actuator是spring boot项目中非常强大一个功能,有助于对应用程序进行监视和管理,通过 restful api 请求来监管、审计、收集应用的运行情况,针对微服务而言它是必不可少的一个环节,本文只介绍如何集成actuator,及actuator最最简单的使用,对于自定义endPoint及actuator的实现原理后续单独介绍。
1、导入依赖包
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-actuator</artifactId>
</dependency>
如果要访问info接口访问maven中配置的内容,需要配置如下插件
<plugin>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-maven-plugin</artifactId>
<executions>
<execution>
<goals>
<goal>build-info</goal>
</goals>
</execution>
</executions>
</plugin>
2、增加相关配置
# 描述信息
info:
blog-url: http://lcl.com
author: lcl
version: @project.version@
# 加载所有的端点/默认只加载了 info / health
management:
endpoints:
web:
exposure:
include: '*'
endpoint:
health:
show-details: always
# 可以关闭制定的端点
shutdown:
enabled: false
# 路径映射,将 health 路径映射成 rest_health 那么在访问 health 路径将为404,因为原路径已经变成 rest_health 了,一般情况下不建议使用
# management.endpoints.web.path-mapping.health=rest_health
此处注意一点,如果使用的是properties配置文件,使用星号时,不需要加单引号,但是使用yml配置文件时,必须要加单引号,否则启动报错。
3、测试
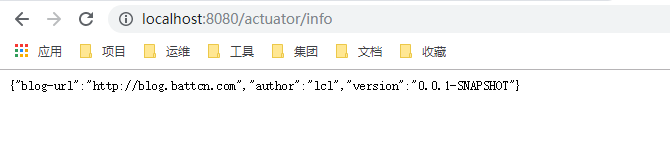
输入http://localhost:8080/actuator/info进行测试
4、自定义检测
虽然actuator拥有强大的功能,但是仍可能不满足我们的需求,就需要自定义端点进行测试,自定义端点测试主要有两种实现方式,实现HealthIndicator接口或继承
AbstractHealthIndicator类,话不多说,直接上代码。(1)实现HealthIndicator接口:
package com.example.demo.health;
import org.springframework.boot.actuate.health.Health;
import org.springframework.boot.actuate.health.HealthIndicator;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
@Component("myhealth1")
public class MyHealth implements HealthIndicator {
private static final String VERSION = "v1.0.0";
@Override
public Health health() {
int code = check();
if(code != 0){
Health.down().withDetail("code",code).withDetail("version", VERSION).build();
}
return Health.up().withDetail("code",code).withDetail("version", VERSION).up().build();
}
private int check() {
return 0;
}
}
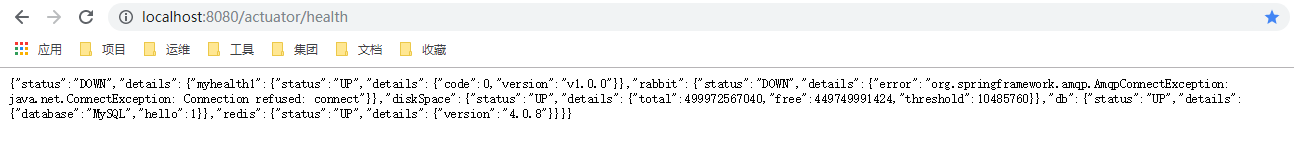
测试:http://localhost:8080/actuator/health
(2)继承AbstractHealthIndicator类
package com.example.demo.health;
import org.springframework.boot.actuate.health.AbstractHealthIndicator;
import org.springframework.boot.actuate.health.Health;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
@Component("myhealth2")
public class MyHealth2 extends AbstractHealthIndicator {
private static final String VERSION = "v1.0.0";
@Override
protected void doHealthCheck(Health.Builder builder) throws Exception {
int code = check();
if (code != 0) {
builder.down().withDetail("code", code).withDetail("version", VERSION).build();
}
builder.withDetail("code", code)
.withDetail("version", VERSION).up().build();
}
private int check() {
return 0;
}
}
测试:http://localhost:8080/actuator/health
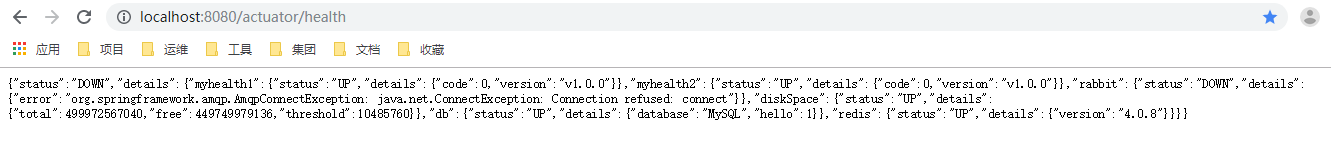
由上可以查看系统集成了redis、mysql和rabbitMQ,其中redis和mysql连接正常,rabbitMQ连接异常。
下列是依赖spring-boot-xxx-starter后相关HealthIndicator的实现(通过management.health.defaults.enabled 属性可以禁用它们),但想要获取一些额外的信息时,自定义的作用就体现出来了…
| 名称 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| CassandraHealthIndicator | 检查 Cassandra 数据库是否启动。 |
| DiskSpaceHealthIndicator | 检查磁盘空间不足。 |
| DataSourceHealthIndicator | 检查是否可以获得连接 DataSource。 |
| ElasticsearchHealthIndicator | 检查 Elasticsearch 集群是否启动。 |
| InfluxDbHealthIndicator | 检查 InfluxDB 服务器是否启动。 |
| JmsHealthIndicator | 检查 JMS 代理是否启动。 |
| MailHealthIndicator | 检查邮件服务器是否启动。 |
| MongoHealthIndicator | 检查 Mongo 数据库是否启动。 |
| Neo4jHealthIndicator | 检查 Neo4j 服务器是否启动。 |
| RabbitHealthIndicator | 检查 Rabbit 服务器是否启动。 |
| RedisHealthIndicator | 检查 Redis 服务器是否启动。 |
| SolrHealthIndicator | 检查 Solr 服务器是否已启动。 |