发送端
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
"""
@File : 200103_obstacle_detection_发送数据_测试udp传输上限.py
@Time : 2020/1/3 14:28
@Author : Dontla
@Email : sxana@qq.com
@Software: PyCharm
"""
import socket
import struct
import time
import numpy as np
import pyrealsense2 as rs
import cv2
import sys
from numba import jit
def udp_send_image(img, pack_size, socket, ip_port):
_, img_encode = cv2.imencode('.jpg', img)
data = img_encode.tobytes()
# print(len(data)) # 有很多超过65535的
# 【定义文件头、数据】(打包名为l?不是,l表示长整型,占四个字节)
fhead = struct.pack('i', len(data))
# 【发送文件头、数据】
socket.sendto(fhead, ip_port)
# 每次发送x字节,计算所需发送次数
send_times = len(data) // pack_size + 1
for count in range(send_times):
# time.sleep(0.01)
if count < send_times - 1:
socket.sendto(
data[pack_size * count:pack_size * (count + 1)], ip_port)
else:
socket.sendto(data[pack_size * count:], ip_port)
# @jit
# 貌似开不了jit,不知啥原因,开了也没明显看到加速
def filter_alpha(depth_image, filter_alpha):
if filter_alpha > 1:
# 获取depth_image宽高
h, w = depth_image.shape[0], depth_image.shape[1] # 360,640
# 创建上下alpha(不同方法都能创建)
# filter_upper = np.array([1] * int(h / 2))
filter_upper = np.full(int(h / 2), 1)
filter_lower = np.linspace(1, filter_alpha, h / 2)
# 将filter_upper和filter_lower连在一起
filter = np.r_[filter_upper, filter_lower]
# print(filter)
# print(filter.shape) # (360,)
# print(filter_alpha_upper)
# print(filter_alpha_upper.shape) # (180,)
# print(filter_alpha_lower)
# print(filter_alpha_lower.shape) # (180,)
return (depth_image.T * filter).T
else:
return depth_image
# 如果要防止下面棉花过近被误探测,可用两层for循环设置梯度过滤
# 不过貌似还得中间对半分,下面直接舍弃掉,只用上面作为判断,因为就算下面用了梯度...(还是得用梯度...)
@jit
def traversing_pixels(depth_image, threshold_dangerous_distance):
num_dangerous = 0
num_all_pixels = 0
depth_image_ravel = depth_image.ravel()
# depth_image_segmentation为分割后的图像(红蓝两色)
depth_image_segmentation_ravel = []
for pixel in depth_image_ravel:
num_all_pixels += 1
# 第一种效果要好一些
if pixel < threshold_dangerous_distance and pixel != 0:
# if pixel < threshold_dangerous_distance:
num_dangerous += 1
depth_image_segmentation_ravel.append(0)
else:
depth_image_segmentation_ravel.append(6000)
depth_image_segmentation = np.array(depth_image_segmentation_ravel).reshape(depth_image.shape)
return num_all_pixels, num_dangerous, depth_image_segmentation
class ObstacleDetection(object):
def __init__(self):
# self.cam_serials = ['838212073161', '827312071726']
# self.cam_serials = ['838212073161', '827312071726', '838212073249', '827312070790', '836612072369',
# '826212070395']
self.cam_serials = ['838212073161']
self.cam_width, self.cam_height = 640, 360
# 【危险距离:单位mm】
self.threshold_dangerous_distance = 3000
# 【摄像头到棉花平面垂直距离(单位mm)】
self.distance_cam_vertical_to_cotton_top = 260
# 【危险距离补偿系数】用于让最下面深度远离临界值,避免造成误检测
self.factor_compensation_dangerous_distance = 1.5
# 【危险距离像素占比】
self.threshold_dangerous_scale = 0.05
# 【摄像头视场角(单位°)】
self.FOV_width = 69.4
self.FOV_height = 42.5
