水果
http://acm.hdu.edu.cn/showproblem.php?pid=1263
Problem Description
夏天来了~~好开心啊,呵呵,好多好多水果~~Joe经营着一个不大的水果店.他认为生存之道就是经营最受顾客欢迎的水果.现在他想要一份水果销售情况的明细表,这样Joe就可以很容易掌握所有水果的销售情况了.
Input
第一行正整数N(0<N<=10)表示有N组测试数据.
每组测试数据的第一行是一个整数M(0<M<=100),表示工有M次成功的交易.其后有M行数据,每行表示一次交易,由水果名称(小写字母组成,长度不超过80),水果产地(小写字母组成,长度不超过80)和交易的水果数目(正整数,不超过100)组成.
Output
对于每一组测试数据,请你输出一份排版格式正确(请分析样本输出)的水果销售情况明细表.这份明细表包括所有水果的产地,名称和销售数目的信息.水果先按产地分类,产地按字母顺序排列;同一产地的水果按照名称排序,名称按字母顺序排序.两组测试数据之间有一个空行.最后一组测试数据之后没有空行.
Sample Input
1 5 apple shandong 3 pineapple guangdong 1 sugarcane guangdong 1 pineapple guangdong 3 pineapple guangdong 1
Sample Output
guangdong |----pineapple(5) |----sugarcane(1) shandong |----apple(3)
map的嵌套
1 #include <stdio.h> 2 #include <iostream> 3 #include <string.h> 4 #include <string> 5 #include <algorithm> 6 #include <map> 7 8 using namespace std; 9 10 int main() 11 { 12 //freopen("sample.txt","r",stdin); 13 int n; 14 cin>>n; 15 for(int i=0;i<n;i++) 16 { 17 if(i!=0) 18 cout<<endl; 19 int m; 20 cin>>m; 21 map<string,map<string,int> > mp; 22 map<string,map<string,int> >::iterator it1; 23 map<string,int>::iterator it2; 24 while(m--) 25 { 26 string fruit,address; 27 int count; 28 cin>>fruit>>address>>count; 29 mp[address][fruit]+=count; //这一步要记住 30 } 31 for(it1=mp.begin();it1!=mp.end();it1++) 32 { 33 cout<<it1->first<<endl; 34 for(it2=it1->second.begin();it2!=it1->second.end();it2++) 35 { 36 cout<<" |----"<<it2->first<<"("<<it2->second<<")"<<endl; 37 } 38 } 39 } 40 return 0; 41 } 1 #include<iostream> 2 #include<string> 3 #include<map> 4 using namespace std; 5 6 struct MyStruct 7 { 8 map <string, int>MyStructma; //存放水果名以及该种水果的数量 9 }; 10 int main() 11 { 12 map <string, MyStruct>ma; //地名 13 map <string, MyStruct>::iterator it; 14 map <string, int>::iterator MyStructmait; 15 string fruit,place; 16 int count; 17 int n,t; 18 cin>>t; 19 while(t--) 20 { 21 ma.clear(); 22 cin>>n; 23 while(n--) 24 { 25 cin>>fruit>>place>>count; 26 ma[place].MyStructma[fruit] += count; 27 } 28 for (it = ma.begin(); it != ma.end(); it++) 29 { 30 cout<<it->first<<endl; 31 for (MyStructmait = it->second.MyStructma.begin(); MyStructmait != it->second.MyStructma.end(); MyStructmait++) 32 { 33 34 cout<<" |----"<<MyStructmait->first<<"("<<MyStructmait->second<<")"<<endl; 35 } 36 } 37 if(t != 0)cout<<endl; 38 } 39 return 0; 40 } 也可以结构体排序,不用STL
1 #include <stdio.h> 2 #include <string.h> 3 #include <algorithm> 4 using namespace std; 5 6 struct Node 7 { 8 char name[100]; 9 char space[100]; 10 int num; 11 } f[110]; 12 13 int cmp(Node x,Node y) 14 { 15 if(strcmp(x.space,y.space)) 16 return strcmp(x.space,y.space)<0; 17 return strcmp(x.name,y.name)<0; 18 } 19 20 int main() 21 { 22 int t,n,i; 23 scanf("%d",&t); 24 while(t--) 25 { 26 scanf("%d%*c",&n); 27 for(i = 0; i<n; i++) 28 { 29 scanf("%s%s%d",f[i].name,f[i].space,&f[i].num); 30 } 31 sort(f,f+n,cmp); 32 char di[100],min[100]; 33 int cnt = 0,flag = 1; 34 