C++的继承方式有三种,分别为:
公有继承:public
私有继承:private
保护继承:protected
定义格式为:
class<派生类名>:<继承方式><基类名>
{
<派生类新定义成员>
};
我们称已存在的用来派生新类的类为基类,又称为父类。由已存在的类派生出的新类称为派生类,又称为子类。
在公有继承(public)时,
基类的公有成员和保护成员作为派生类的成员时,
它们都保持原有的状态,而基类的私有成员仍然是私有的,不能
被这个派生类的子类所访问。
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
class People {
private:
char *name = NULL;
int ID;
char *gender = NULL;
float height;
public:
People();
People(char Name[], int id, char Gender[], float Height, char Address[]);
int GetID();
float Getheight();
void DisplayPeople();
char* Getname();
char* Getgender();
char* Getaddress();
protected:
char *address = NULL;
};
People::People()
{
}
char* People::Getaddress()
{
return address;
}
char* People::Getgender()
{
return gender;
}
char* People::Getname()
{
return name;
}
void People::DisplayPeople()
{
cout << "姓名:" << name << endl;
cout << "身份证号:" << ID << endl;
cout << "性别:" << gender << endl;
cout << "身高:" << height << endl;
cout << "地址:" << address << endl;
}
People::People(char Name[], int id, char Gender[], float Height, char Address[])
{
name = Name;
ID = id;
gender = Gender;
height = Height;
address = Address;
}
int People::GetID()
{
return ID;
}
float People::Getheight()
{
return height;
}
class Student :public People//类Student以公有继承的方式继承类People
{
private:
int StudentId;
char *Class;
public:
Student(char Name[], int id, char Gender[], float Height, char Address[], int studentid, char clas[]);
void DisplayStudent();
Student();
float GetHeight();
};
float Student::GetHeight()
{
return Student::Getheight();
}
Student::Student()
{
}
void Student::DisplayStudent()
{
cout << endl;
People::DisplayPeople();
cout << "学生学号:" << StudentId << endl;
cout << "学生所在班级:" << Class << endl;
}
Student::Student(char Name[], int id, char Gender[], float Height, char Address[], int studentid, char clas[]) :People(Name, id, Gender, Height, Address)
//派生类的构造函数
{
StudentId = studentid;
Class = clas;
}
int main()
{
char s1[20];
cout << "输入姓名 :";
cin >> s1;//输入姓名
char s2[10];
cout << "输入性别 :";
cin >> s2;//输入性别
char s3[15];
cout << "输入地址 :";
cin >> s3;//输入地址
int a;
cout << "请输入身份证号:";
cin >> a;
float b ;
cout << "请输入身高:";
cin >> b;
People people(s1, a, s2, b, s3);
char S1[20];
cout << "输入所在班级 :";
cin >> S1;//输入所在班级
int number;
cout << "输入学号 :";
cin >> number;//输入学号
Student student1(s1, a, s2, b, s3, number, S1);
student1.DisplayStudent();//派生类调用基类中的public成员函数
cout << endl << student1.Getheight() << endl;//派生类调用基类的成员函数访问基类的私有成员height
system("pause");
return 0;
}
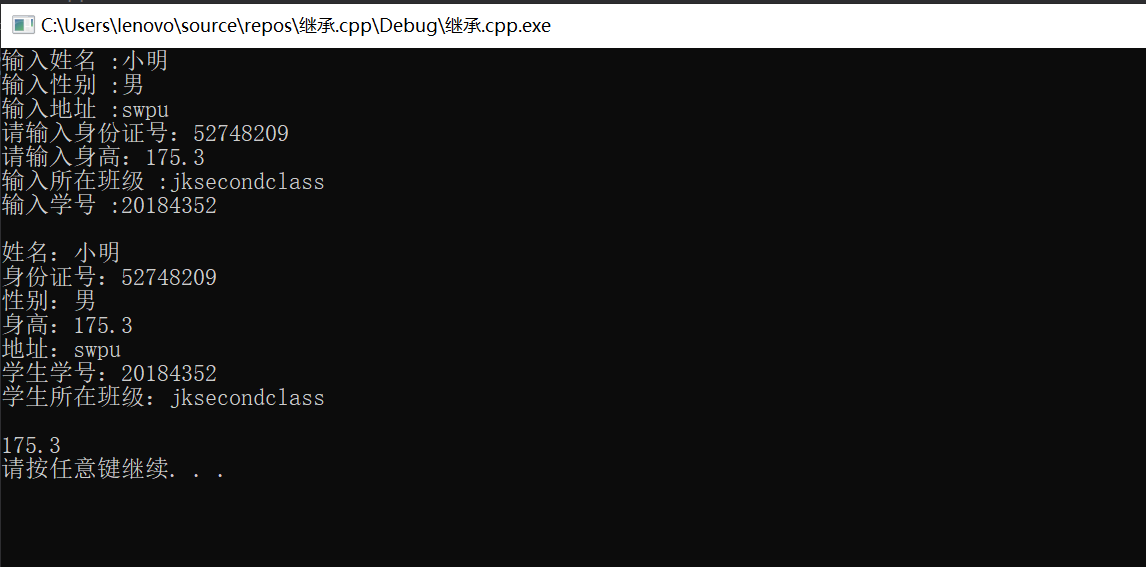
这个派生类采用公有继承方式,所以可以调用基类中的成员函数。但若我们用派生类直接访问基类中的私有成员,
cout << student1.ID << endl;
则会出现以下错误: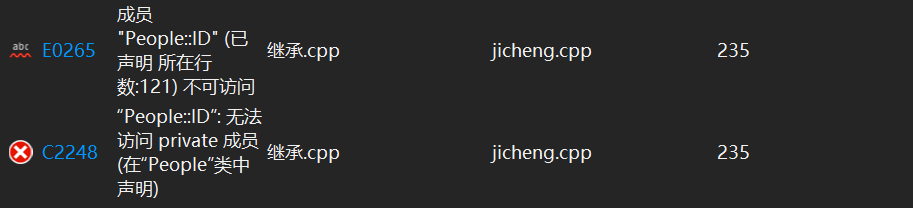
说明派生类也不可直接访问基类中的私有成员。
在私有继承(private)时,
基类的公有成员和保护成员都作为派生类的私有
