.common.util.concurrent.RateLimiter;
2
3 public class User implements Runnable{
4 //设定每秒处理2个请求
5 static RateLimiter t = RateLimiter.create(2);
6
7 public void run() {
8 System.out.println(System.currentTimeMillis());
9 }
10
11 public static void main(String[] args) {
12 for (int i = 0; i < 50; i++) {
13 t.acquire();
14 new Thread(new User()).start();
15 }
16 }
17 }
来源:https://www.cnblogs.com/vshen999/p/12404615.html