利用顺序存储方式实现的栈称为顺序栈。类似于顺序表的定义,栈中的数据元素用一个预设的足够长度的一维数组来实现:datatype data[MAXSIZE],栈底位置可以设置在数组的任一个端点,而栈顶是随着插入和删除而变化的,用一个 int top 来作为栈顶的指针,指明当前栈顶的位置,同样将 data 和 top 封装在一个结构中。
顺序栈的类型描述如下:
typedef struct {
datatype data[MAXSIZE];
int top;
}seqStack;
定义一个指向顺序栈的指针:
SeqStack *s;
通常0下标端设为栈底,这样空栈时栈顶指针 top=-1;入栈时,栈顶指针加1,即 s->top++;出栈时栈顶指针减1,即 s->top--。
以下是栈的几种基本操作:
(1) 置空栈
seqStack *init_seqStack() {
seqStack *s;
s = (seqStack *)malloc(sizeof(seqStack));
s->top = -1;
return s;
}
(2) 判栈空
int empty_seqStack(seqStack *s) {
if (s->top == -1) {
return TRUE;
}
return FALSE;
}
(3) 判栈满
int full_seqStack(seqStack *s) {
if (s->top == MAXSIZE - 1) {
return TRUE;
}
return FALSE;
}
(4) 入栈
int push_seqStack(seqStack *s, int x) {
if (full_seqStack(s)) {
return FAILURE;
}
s->top++;
s->data[s->top] = x;
return SUCCESS;
}
(5) 出栈
int pop_seqStack(seqStack *s, int *x) {
if (empty_seqStack(s)) {
return FAILURE;
}
*x = s->data[s->top];
s->top--;
return SUCCESS;
}
(6) 取栈顶元素
int gettop_seqStack(seqStack *s, int *x) {
if (empty_seqStack(s)) {
return FAILURE;
}
*x = s->data[s->top];
return SUCCESS;
}
(7) 释放空间
void free_seqStack(seqStack **s) {
if (*s == NULL) {
return;
}
free(*s);
*s = NULL;
}
这里我们定义一个测试函数 test_seqStack() 来了解一下顺序栈是如何操作的,测试时 datatype 定义为 int 类型。
我们先定义一个头文件 seqStack.h。
/**********************************************
** file name : seqStack.h
** description :
** writer by : Adam
** create date : 2016-10-22
**********************************************/
#ifndef SEQSTACK_H
#define SEQSTACK_H
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<conio.h>
#define TRUE 1
#define FALSE 0
#define SUCCESS 1
#define FAILURE 0
#define MAXSIZE 100
typedef struct {
int data[MAXSIZE];
int top;
}seqStack;
seqStack *init_seqStack(); // 置空栈
int empty_seqStack(seqStack *s); // 判栈空
int full_seqStack(seqStack *s); // 判栈满
int push_seqStack(seqStack *s, int x); // 入栈
int pop_seqStack(seqStack *s, int *x); // 出栈
int gettop_seqStack(seqStack *s, int *x); // 取栈顶元素
void show_seqStack(seqStack *s); // 输出
void free_seqStack(seqStack **s); // 释放空间
void test_seqStack();
#endif //SEQSTACK_H
/********************END**********************/
然后定义一个 seqStack.cpp 文件。
/**********************************************
** file name : seqStack.cpp
** description :
** writer by : Adam
** create date : 2016-10-22
**********************************************/
#include "seqStack.h"