成员,并且不能被这个派生类的子类所访问。
在上面代码不变的基础上,将继承方式由公有继承(public)改为私有继承(private),
class Student :private People//类Student以私有继承的方式继承类People
{
private:
int StudentId;
char *Class;
public:
Student(char Name[], int id, char Gender[], float Height, char Address[], int studentid, char clas[]);
void DisplayStudent();
Student();
float GetHeight();
};
会发生如下报错:
说明在私有继承中,基类中的成员函数对于派生类来说是不可见的,不被允许访问的,若我们想访问基类中的
私有成员变量,可以通过派生类成员函数间接地访问,代码如下:
float Student::GetHeight()
{
cout << endl<< "访问基类成员height成功:";
return Student::Getheight();
}
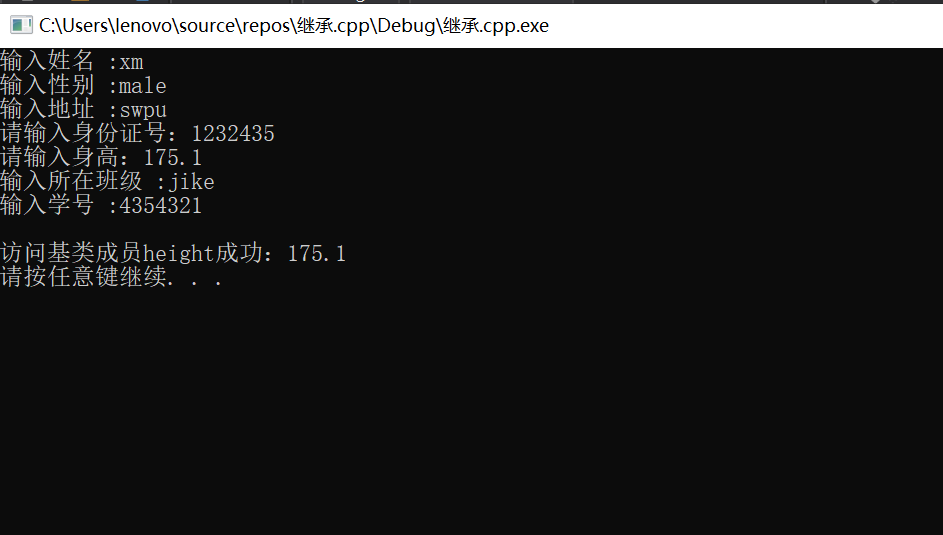
在派生类函数中,我们调用了基类成员函数成功访问了基类私有成员。
在保护继承(protected)时,
基类的所有公有成员和保护成员都成为派生类
的保护成员,并且只能被它的派生类成员函数或友元访问,基类的私有成员
仍然是私有的。
将继承方式改为保护继承(protected),
class Student :protected People//类Student以保护继承的方式继承类People
{
private:
int StudentId;
char *Class;
public:
Student(char Name[], int id, char Gender[], float Height, char Address[], int studentid, char clas[]);
void DisplayStudent();
Student();
float GetHeight();
};
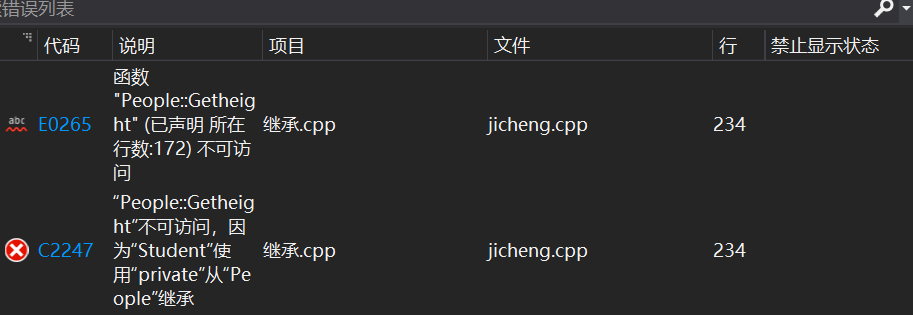
此时,当我们通过派生类访问基类成员函数时,
cout << student1.DisplayPeople() << endl; cout << student1.Getgender() << endl;
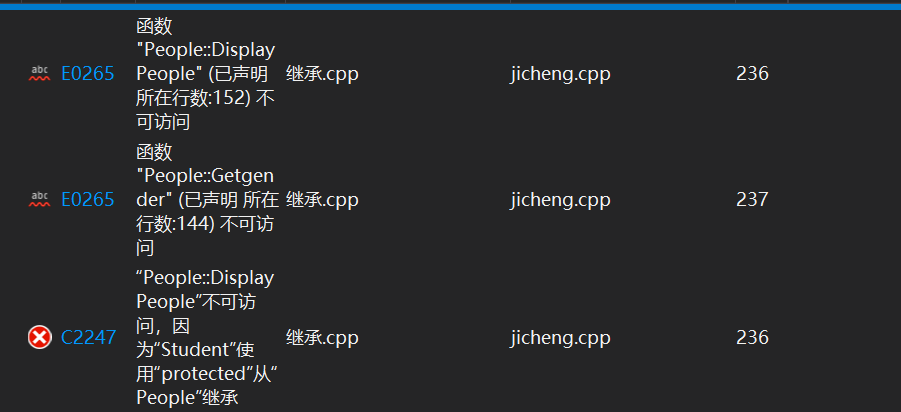
报错提示函数DisplayPeople() ,Getgender()不能被直接访问,因为在保护继承方式中,基类的public成员
对于派生类而言是protected成员,不能被直接访问。
若我们想要访问,可以通过构造派生类的成员函数访问,如下:
char* Student::GetPeopleName()
{
return People::Getname();
}
结语
通过对累的派生,我们可以使一个类的属性多样化,也有利于我们后期的设计。