strcpy(di,f[0].space); 35 strcpy(min,f[0].name); 36 for(i = 0; i<n; i++) 37 { 38 if(strcmp(di,f[i].space)) 39 { 40 strcpy(di,f[i].space); 41 strcpy(min,f[i].name); 42 flag = 1; 43 cnt = 0; 44 } 45 if(!strcmp(di,f[i].space)) 46 { 47 if(flag) 48 { 49 printf("%s\n",di); 50 flag = 0; 51 } 52 if(!strcmp(min,f[i].name)) 53 { 54 while(!strcmp(min,f[i].name) && !strcmp(di,f[i].space))//产地与水果名都必须相同 55 { 56 cnt+=f[i].num; 57 i++; 58 } 59 printf(" |----%s(%d)\n",min,cnt); 60 strcpy(min,f[i].name); 61 i--; 62 cnt = 0; 63 } 64 } 65 } 66 if(t) 67 printf("\n"); 68 } 69 70 return 0; 71 } 另一种解法
1 #include<cstdio> 2 #include<iostream> 3 #include<map> 4 #include<string> 5 using namespace std; 6 7 int main(){ 8 int n,m; 9 string color; 10 map<string,int>mp; 11 while(scanf("%d",&m)!=EOF && m){ 12 while(m--){ 13 cin>>color; 14 mp[color]++; 15 } 16 int max = 0; 17 string a; 18 for(map<string,int>::iterator it=mp.begin();it!=mp.end();it++){ 19 if(max<=it->second){ 20 max = it->second; 21 a = it->first; 22 } 23 } 24 cout<<a<<endl; 25 mp.clear(); 26 } 27 return 0; 28 } from:https://www.cnblogs.com/1114250779boke/archive/2012/08/07/2626477.html
对于传统的map:
1 #include <iostream> 2 #include <map> 3 4 using namespace std; 5 6 int main() 7 { 8 map<int, string> scores; 9 10 scores.insert(make_pair(100,"maxi")); 11 12 scores[100]="MAXI"; 13 14 scores.insert(make_pair(300,"xiaoyu")); 15 16 scores.insert(make_pair(300,"xiao")); 17 18 scores[200]="xiaoma"; 19 20 map<int,string>::iterator pScores; 21 22 for(pScores=scores.begin();pScores!=scores.end();pScores++) 23 { 24 std::cout<<pScores->first<<" "<<pScores->second<<endl; 25 } 26 return 0; 27 } 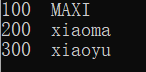
由此可以看出,scores[100]="MAXI"会直接替换掉原来100map对应的value,而如果调用scores.insert()函数,则由于本map是单映射的,300 map的value:xiao就不会替换掉原来300 map对应的value:xiaoyu
但如果我想定义嵌套的map并对它进行遍历,该如何进行呢:
1 #include<iostream> 2 #include<map> 3 4 using namespace std; 5 int main() 6 { 7 //对于这样的map嵌套定义,有两种插入方法: 8 //定义一个map<int, string>变量,对其定义后在插入multiMap 9 map<int,map<int,string> >multiMap; 10 11 map<int, string> temp; 12 13 temp.insert(make_pair(90,"hi")); 14 15 temp.insert(pair<int,string>(100,"maxi")); //pair<int,string>()和make_pair()有相同作用 16 17 multiMap.insert(make_pair(10, temp)); //将临时变量插入到multiMap中 18 //也可以直接赋值 19 multiMap[10][80]="xiaoyu"; 20 21 multiMap[5][30]="xiaoma"; 22 23 // 以下是如何遍历本multiMap 24 map<int,map<int,string> >::iterator multitr; 25 map<int,string>::iterator intertr; 26 for(multitr=multiMap.begin();multitr!=multiMap.end();multitr++) 27 { 28 for(intertr= multitr ->second.begin(); intertr != multitr ->second.end(); intertr ++) 29 std::cout<< multitr ->first<<" "<<intertr->first<<" ("<< intertr -> second <<")"<<endl; 30 } 31 return 0; 32 } 运行结果如下:
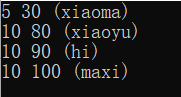
总结,map的成员加入有两种赋值方法,一种是调用map.insert()函数,这样,由于是单映射,后面加入的新的pair对如果有key值和前面一样,那么后面的pair对元素将不会被加入到map中;但如果是直接[ ]=赋值操作的话,相当于数组赋值,会直接替换掉原来具有相同key域的pair对。