一、容器
1、vector
vector 是STL的动态数组,索引可以在常数时间内完成,插入或删除中间某一项需要线性时间,时间复杂度是O(n)
vector<int> b(a); //用a定义b vector<int> a(100); //a有100个值为0的元素 vector<int> a(100, 6) //a有100个值为6的元素 vector<string> a(10, "hello"); vector<string> b(a.begin(), a.end()); // b是a的复制 a.insert(a.begin() + i, k); // 在第i个元素前插入k a.erase(a.begin() + i, a.bejin() + j); //删除区间[i, j - 1]的元素 a.erase(a.begin() + 2); // 删除第三个元素 reverse(a.begin(), a.end()); //翻转数组
hdu 4841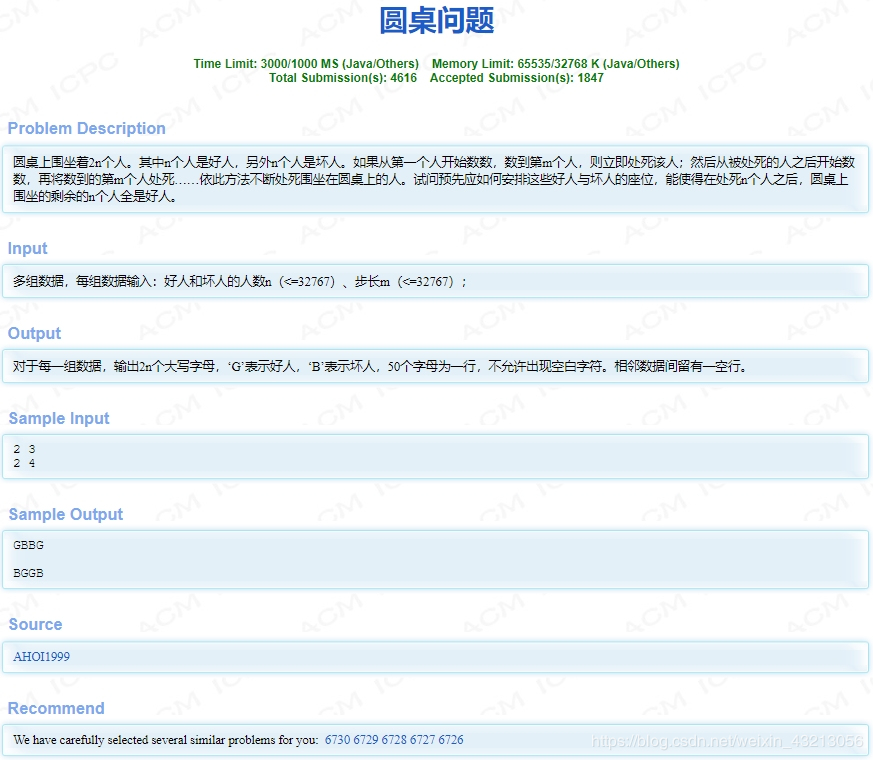
//#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#include <vector>
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main(){
vector<int> table;
int n, m;
while(cin >> n >> m){
table.clear();
for(int i = 0; i < 2 * n; i++) table.push_back(i);
int pos = 0;
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++){
pos = (pos + m - 1) % table.size();
table.erase(table.begin() + pos);
}
int j = 0;
for(int i = 0; i < 2 * n; i++){
if(!(i % 50) && i) cout << endl;
if(j < table.size() && i == table[j]){
j++;
cout << "G";
}
else
cout << "B";
}
cout << endl << endl;
}
return 0;
}
2、stack、queue
栈需要空间存储,如果深度太大,或者存储进栈的数组太大,那么总数会超过系统为栈分配的空间,这样就会爆栈,即栈溢出
可以手工写栈解决这个问题
// stack s.push(item); s.top(); s.pop(); s.size(); s.empty(); // queue q.push(item); q.front(); //返回队首元素,但不会删除 q.pop(); // 删除队首元素 q.back(); // 返回队尾元素
hdu 1062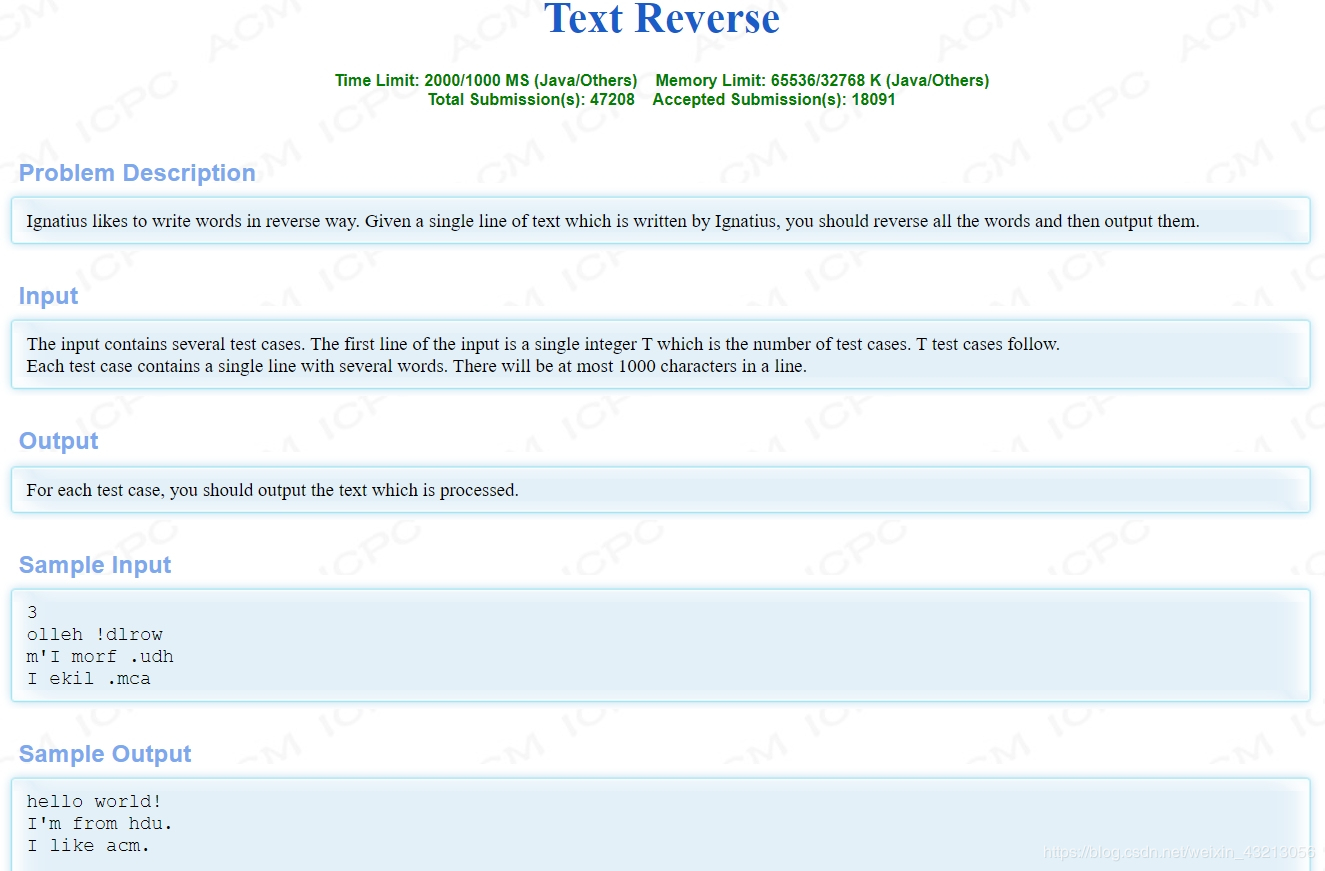
//#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#include <iostream>
