委托声明
委托是一种可以指向方法的数据类型。
比如delegate void MyDelgate(int n);
委托实例
class Program { delegate void MyDel(string name);//声明委托 static void Main(string[] args) { //委托将要指向的方法必须的参数个数、类型和返回值类型都必须要与委托声明的一样 MyDel myDel = new MyDel(SayHello);//这里不要写成SayHello() myDel("蛋蛋");//输出"蛋蛋你好" myDel = null; myDel("蛋蛋");//会抛出空引用异常 Console.ReadKey(); } static void SayHello(string name) { Console.WriteLine(name + "你好!"); } } } MyDelgate myDel = new MyDelgate(方法名);
也可以写成简化形式:
MyDelgate myDel = 方法名;
//编译器会自动搞成new Mydel (SayHello);注意方法名不能带括号
在写一个例子,获取一个数组中最大值;由于类型不定,所以最大值的算法也不一样,可以使用委托把最大算法稳定下来,把比较规则通过委托进行开放。
class Program { delegate bool CompareNum(object obj1, object obj2); static void Main(string[] args) { object[] objs = { 1, 2, 4, 4, 2, 1, 2, 3 }; //通过这样写,获取最大值的算法已经确定,在传参数的是后指定上比较方法就好了 //用委托后,我们不在为每个获取最大值的方法都去写一种算法 int max=(int)GetMax(objs, CompareInt);//原生的写法为GetMax(objs,new CompareNum(CompareInt));//只不过编译器帮我们进行了处理 Console.WriteLine(max); Console.ReadKey(); } //int比较方法,与委托参数一致 static bool CompareInt(object obj1, object obj2) { int i1 = (int)obj1; int i2 = (int)obj2; return i1 > i2; } //获取最大值,将要比较的参数和比较使用的方法名传入,返回最大值 static object GetMax(object[] obj, CompareNum cpn) { object max = obj[0]; for (int i = 1; i < obj.Length; i++) { if (!cpn(max, obj[i])) { max = obj[i]; } } return max; } } //float比较方法,与委托参数一致 static bool CompareFloat(object obj1, object obj2) { float f1 = (float)obj1; float f2 = (float)obj2; return f1 > f2; } float max=(float)GetMax(objs, CompareFloat);
首先我们先看 他们的定义:Func是有返回值的委托;Action是没有返回值的委托
使用这个两个委托重写上面代码如下:
class Program { static void Main(string[] args) { Action<string> ac = new Action<string>(Greeting);//没有返回值的内置委托 ac("蛋蛋"); Func<string, string> fu = new Func<string, string>(GreetingForR);//有返回值的内置委托 string msg = fu("建国"); Console.WriteLine(msg); Console.ReadKey(); } static string GreetingForR(string name) { return name + "你好"; } static void Greeting(string name) { Console.WriteLine(name + "你好"); } } 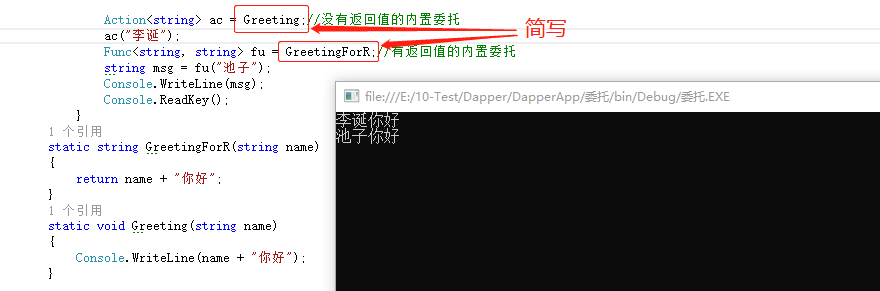
匿名方法
使用Delegate的时候很多时候没必要使用一个普通的方法,因为这个方法只有这个Delegate会用,并且只用一次,这时候使用匿名方法最合适。
匿名方法就是没有名字的方法,格式:MyDelegate p = delegate(int s){s=10;};
例如改造getMax代码
class Program { delegate bool CompareNum(object obj1, object obj2); static void Main(string[] args) { object[] objs = { 1, 2, 4, 4, 2, 1, 2, 3 }; //通过这样写,获取最大值的算法已经确定,在传参数的是后指定上比较方法就好了 //用委托后,我们不在为每个获取最大值的方法都去写一种算法 CompareNum cpn = delegate (object obj1, object obj2) { int i1 = (int)obj1; int i2 = (int)obj2; return i1 > i2; }; //int max=(int)GetMax(objs, CompareInt);//原生的写法为GetMax(objs,new CompareNum(CompareInt));//只不过编译器帮我们进行了处理 int max = (int)GetMax(objs, cpn);//使用匿名方法 Console.WriteLine(max); Console.ReadKey(); } static bool CompareInt(object obj1, object obj2) { int i1 = (int)obj1; int i2 = (int)obj2; return i1 > i2; } static object GetMax(object[] obj, CompareNum cpn) { object max = obj[0]; for (int i = 1; i < obj.Length; i++) { if (!cpn(max, obj[i])) { max = obj[i]; } } return max; } } ①Lambda表达式中的参数列表(参数数量、类型和位置)必须与委托相匹配;
