我对红黑树不是很了解,所以解说不是很好。还有remove等方法没写,以后再说。linkedHashMap,treeMap,也在说
hashMap由数组、链表、红黑树组成。
why?
数组,查找快!只要知道下标,Array[index]就查到了,但是向指定下标插入一个值,当该位置有值(我称之为原值)时,则要考虑原值的去留问题!
链表,插入、删除快!只要更改prev、next的指向即可,但是,查找慢,得一个个遍历!
红黑树,插入、查找、删除都快!但是比较复杂。后面有时间,我会慢慢搞透他!
如下图所示:
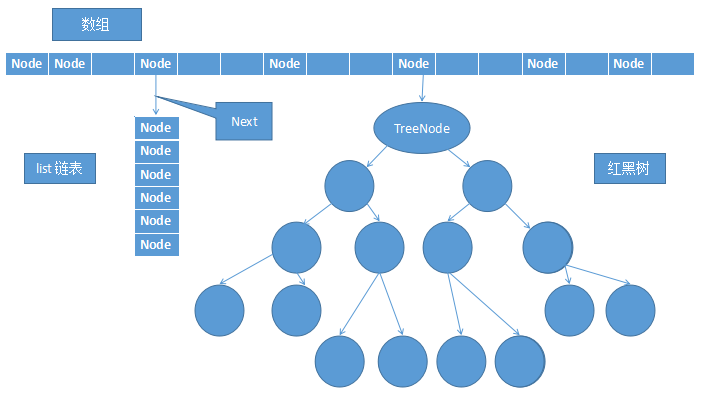
图一 hashMap基础数据结构
1. 概述
hashMap由 transient Node<K,V>[] table (这就是数组) 组成。Node包含键值等属性
/**
* 基本的桶节点,大多数实体都会用到:存储的<key,value>对应Node的key,value
* Basic hash bin node, used for most entries. (See below for
* TreeNode subclass, and in LinkedHashMap for its Entry subclass.)
*/
static class Node<K,V> implements Map.Entry<K,V> {
final int hash;
final K key;
V value;
Node<K,V> next;
Node(int hash, K key, V value, Node<K,V> next) {
this.hash = hash;
this.key = key;
this.value = value;
this.next = next;
}
...
}treeNode是红黑树的结点,是Node的子类
/**
* Entry for Tree bins. Extends LinkedHashMap.Entry (which in turn
* extends Node) so can be used as extension of either regular or
* linked node.
*/
static final class TreeNode<K,V> extends LinkedHashMap.Entry<K,V> {
TreeNode<K,V> parent; // red-black tree links
TreeNode<K,V> left;
TreeNode<K,V> right;
TreeNode<K,V> prev; // needed to unlink next upon deletion
boolean red;
...
}2. 属性
/**
* The table, initialized on first use, and resized as
* necessary. When allocated, length is always a power of two.
* (We also tolerate length zero in some operations to allow
* bootstrapping mechanics that are currently not needed.)
*/
transient Node<K,V>[] table;
/**
* Holds cached entrySet(). Note that AbstractMap fields are used
* for keySet() and values().
*/
transient Set<Map.Entry<K,V>> entrySet;
/**
* The number of key-value mappings contained in this map.
*/
transient int size;
/**
* The number of times this HashMap has been structurally modified
* Structural modifications are those that change the number of mappings in
* the HashMap or otherwise modify its internal structure (e.g.,
* rehash). This field is used to make iterators on Collection-views of
* the HashMap fail-fast. (See ConcurrentModificationException).
*/
transient int modCount;
/**
* The next size value at which to resize (capacity * load factor).
*
* @serial
*/
// (The javadoc description is true upon serialization.
// Additionally, if the table array has not been allocated, this
// field holds the initial array capacity, or zero signifying
// DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY.)
int threshold;
/**
* The load factor for the hash table.