#include <stack>
using namespace std;
int main(){
int n;
char ch;
scanf("%d", &n); getchar();
while(n--){
stack<char> s;
while(true){
ch = getchar();
if(ch == ' ' || ch == '\n' || ch == EOF){
while(!s.empty()){
printf("%c", s.top());
s.pop();
}
if(ch == '\n' || ch == EOF) break;
printf(" ");
}
else s.push(ch);
}
printf("\n");
}
return 0;
}
hdu 1702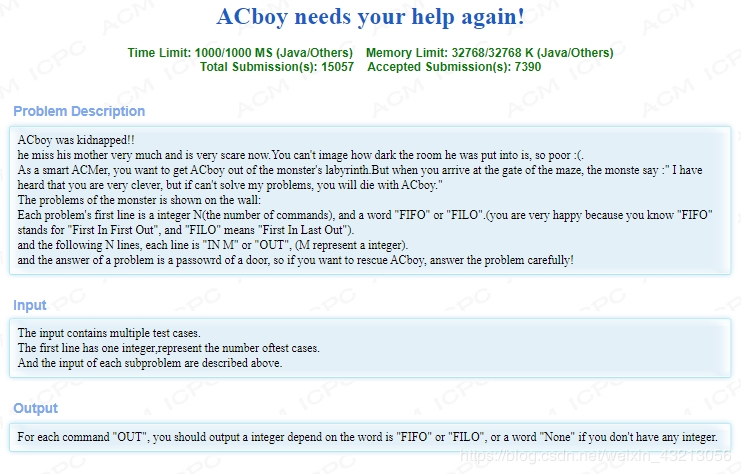
c //#include <bits/stdc++.h> #include <iostream> #include <stack> #include <string> #include <queue> #include <stack> using namespace std; int main(){ int t, n, temp; cin >> t; while(t--){ string str, str1; queue<int> Q; stack<int> S; cin >> n >> str; for(int i = 0; i < n; i++) { if (str == "FIFO") { cin >> str1; if (str1 == "IN") { cin >> temp; Q.push(temp); } if (str1 == "OUT") { if (Q.empty()) cout << "None" << endl; else { cout << Q.front() << endl; Q.pop(); } } } else { cin >> str1; if (str1 == "IN") { cin >> temp; S.push(temp); } if (str1 == "OUT") { if (S.empty()) cout << "None" << endl; else { cout << S.top() << endl; S.pop(); } } } } } return 0; }
3、list
list是数据结构的双向链表,它的内存空间可以是不连续的,通过指针进行数据的访问,它可以高效的在任意地方删除和插入,插入和删除操做是常数时间的。
list 和 vector 的优缺点正好相反,它们的应用场景不同。
(1)vector:插入和删除次数较少,随机访问元素频繁。
(2)list:插入和删除频繁,随机访问较少。
hdu 1276
//#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#include <iostream>
#include <stack>
#include <string>