self.FOV_scale = self.FOV_height / self.FOV_width # 0.6123919308357348
# 【实际变换后height视场角】
if self.cam_height / self.cam_width < self.FOV_scale:
self.FOV_height_actual = self.FOV_width * self.cam_height / self.cam_width
else:
self.FOV_height_actual = self.FOV_height
# 【计算过滤α值(distance_min为图像最下方的深度,看到最近棉花的距离)】
# 当摄像头到棉花顶垂直距离为800,最小距离为2256,当危险距离为2000时,alpha滤值为0.88
# 当摄像头到棉花顶垂直距离为800,最小距离为2256,当危险距离为3000时,alpha滤值为1.32
# 所以,后面进行滤值时需判断self.filter_alpha的值是否大于1(已添加进filter_alpha()函数中)
self.distance_min = self.distance_cam_vertical_to_cotton_top / (
np.tan(self.FOV_height_actual / 2 * np.pi / 180))
self.filter_alpha = self.threshold_dangerous_distance / self.distance_min * self.factor_compensation_dangerous_distance
# 【UDP信号发送模块】
# 远程主机ip地址及端口
self.ip_port = ('192.168.1.49', 9000)
self.udp_server_client = socket.socket(socket.AF_INET, socket.SOCK_DGRAM)
# self.bytes_udp_pack = 1024
self.bytes_udp_pack = 65507
def obstacle_detection(self):
# print(self.distance_min) # 2256.7829632201597
# print(self.filter_alpha) # 0.8862172537611853
# 摄像头个数(在这里设置所需使用摄像头的总个数)
cam_num = 6
ctx = rs.context()
'''连续验证机制'''
# D·C 1911202:创建最大验证次数max_veri_times;创建连续稳定值continuous_stable_value,用于判断设备重置后是否处于稳定状态
max_veri_times = 100
continuous_stable_value = 5
print('\n', end='')
print('开始连续验证,连续验证稳定值:{},最大验证次数:{}:'.format(continuous_stable_value, max_veri_times))
continuous_value = 0
veri_times = 0
while True:
devices = ctx.query_devices()
connected_cam_num = len(devices)
print('摄像头个数:{}'.format(connected_cam_num))
if connected_cam_num == cam_num:
continuous_value += 1
if continuous_value == continuous_stable_value:
break
else:
continuous_value = 0
veri_times += 1
if veri_times == max_veri_times:
print("检测超时,请检查摄像头连接!")
sys.exit()
'''循环reset摄像头'''
# hardware_reset()后是不是应该延迟一段时间?不延迟就会报错
print('\n', end='')
print('开始初始化摄像头:')
for dev in ctx.query_devices():
# 先将设备的序列号放进一个变量里,免得在下面for循环里访问设备的信息过多(虽然不知道它会不会每次都重新访问)
dev_serial = dev.get_info(rs.camera_info.serial_number)
# 匹配序列号,重置我们需重置的特定摄像头(注意两个for循环顺序,哪个在外哪个在内很重要,不然会导致刚重置的摄像头又被访问导致报错)
for serial in self.cam_serials:
if serial == dev_serial:
dev.hardware_reset()
# 像下面这条语句居然不会报错,不是刚刚才重置了dev吗?莫非区别在于没有通过for循环ctx.query_devices()去访问?
# 是不是刚重置后可以通过ctx.query_devices()去查看有这个设备,但是却没有存储设备地址?如果是这样,
# 也就能够解释为啥能够通过len(ctx.query_devices())函数获取设备数量,但访问序列号等信息就会报错的原因了
print('摄像头{}初始化成功'.format(dev.get_info(rs.camera_info.serial_number)))
'''连续验证机制'''
# D·C 1911202:创建最大验证次数max_veri_times;创建连续稳定值continuous_stable_value,用于判断设备重置后是否处于稳定状态
print('\n', end='')
print('开始连续验证,连续验证稳定值:{},最大验证次数:{}:'.format(continuous_stable_value, max_veri_times))
continuous_value = 0
veri_times = 0
while True:
devices = ctx.query_devices()
connected_cam_num = len(devices)
print('摄像头个数:{}'.format(connected_cam_num))
if connected_cam_num == cam_num:
continuous_value += 1
if continuous_value == continuous_stable_value:
break
else:
continuous_value = 0
veri_times += 1
if veri_times == max_veri_times:
print("检测超时,请检查摄像头连接!")