②表达式中的参数列表不一定需要包含类型,除非委托有ref或out关键字(此时必须显示声明);
③如果没有参数,必须使用一组空的圆括号;
class Program { delegate bool CompareNum(object obj1, object obj2); static void Main(string[] args) { //1、匿名方法 Action<string, bool> a1 = delegate (string s, bool b) { if (b) { Console.WriteLine("true" + s); } else { Console.WriteLine("false" + s); } }; //2、简化后 Action<string, bool> a2 = (s, b) => { if (b) { Console.WriteLine("true" + s); } else { Console.WriteLine("false" + s); } }; a2("hello", true); //1、匿名方法 Func<string, int> f1 = delegate (string str) { return Convert.ToInt32(str); }; //2、简化后 Func<string, int> f2 = (str) => Convert.ToInt32(str); ; int i = f2("1"); Console.WriteLine(i); Console.ReadKey(); } } //1、 Action<string, int> a11 = (s1, i1) => { Console.WriteLine("s1=" + s1 + ",i1=" + i1); }; //还原后 Action<string, int> a12 = delegate (string s1, int i1) { Console.WriteLine("s1=" + s1 + ",i1=" + i1); }; //2、 Func<int, string> f11 = n => (n + 1).ToString(); //还原后 Func<int, string> f12 = delegate (int n) { return (n + 1).ToString(); }; //3、 Func<int, int> f13 = n => n * 2; //还原后 Func<int, int> f14 = delegate (int n) { return n * 2; }; 写出下面一个lambda表达式的委托类型及非匿名函数格式
class Program { static void Main(string[] args) { //Func<int, bool> f15 =n=>n>0; Func<int, bool> f15 = delegate (int n) { return n > 0; }; Func<int, bool> f16 = IsDYl; bool i=f16(-1); Console.WriteLine(i); Console.ReadKey(); } static bool IsDYl(int n) { return n > 0; } } class Program { static void Main(string[] args) { object[] objs = { 1, 2, 4, 4, 2, 1, 2, 3 }; Func<object, object, bool> cpn = (obj1, obj2) => { int i1 = (int)obj1; int i2 = (int)obj2; return i1 > i2; }; int max = (int)GetMax(objs, cpn);//使用匿名方法 Console.WriteLine(max); Console.ReadKey(); } static bool CompareInt(object obj1, object obj2) { int i1 = (int)obj1; int i2 = (int)obj2; return i1 > i2; } static object GetMax(object[] obj, Func<object,object,bool> cpn) { object max = obj[0]; for (int i = 1; i < obj.Length; i++) { if (!cpn(max, obj[i])) { max = obj[i]; } } return max; } } 委托深入
集合常用扩展方法:
WhereSelectMaxMinOrderBy
First
FirstOrDefault
Single
SingleOrDefault
“+MyDel m5 = m1+m2+m3;
组合的委托必须是同一个委托类型
(*)-
(*)
class Program { delegate void MyDel(); static void Main(string[] args) { MyDel myDel = del1; myDel += del2; myDel(); myDel -= del1; myDel(); Console.ReadKey(); } static void del1() { Console.WriteLine("第1个委托"); } static void del2() { Console.WriteLine("第2个委托"); } }