void test_seqStack() {
seqStack *s;
int i, x;
s = init_seqStack();
show_seqStack(s);
for (i = 1; i <= 101; i++) {
if (push_seqStack(s, i) == FAILURE) {
printf("Stack overflowed!\n");
_getch();
break;
}
}
show_seqStack(s);
if (pop_seqStack(s, &x) == FAILURE) {
printf("Stack empty!");
_getch();
}
else
{
printf("Pop Stack=%d\n", x);
}
show_seqStack(s);
if (gettop_seqStack(s, &x) == FAILURE) {
printf("Get top of Stack failed!\n");
_getch();
}
else
{
printf("Top Stack=%d\n", x);
}
show_seqStack(s);
free_seqStack(&s);
}
seqStack *init_seqStack() {
seqStack *s;
s = (seqStack *)malloc(sizeof(seqStack));
s->top = -1;
return s;
}
int empty_seqStack(seqStack *s) {
if (s->top == -1) {
return TRUE;
}
return FALSE;
}
int full_seqStack(seqStack *s) {
if (s->top == MAXSIZE - 1) {
return TRUE;
}
return FALSE;
}
int push_seqStack(seqStack *s, int x) {
if (full_seqStack(s)) {
return FAILURE;
}
s->top++;
s->data[s->top] = x;
return SUCCESS;
}
int pop_seqStack(seqStack *s, int *x) {
if (empty_seqStack(s)) {
return FAILURE;
}
*x = s->data[s->top];
s->top--;
return SUCCESS;
}
int gettop_seqStack(seqStack *s, int *x) {
if (empty_seqStack(s)) {
return FAILURE;
}
*x = s->data[s->top];
return SUCCESS;
}
void show_seqStack(seqStack *s) {
int i;
if (empty_seqStack(s)) {
printf("The stack is empty!\n");
_getch();
return;
}
for (i = s->top; i >= 0; i--) {
printf("%d\t", s->data[i]);
}
printf("\nshow finished!\n");
_getch();
}
void free_seqStack(seqStack **s) {
if (*s == NULL) {
return;
}
free(*s);
*s = NULL;
}
/********************END**********************/
最后再通过主函数来调用 seqStack.cpp 函数。
/**********************************************
** file name : main.cpp
** description :
** writer by : Adam
** create date : 2016-10-22
**********************************************/
#include "seqStack.h";
void main() {
test_seqStack();
}
/********************END**********************/
运行结果如下:
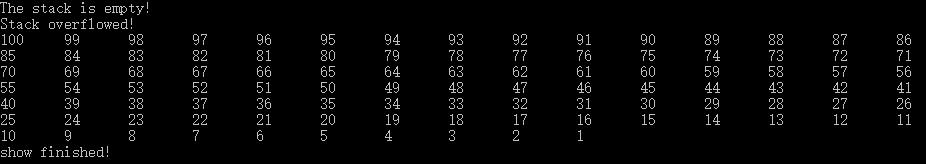

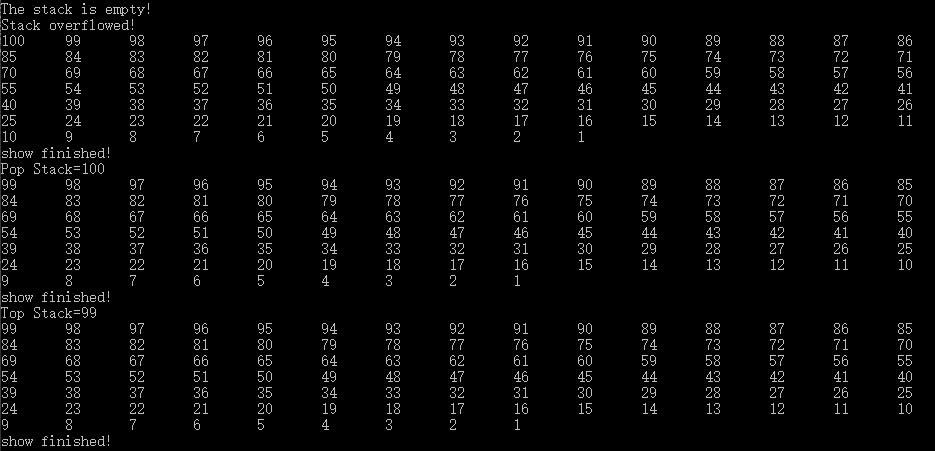
借此我们就可以直观的看出栈的运行状态及过程。
注意以下几点:
(1) 对于顺序栈,入栈时,首先判断栈是否满了,栈满的条件为: s->top == MAXSIZE-1,栈满时,不能入栈;否则出现空间溢出,引起错误,这种现象称为上溢。
(2) 出栈和读栈顶元素操作,先判栈是否为空,为空时不能操作否则产生错误。通常栈空时常作为一种控制转移的条件。
(3) 取栈顶元素与出栈的不同之处在于出栈操作改变栈顶指针 top 的位置(栈顶指针下移一个位置),而取栈顶元素操作只是读出栈顶元素的值,栈顶指针 top 位置不改变。
来源:https://www.cnblogs.com/adamjwh/p/6476384.html