sys.exit()
'''配置各个摄像头的基本对象'''
for i in range(len(self.cam_serials)):
locals()['pipeline' + str(i)] = rs.pipeline(ctx)
locals()['config' + str(i)] = rs.config()
locals()['config' + str(i)].enable_device(self.cam_serials[i])
# 为啥我设置成1280×720就报错呢?明明Intel Realsense的usb接口已经显示为3.0了
# locals()['config' + str(i)].enable_stream(rs.stream.depth, 640, 480, rs.format.z16, 30)
# locals()['config' + str(i)].enable_stream(rs.stream.color, 640, 480, rs.format.bgr8, 30)
locals()['config' + str(i)].enable_stream(rs.stream.depth, self.cam_width, self.cam_height, rs.format.z16,
30)
locals()['config' + str(i)].enable_stream(rs.stream.color, self.cam_width, self.cam_height, rs.format.bgr8,
30)
locals()['pipeline' + str(i)].start(locals()['config' + str(i)])
# 创建对齐对象(深度对齐颜色)
locals()['align' + str(i)] = rs.align(rs.stream.color)
'''运行摄像头'''
try:
while True:
start_time = time.time()
for i in range(len(self.cam_serials)):
locals()['frames' + str(i)] = locals()['pipeline' + str(i)].wait_for_frames()
# 获取对齐帧集
locals()['aligned_frames' + str(i)] = locals()['align' + str(i)].process(
locals()['frames' + str(i)])
# 获取对齐后的深度帧和彩色帧
locals()['aligned_depth_frame' + str(i)] = locals()[
'aligned_frames' + str(i)].get_depth_frame()
locals()['color_frame' + str(i)] = locals()['aligned_frames' + str(i)].get_color_frame()
if not locals()['aligned_depth_frame' + str(i)] or not locals()['color_frame' + str(i)]:
continue
# 获取颜色帧内参
locals()['color_profile' + str(i)] = locals()['color_frame' + str(i)].get_profile()
locals()['cvsprofile' + str(i)] = rs.video_stream_profile(
locals()['color_profile' + str(i)])
locals()['color_intrin' + str(i)] = locals()['cvsprofile' + str(i)].get_intrinsics()
locals()['color_intrin_part' + str(i)] = [locals()['color_intrin' + str(i)].ppx,
locals()['color_intrin' + str(i)].ppy,
locals()['color_intrin' + str(i)].fx,
locals()['color_intrin' + str(i)].fy]
locals()['color_image' + str(i)] = np.asanyarray(
locals()['color_frame' + str(i)].get_data())
locals()['depth_image' + str(i)] = np.asanyarray(
locals()['aligned_depth_frame' + str(i)].get_data())
# 【阿尔法过滤】
locals()['depth_image_alpha_filter' + str(i)] = filter_alpha(locals()['depth_image' + str(i)],
self.filter_alpha)
# 【遍历深度图像素值,如存在小于危险值范围比例超过阈值,则告警】
locals()['num_all_pixels' + str(i)], locals()['num_dangerous' + str(i)], locals()[
'depth_image_segmentation' + str(i)] = traversing_pixels(
locals()['depth_image_alpha_filter' + str(i)], self.threshold_dangerous_distance)
print('num_all_pixels:{}'.format(locals()['num_all_pixels' + str(i)]))
print('num_dangerous:{}'.format(locals()['num_dangerous' + str(i)]))
locals()['dangerous_scale' + str(i)] = locals()['num_dangerous' + str(i)] / locals()[
'num_all_pixels' + str(i)]
print('危险比例:{}'.format(locals()['dangerous_scale' + str(i)]))
locals()['depth_colormap' + str(i)] = cv2.applyColorMap(
cv2.convertScaleAbs(locals()['depth_image_segmentation' + str(i)], alpha=0.0425),
cv2.COLORMAP_JET)
locals()['image' + str(i)] = np.hstack(
(locals()['color_image' + str(i)], locals()['depth_colormap' + str(i)]))
# 注意: 窗口名不要用中文字符, 小心乱码
cv2.imshow('win{}:{}'.format(i, self.cam_serials[i]), locals()['image' + str(i)])
# cv2.imshow('colorWin{}: {}'.format(i, self.cam_serials[i]), locals()['color_image' + str(i)])
# cv2.imshow('depthWin{}: {}'.format(i, self.cam_serials[i]), locals()['depth_colormap' + str(i)])
cv2.waitKey(1)
# 【向远端发送告警信号及图片:】
if locals()['dangerous_scale' + str(i)] > self.threshold_dangerous_scale:
print("距离警告,向远端发送告警信息!")