*
* @serial
*/
final float loadFactor;3. 方法
3.1 构造方法
一共有4种构造方法,DEFAULT_LOAD_FACTOR = 0.75f
public HashMap(int initialCapacity, float loadFactor) //指定table[]初始大小和负载因子
public HashMap(int initialCapacity) { //指定table[]初始大小
this(initialCapacity, DEFAULT_LOAD_FACTOR);
}
public HashMap() { //无参构造函数
this.loadFactor = DEFAULT_LOAD_FACTOR; // all other fields defaulted
}
public HashMap(Map<? extends K, ? extends V> m) { //根据旧map,生成新map
this.loadFactor = DEFAULT_LOAD_FACTOR;
putMapEntries(m, false);
}重点看第一种
public HashMap(int initialCapacity, float loadFactor) { //初始化大小 和 负载因子
if (initialCapacity < 0)
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Illegal initial capacity: " +
initialCapacity);
if (initialCapacity > MAXIMUM_CAPACITY) //MAXIMUM_CAPACITY = 1 << 30
initialCapacity = MAXIMUM_CAPACITY;
if (loadFactor <= 0 || Float.isNaN(loadFactor))
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Illegal load factor: " +
loadFactor);
this.loadFactor = loadFactor;
this.threshold = tableSizeFor(initialCapacity);
}
调用了tableSizeFor(initialCapacity),作用是返回>=初始化大小的 最小的 2的n次方。如1->2,15->16,32->32...上图中将tableSize赋给threshold,在后期会付给table数组的初始化大小——table[]的size始终是2的n次方!这便于快速定位数组的下标( key.hashCode&(table.size-1) )
/**
* Returns a power of two size for the given target capacity.
*/
static final int tableSizeFor(int cap) {
int n = cap - 1;
n |= n >>> 1;//无符号右移1位(2进制)
n |= n >>> 2;
n |= n >>> 4;
n |= n >>> 8;
n |= n >>> 16;
return (n < 0) ? 1 : (n >= MAXIMUM_CAPACITY) ? MAXIMUM_CAPACITY : n + 1;
}
4种构造方法,有三种未初始化table数组,这是一种懒加载机制——(并不需要一开始就创建数组,而是需要用到他的时候创建,比如put)
3.2 put
/**
* Associates the specified value with the specified key in this map.
* If the map previously contained a mapping for the key, the old
* value is replaced.
* 插入键 - 值,返回该键对应的 旧值
* @param key key with which the specified value is to be associated
* @param value value to be associated with the specified key
* @return the previous value associated with <tt>key</tt>, or
* <tt>null</tt> if there was no mapping for <tt>key</tt>.
* (A <tt>null</tt> return can also indicate that the map
* previously associated <tt>null</tt> with <tt>key</tt>.)
*/
public V put(K key, V value) {
return putVal(hash(key), key, value, false, true);
}
static final int hash(Object key) {
int h;
return (key == null) ? 0 : (h = key.hashCode()) ^ (h >>> 16);//哈希值与他的无符号高16位 亦或
}
/**
* Implements Map.put and related methods
*
* @param hash hash for key
* @param key the key
* @param value the value to put
* @param onlyIfAbsent if true, don't change existing value
* @param evict if false, the table is in creation mode.
