问题
I'm new with Python and I'm completely stuck when filtering a signal. This is the code:
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from scipy import signal
fs=105e6
fin=70.1e6
N=np.arange(0,21e3,1)
# Create a input sin signal of 70.1 MHz sampled at 105 MHz
x_in=np.sin(2*np.pi*(fin/fs)*N)
# Define the "b" and "a" polynomials to create a CIC filter (R=8,M=2,N=6)
b=np.zeros(97)
b[[0,16,32,48,64,80,96]]=[1,-6,15,-20,15,-6,1]
a=np.zeros(7)
a[[0,1,2,3,4,5,6]]=[1,-6,15,-20,15,-6,1]
w,h=signal.freqz(b,a)
plt.plot(w/max(w),20*np.log10(abs(h)/np.nanmax(h)))
plt.title('CIC Filter Response')
output_nco_cic=signal.lfilter(b,a,x_in)
plt.figure()
plt.plot(x_in)
plt.title('Input Signal')
plt.figure()
plt.plot(output_nco_cic)
plt.title('Filtered Signal')
And the plots:
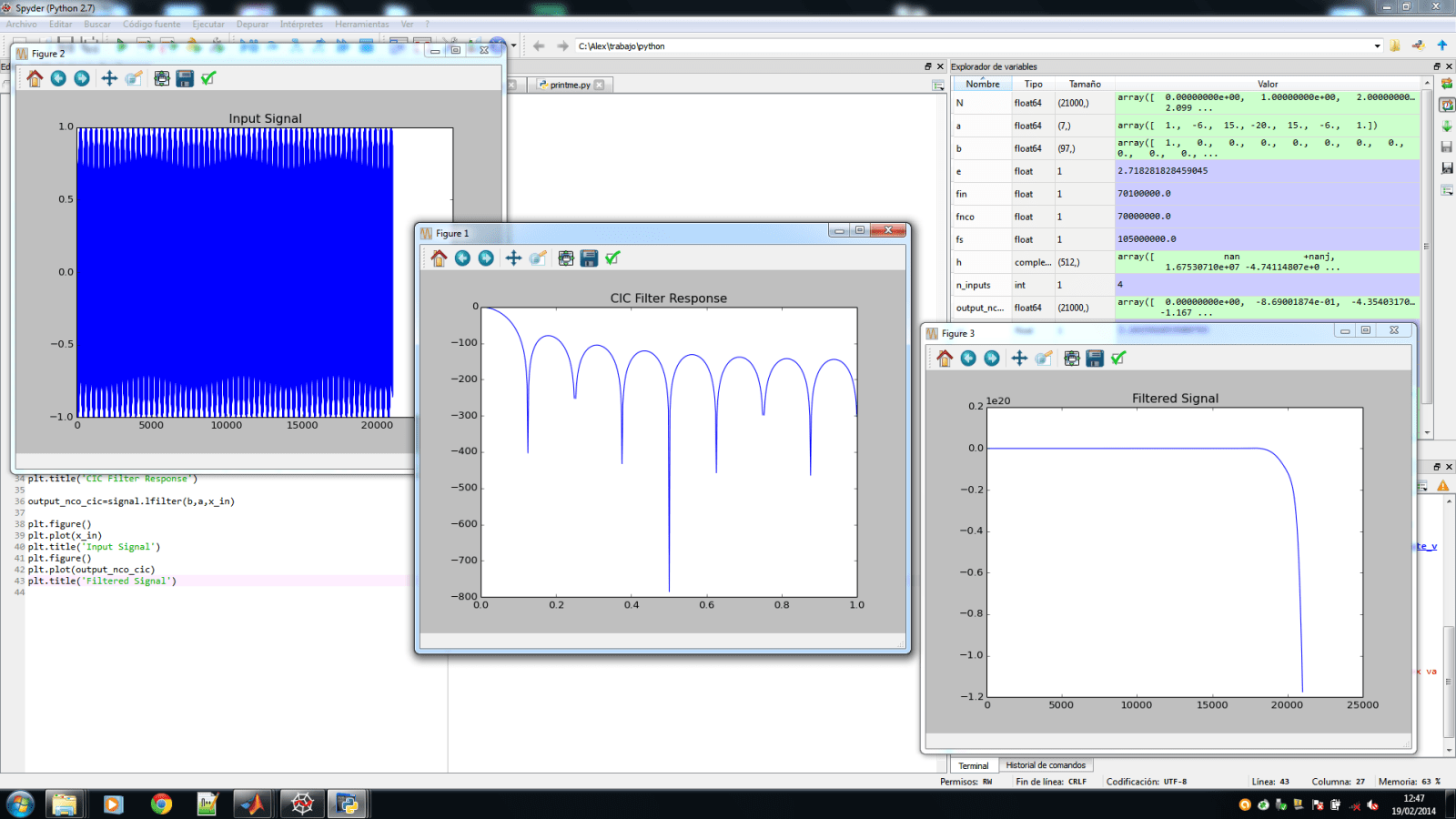
As you can see, although the filter transfer function is correct, the output isn't. And I can't see why my code isn't working. I've coded the same in Matlab and the output looks ok.
Thaks for the help!
回答1:
I don't find it confusing that this didn't work with Python, but I do find it confusing that it worked with Matlab.
CIC filters don't work with floating point numbers.
UPDATE:
Interestingly, at least with the version of scipy I have, lfilter doesn't work with integer arrays -- I get a NotImplemented error. Here is a numpy version of a CIC filter that is about twice as fast as a pure Python implementation on my machine:
# Implements an in-memory CIC decimator using numpy.
from math import log
from numpy import int32, int64, array
def cic_decimator(source, decimation_factor=32, order=5, ibits=1, obits=16):
# Calculate the total number of bits used internally, and the output
# shift and mask required.
numbits = order * int(round(log(decimation_factor) / log(2))) + ibits
outshift = numbits - obits
outmask = (1 << obits) - 1
# If we need more than 64 bits, we can't do it...
assert numbits <= 64
# Create a numpy array with the source
result = array(source, int64 if numbits > 32 else int32)
# Do the integration stages
for i in range(order):
result.cumsum(out=result)
# Decimate
result = array(result[decimation_factor - 1 : : decimation_factor])
# Do the comb stages. Iterate backwards through the array,
# because we use each value before we replace it.
for i in range(order):
result[len(result) - 1 : 0 : -1] -= result[len(result) - 2 : : -1]
# Normalize the output
result >>= outshift
result &= outmask
return result
回答2:
The code is fine, and lfilter works fine on the float64 arrays that it creates. But the denominator polynomial "a" has all its roots at z = 1, which makes the filter "conditionally stable". Due to numerically inaccuracy, it will eventually diverge. And the input signal at 70.1 MHz is way outside the passband, so it doesn't show up much in the output. If you change the input to 0.701 MHz or thereabouts, and shorten the signal to 1000 samples instead of 21000, you'll see that it works as-is. Try these changes and you'll see what happens after that: fin=70.1e4 N=np.arange(0,2000,1) (and to get rid of the divide by zero complaint, add 1.0e-12 inside the log10)
To do a CIC right, you need an implementation that deals correctly with the conditionally stable poles.
来源:https://stackoverflow.com/questions/21879676/filtering-signal-with-python-lfilter