版权声明:欢迎交流学习,如需转载,请注明出处~~~ https://blog.csdn.net/qq_39141406/article/details/90487636
概述
- 链表特点:
1、元素在内存中位置随机(数组元素的地址是数学公式决定的)
2、每个元素有一个明确的“链”指向线性表的下一个元素 - 链表分类:
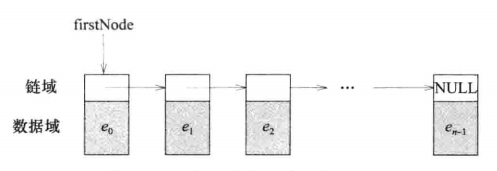
1、单向链表:x.firstNode指向链表首节点,当x.firstNode=NULL时为空表,最后节点的链指针为NULL;
2、单向循环链表:最后节点的链指针指向第一个节点;
3、双向链表:两个指针域next和previous,最后节点的next指针为NULL,首节点的previous指针为NULL;
4、双向循环链表:首节点的previous指向尾节点,尾节点的next指针指向首节点。
注:以上分类均默认没有头结点,如果引入头结点,每个链表(包括空表)都至少包括一个节点(头结点)
单向链表性质与实现
1、单向链表
- 一个线性表的链式描述

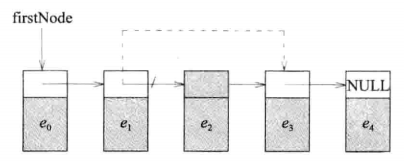
- 链表的删除操作

两个步骤:
(1)找到第二个节点
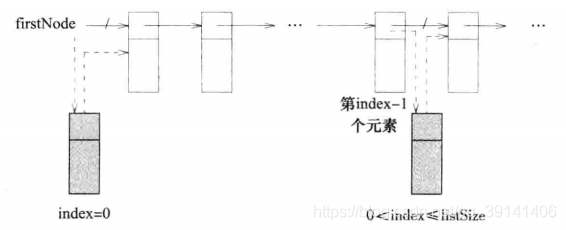
(2)把第二个节点和第四个节点链接起来 - 链表的插入操作