# self.udp_server_client.sendto('摄像头{}告警'.format(i).encode('utf-8'), self.ip_port)
# print(locals()['image' + str(i)].shape) # (360, 1280, 3)
udp_send_image(locals()['image' + str(i)], self.bytes_udp_pack, self.udp_server_client,
self.ip_port)
end_time = time.time()
# print('单帧运行时间:{}'.format(end_time - start_time))
# 遇到异常再次启动检测函数,如有需要可以将连续监测和摄像头重置全放进去
# except:
# print('\n出现异常,请重新检查摄像头连接!\n')
# for i in range(len(self.cam_serials)):
# cv2.destroyAllWindows()
# locals()['pipeline' + str(i)].stop()
# ObstacleDetection().obstacle_detection()
finally:
for i in range(len(self.cam_serials)):
locals()['pipeline' + str(i)].stop()
if __name__ == '__main__':
ObstacleDetection().obstacle_detection()
接收端
# -*- encoding: utf-8 -*-
"""
@File : 201003_避障程序信号及图像接收端_测试udp传输上限.py
@Time : 2020/1/3 14:32
@Author : Dontla
@Email : sxana@qq.com
@Software: PyCharm
"""
import socket
import struct
import time
import cv2
import numpy as np
ip_port = ('192.168.1.49', 9000)
BUFSIZE = 65507
udp_server_client = socket.socket(socket.AF_INET, socket.SOCK_DGRAM)
udp_server_client.bind(ip_port)
def receive():
while True:
try:
while True:
# 计算fmt字节长度(貌似没必要我先注释掉了)
# fhead_size = struct.calcsize('i')
# print('fhead_size大小:{}'.format(fhead_size)) # 4
# 获取数据头信息,第一个参数为信息,第二个参数是发送方ip地址
buffer, _ = udp_server_client.recvfrom(BUFSIZE)
# print(buffer)
# print(len(buffer)) # 可能为4或60000+
if len(buffer) == 4:
# print(buffer) # b';\xfb\x00\x00' # 每次都不一样的
# 解包,看看有多大(unpack返回的是只有一个元素的元组,如(64282,),元素个数貌似取决于fmt)
data_size = struct.unpack('i', buffer)[0]
# data_size = struct.unpack('i', buf)[0]
# print(data_size) # 64315
else:
print('不是struct头,继续下次循环!')
# cv2.destroyAllWindows()
continue
# 重写接收程序
recv_times = data_size // BUFSIZE + 1
# print(recv_times) # 按目前的BUFSIZE,为1或2,大部分为2
data_total = b''
recvd_size = 0
for count in range(recv_times):
data, _ = udp_server_client.recvfrom(BUFSIZE)
recvd_size += len(data)
data_total += data
# 判断data_total长度是否等于图片长度,不是就继续下次循环
# print(len(data_total))
if len(data_total) != data_size:
print('一定又是哪接收出错了,导致没接收上,继续下轮循环!')
continue
# recvd_size = 0
# data_total = b''
# while recvd_size < data_size:
# if data_size - recvd_size >= BUFSIZE:
# data, _ = udp_server_client.recvfrom(BUFSIZE)
# recvd_size += len(data)
# else:
# data, _ = udp_server_client.recvfrom(data_size - recvd_size)
# recvd_size += len(data)
# data_total += data
print('received!')