* @return previous value, or null if none(如果该key存在对应的value,则修改,并返回旧值。如果不存在,插入,并返回null)
*/
final V putVal(int hash, K key, V value, boolean onlyIfAbsent,
boolean evict) {
Node<K,V>[] tab; Node<K,V> p; int n, i;
if ((tab = table) == null || (n = tab.length) == 0)//用本地变量tab指向全局table[],
n = (tab = resize()).length; //如果table[]没有初始化,调用resize初始化,n为table的长度
if ((p = tab[i = (n - 1) & hash]) == null) //(n - 1) & hash,代表该key在table中的下标,记为 位置A,p指向位置A的,唯一的Node,或链表、红黑树的头结点
tab[i] = newNode(hash, key, value, null); //如果位置A没有值,则新建一个Node,next=null
else { //如果位置A有值,则根据实际情况:1.修改 2.插入链表 3.插入红黑树
Node<K,V> e; K k;
if (p.hash == hash &&
((k = p.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k))))
e = p; //key与p.key相同,做修改操作(此时,p可能是单节点,或链表、树的头,但是不重要,由判断条件知道,K要重写equals和hashCode方法)
else if (p instanceof TreeNode) //key与p.key不相同,且p是红黑树的节点(头结点)
e = ((TreeNode<K,V>)p).putTreeVal(this, tab, hash, key, value);//修改或插入红黑树
else { //p是链表的(头)结点
for (int binCount = 0; ; ++binCount) { //遍历链表
if ((e = p.next) == null) { //到了链表的尾部-tail
p.next = newNode(hash, key, value, null);//创建一个新节点到尾部
if (binCount >= TREEIFY_THRESHOLD - 1) // -1 for 1st(链表长度大于等于8时,将链表转成红黑树)
treeifyBin(tab, hash); //转成红黑树,或扩容
break;
}
if (e.hash == hash &&
((k = e.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k))))//key完全相同,则替换值
break;
p = e;
}
}
if (e != null) { // existing mapping for key
V oldValue = e.value;
if (!onlyIfAbsent || oldValue == null)
e.value = value;
afterNodeAccess(e); // Callbacks to allow LinkedHashMap post-actions
return oldValue;
}
}
++modCount; //走到这一步、说明有新节点加入。modCount,本map的修改次数,便利时用到,防止concurrentModifition
if (++size > threshold) //如果map的大小超过阀值,扩容(1.7版 会rehash)
resize();
afterNodeInsertion(evict); // Callbacks to allow LinkedHashMap post-actions
return null;
}
putTreeVal 不太懂
/**
* Tree version of putVal.
*/
final TreeNode<K,V> putTreeVal(HashMap<K,V> map, Node<K,V>[] tab,
int h, K k, V v) {
Class<?> kc = null;
boolean searched = false;
TreeNode<K,V> root = (parent != null) ? root() : this;
for (TreeNode<K,V> p = root;;) {
int dir, ph; K pk;
if ((ph = p.hash) > h)
dir = -1;
else if (ph < h)
dir = 1;
else if ((pk = p.key) == k || (k != null && k.equals(pk)))
return p;
else if ((kc == null &&
(kc = comparableClassFor(k)) == null) ||
(dir = compareComparables(kc, k, pk)) == 0) {
if (!searched) {
TreeNode<K,V> q, ch;
searched = true;
if (((ch = p.left) != null &&
(q = ch.find(h, k, kc)) != null) ||
((ch = p.right) != null &&
(q = ch.find(h, k, kc)) != null))
return q;
}
dir = tieBreakOrder(k, pk);
}
TreeNode<K,V> xp = p;
if ((p = (dir <= 0) ? p.left : p.right) == null) {
Node<K,V> xpn = xp.next;
TreeNode<K,V> x = map.newTreeNode(h, k, v, xpn);
if (dir <= 0)
xp.left = x;
else
xp.right = x;
xp.next = x;
x.parent = x.prev = xp;
if (xpn != null)
((TreeNode<K,V>)xpn).prev = x;
moveRootToFront(tab, balanceInsertion(root, x));
return null;
}
}
}
不太懂
/**
* Replaces all linked nodes in bin at index for given hash unless
* table is too small, in which case resizes instead.