两个步骤:
(1)找到索引为index-1的节点
(2)改变前后节点的指针
2、C++语言实现
2.1 结构chainNode
存储数据成员和指针:
template <class T> struct chainNode { // data members T element; chainNode<T>* next; // methods chainNode() {} chainNode(const T& element) { this->element = element; } chainNode(const T& element, chainNode<T>* next) { this->element = element; this->next = next; } }; 2.2 类chain
声明代码:
template<class T> class chain : public linearList<T> { friend linkedDigraph; friend linkedWDigraph<int>; friend linkedWDigraph<float>; friend linkedWDigraph<double>; public: // constructor, copy constructor and destructor chain(int initialCapacity = 10); chain(const chain<T>&); ~chain(); // ADT methods bool empty() const { return listSize == 0; } int size() const { return listSize; } T& get(int theIndex) const; int indexOf(const T& theElement) const; void erase(int theIndex); void insert(int theIndex, const T& theElement); void output(ostream& out) const; protected: void checkIndex(int theIndex) const; // throw illegalIndex if theIndex invalid chainNode<T>* firstNode; // pointer to first node in chain int listSize; // number of elements in list }; 实现代码:
template<class T> chain<T>::chain(int initialCapacity) {// Constructor. if (initialCapacity < 1) { ostringstream s; s << "Initial capacity = " << initialCapacity << " Must be > 0"; throw illegalParameterValue(s.str()); } firstNode = NULL; listSize = 0; } template<class T> chain<T>::chain(const chain<T>& theList) {// Copy constructor. listSize = theList.listSize; if (listSize == 0) {// theList is empty firstNode = NULL; return; } // non-empty list chainNode<T>* sourceNode = theList.firstNode; // node in theList to copy from firstNode = new chainNode<T>(sourceNode->element); // copy first element of theList sourceNode = sourceNode->next; chainNode<T>* targetNode = firstNode; // current last node in *this while (sourceNode != NULL) {// copy remaining elements targetNode->next = new chainNode<T>(sourceNode->element); targetNode = targetNode->next; sourceNode = sourceNode->next; } targetNode->next = NULL; // end the chain } template<class T> chain<T>::~chain() {// Chain destructor. Delete all nodes in chain. while (firstNode != NULL) {// delete firstNode chainNode<T>* nextNode = firstNode->next; delete firstNode; firstNode = nextNode; } } template<class T> void chain<T>::checkIndex(int theIndex) const {// Verify that theIndex is between 0 and listSize - 1. if (theIndex < 0 || theIndex >= listSize) { ostringstream s; s << "index = " << theIndex << " size = " << listSize; throw illegalIndex(s.str()); } } template<class T> T& chain<T>::get(int theIndex) const {// Return element whose index is theIndex. // Throw illegalIndex exception if no such element. checkIndex(theIndex); // move to desired node chainNode<T>* currentNode = firstNode; for (int i = 0; i < theIndex; i++) currentNode = currentNode->next; return currentNode->element; } template<class T> int chain<T>::indexOf(const T & theElement) const {// Return index of first occurrence of theElement. // Return -1 if theElement not in list. // search the chain for theElement chainNode<T>* currentNode = firstNode; int index = 0; // index of currentNode while (currentNode != NULL && currentNode->element != theElement) { // move to next node currentNode = currentNode->next; index++; } // make sure we found matching element if (currentNode == NULL) return -1; else return index; } template<class T> void chain<T>::erase(int theIndex) {// Delete the element whose index is theIndex. // Throw illegalIndex exception if no such element. checkIndex(theIndex); // valid index, locate node with element to delete chainNode<T>* deleteNode; if (theIndex == 0) {// remove first node from chain deleteNode = firstNode; firstNode = firstNode->next; } else { // use p to get to predecessor of desired node chainNode<T>* p = firstNode; for (int i = 0; i < theIndex - 1; i++) p = p->next; deleteNode = p->next; p->next = p->next->next; // remove deleteNode from chain } listSize--; delete deleteNode; } template<class T> void chain<T>::insert(int theIndex, const T & theElement) {// Insert theElement so that its index is theIndex. if (theIndex < 0 || theIndex > listSize) {// invalid index ostringstream s; s << "index = " << theIndex << " size = " << listSize; throw illegalIndex(s.str()); } if (theIndex == 0) // insert at front firstNode = new chainNode<T>(theElement, firstNode); else { // find predecessor of new element chainNode<T>* p = firstNode; for (int i = 0; i < theIndex - 1; i++) p = p->next; // insert after p p->next = new chainNode<T>(theElement, p->next); } listSize++; } template<class T> void chain<T>::output(ostream & out) const {// Put the list into the stream out. for (chainNode<T>* currentNode = firstNode; currentNode != NULL; currentNode = currentNode->next) out << currentNode->element << " "; } // overload << template <class T> ostream & operator<<(ostream & out, const chain<T> & x) { x.output(out); return out; } 注:链表在创建的时候不需要估计元素的最大个数;构造函数有一个表示初试容量的形参initialCapacity,目的是与arrayList相容
3、总结
(1)可以在上述简单实现的基础上添加链表的成员类Iterator,由于链表是单向的,所以只能定义一个向前迭代器
(2)如果想对链表操作进行扩充,首先要对抽象数据类型linearList进行扩充,比如添加clear和push_back(添加元素到表尾)等。
例如:为了快速在表尾插入元素,可以增加数据成员lastNode(指向链表结尾点的指针)。需要完成的工作有:声明一个数据成员lastNode;提供改进的erase和insert代码;定义在linearList中剩余的纯虚函数;实现clear和push_back方法。
循环列表和头节点
- 两条措施可以让链表更加简洁和高效:
- 单向链表尾节点和头节点链接起来构成循环列表;
- 链表前面添加头结点
循环链表: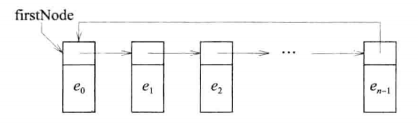
带头结点的循环列表: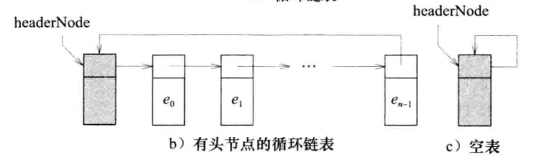
双向列表
一个节点存在两个指针,分别指向前驱节点和后继节点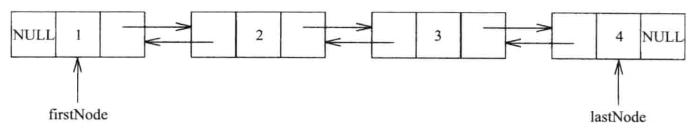
文章来源: https://blog.csdn.net/qq_39141406/article/details/90487636