# print(data_total)
# print(type(data_total))
# <class 'bytes'>
nparr = np.fromstring(data_total, np.uint8)
# print(nparr) # [255 216 255 ... 15 255 217] # 每次不一样的
img_decode = cv2.imdecode(nparr, cv2.IMREAD_COLOR)
cv2.imshow('win', img_decode)
# 保存截图
# cv2.imwrite('{}.jpg'.format(time.clock()), img_decode)
cv2.waitKey(1)
# data, addr = udp_server_client.recvfrom(BUFSIZE)
# print(data.decode('utf-8'), addr)
# print(data, addr)
# nparr = np.fromstring(data, np.uint8)
# img_decode = cv2.imdecode(nparr, cv2.IMREAD_COLOR)
# cv2.imshow('result', img_decode)
# cv2.waitKey()
except:
print('出现异常,继续调用receive()函数!')
# receive()
finally:
# cv2.destroyAllWindows()
pass
# break
if __name__ == '__main__':
receive()
执行结果
发送端
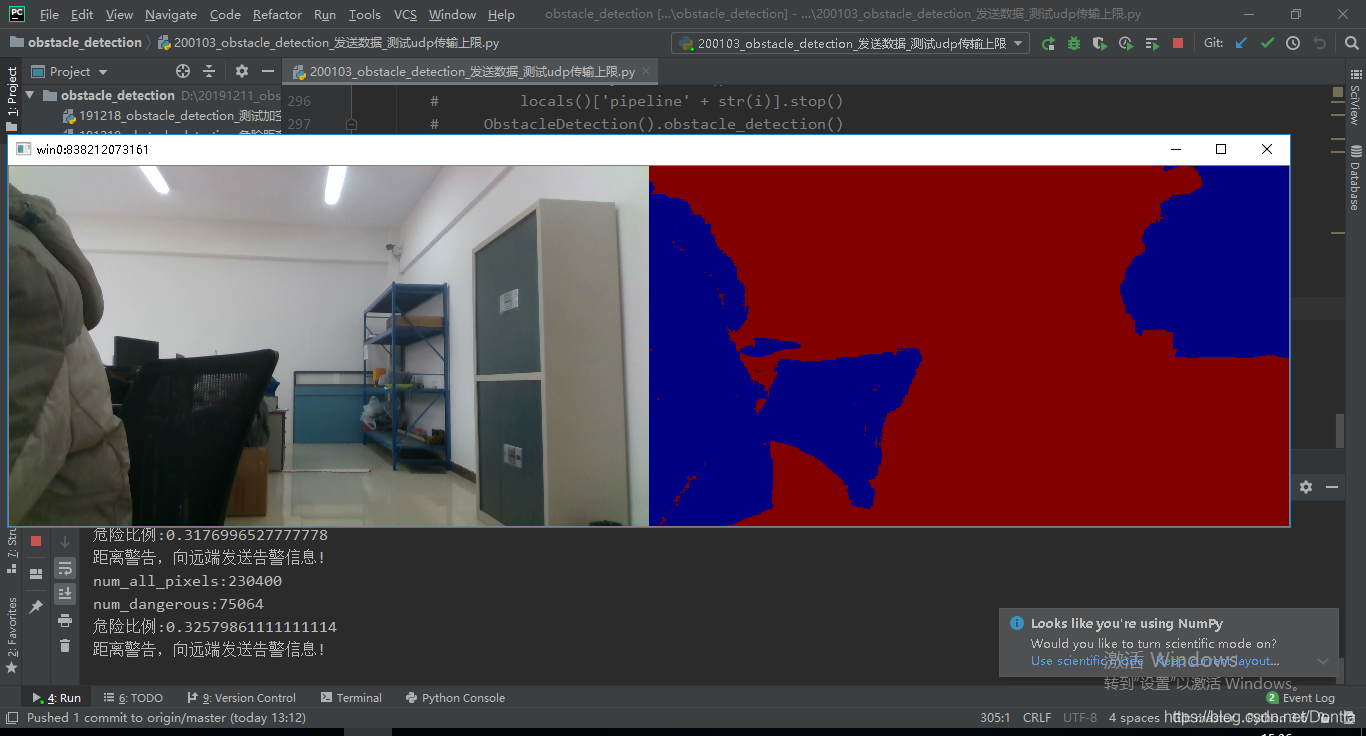
接收端

来源:CSDN
作者:Dontla
链接:https://blog.csdn.net/Dontla/article/details/103833581