*/
final void treeifyBin(Node<K,V>[] tab, int hash) {
int n, index; Node<K,V> e;
if (tab == null || (n = tab.length) < MIN_TREEIFY_CAPACITY)
resize();
else if ((e = tab[index = (n - 1) & hash]) != null) {
TreeNode<K,V> hd = null, tl = null;
do {
TreeNode<K,V> p = replacementTreeNode(e, null);
if (tl == null)
hd = p;
else {
p.prev = tl;
tl.next = p;
}
tl = p;
} while ((e = e.next) != null);
if ((tab[index] = hd) != null)
hd.treeify(tab);
}
}
小总结:put<key, value>操作,包含着插入、修改两重语义。当map中存在该key时,执行修改操作,比较简单。当map中不存在该key,执行插入操作,该操作会导致插入链表 || map扩容 || 链表转红黑树 || 插入红黑树,并修改全局变量modCount,如果遍历(for循环)map时执行put操作,可能会导致concurrentModifitionException,可以使用concurrentHashMap代替,后期会讲它
3.3 get方法
public V get(Object key) {
Node<K,V> e;
return (e = getNode(hash(key), key)) == null ? null : e.value;
}
final Node<K,V> getNode(int hash, Object key) {
Node<K,V>[] tab; Node<K,V> first, e; int n; K k;
if ((tab = table) != null && (n = tab.length) > 0 &&
(first = tab[(n - 1) & hash]) != null) { //hashMap通过(length - 1) & hash快速定位,这是数组的优点
if (first.hash == hash && // always check first node
((k = first.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k))))//如果是链表的头结点/树的根节点,直接返回
return first;
if ((e = first.next) != null) {
if (first instanceof TreeNode) //是树节点,则通过树的方式(左子节点-右子节点-左...)返回,
return ((TreeNode<K,V>)first).getTreeNode(hash, key);
do {
if (e.hash == hash &&
((k = e.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k))))
return e;
} while ((e = e.next) != null); //是链表,则遍历(链表最大长度为8)
}
}
return null;
}
/**
* Calls find for root node.
*/
final TreeNode<K,V> getTreeNode(int h, Object k) {
return ((parent != null) ? root() : this).find(h, k, null); //先获取树的root结点,然后调用find方法
}
/**
* Returns root of tree containing this node.
*/
final TreeNode<K,V> root() {
for (TreeNode<K,V> r = this, p;;) {
if ((p = r.parent) == null)
return r;
r = p;
}
}
/**
* Finds the node starting at root p with the given hash and key.
* The kc argument caches comparableClassFor(key) upon first use
* comparing keys.
*/
final TreeNode<K,V> find(int h, Object k, Class<?> kc) {
TreeNode<K,V> p = this;
do {
int ph, dir; K pk; //ph-当前结点的hash
TreeNode<K,V> pl = p.left, pr = p.right, q; //hash = (key == null) ? 0 : (h = key.hashCode()) ^ (h >>> 16)
if ((ph = p.hash) > h) //如果h<当前结点的hash,p = p的左子节点
p = pl;
else if (ph < h) //如果h>当前结点的hash,p = p的右子节点
p = pr;
else if ((pk = p.key) == k || (k != null && k.equals(pk)))//key相同,直接返回
return p;
else if (pl == null)
p = pr;
else if (pr == null)
p = pl;
else if ((kc != null ||
(kc = comparableClassFor(k)) != null) &&
(dir = compareComparables(kc, k, pk)) != 0)
p = (dir < 0) ? pl : pr;
else if ((q = pr.find(h, k, kc)) != null)
return q;
else
p = pl;
} while (p != null);
return null;
}上面用到两个方法,很有意思,可以自己意会
/**
* Returns x's Class if it is of the form "class C implements
* Comparable<C>", else null.
*/
static Class<?> comparableClassFor(Object x) {
if (x instanceof Comparable) {
Class<?> c; Type[] ts, as; Type t; ParameterizedType p;
if ((c = x.getClass()) == String.class) // bypass checks
return c;
if ((ts = c.getGenericInterfaces()) != null) {
for (int i = 0; i < ts.length; ++i) {
if (((t = ts[i]) instanceof ParameterizedType) &&
((p = (ParameterizedType)t).getRawType() ==
Comparable.class) &&
(as = p.getActualTypeArguments()) != null &&
as.length == 1 && as[0] == c) // type arg is c
return c;
}
}
}
return null;
}
/**
* Returns k.compareTo(x) if x matches kc (k's screened comparable
* class), else 0.
*/
@SuppressWarnings({"rawtypes","unchecked"}) // for cast to Comparable
static int compareComparables(Class<?> kc, Object k, Object x) {
return (x == null || x.getClass() != kc ? 0 :
((Comparable)k).compareTo(x));
}
来源:oschina
链接:https://my.oschina.net/u/1380557/blog/793254