#include <queue>
#include <stack>
#include <list>
using namespace std;
int main(){
int t, n;
cin >> t;
while(t--){
cin >> n;
int k = 2;
list<int> mylist;
list<int>:: iterator it;
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++) mylist.push_back(i);
while(mylist.size() > 3){
int num = 1;
for(it = mylist.begin(); it != mylist.end();){
if(num++ % k == 0){
it = mylist.erase(it);
}
else it++;
}
k == 2? k = 3: k = 2;
}
for(it = mylist.begin(); it != mylist.end(); it++){
if(it != mylist.begin()){
cout << " ";
}
cout << *it;
}
cout << endl;
}
return 0;
}
4、set
set 就是集合。STL的set用二叉搜索树实现,集合中的每一个元素只出现一次,并且是排好序的。访问元素的时间复杂度是O(logn) 非常高效。
a.insert(item); //插入 a.erase(item); //删除 a.find(k); //返回一个迭代器,指向k a.lower_bound(); // 返回一个迭代器,指向键值不小于k的第一跟元素 a.upper_bound(); // 返回一个迭代器,指向键值大于k的第一个元素
hdu 2094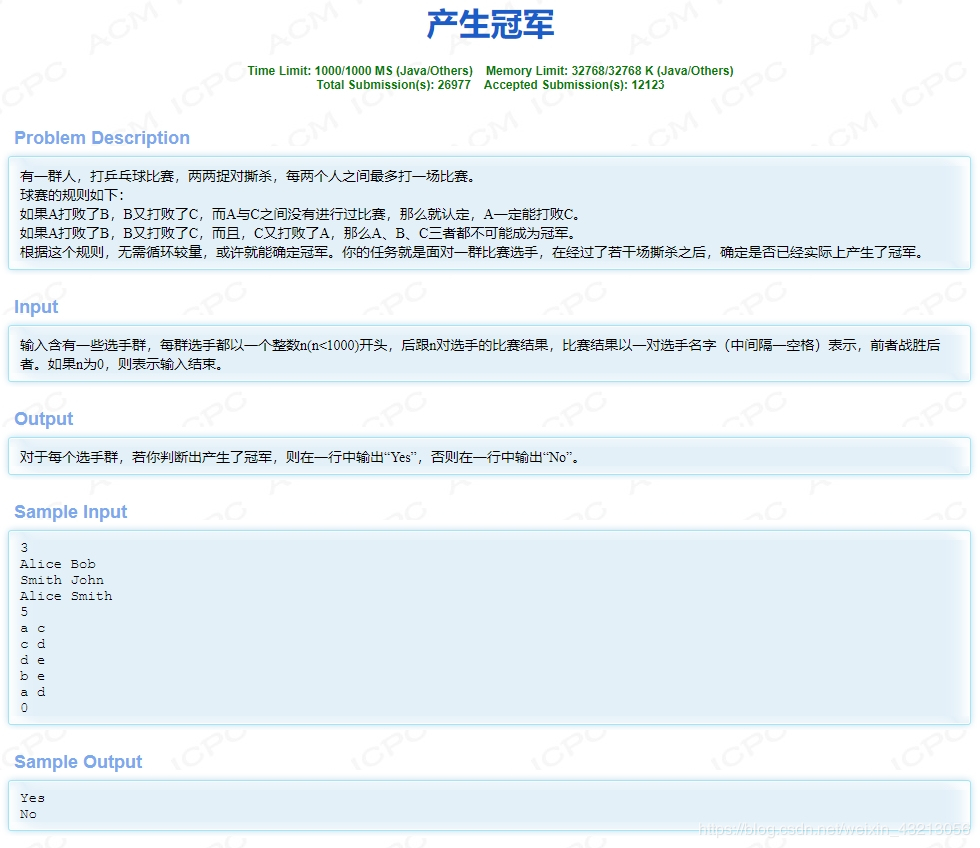
//#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#include <iostream>
#include <stack>
#include <string>
#include <queue>
#include <stack>
#include <set>
#include <list>
using namespace std;
int main(){
set<string> A, B;
string s1, s2;
int n;
while (cin >> n && n){
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++){
cin >> s1 >> s2;
A.insert(s1);
A.insert(s2);
B.insert(s2);
}
if(A.size() - B.size() == 1){
cout << "Yes" << endl;
}
else cout << "No" << endl;
A.clear();
B.clear();
}
return 0;
}
5、map
利用STL中的map实现查找,复杂度是O(logn)
hdu 2648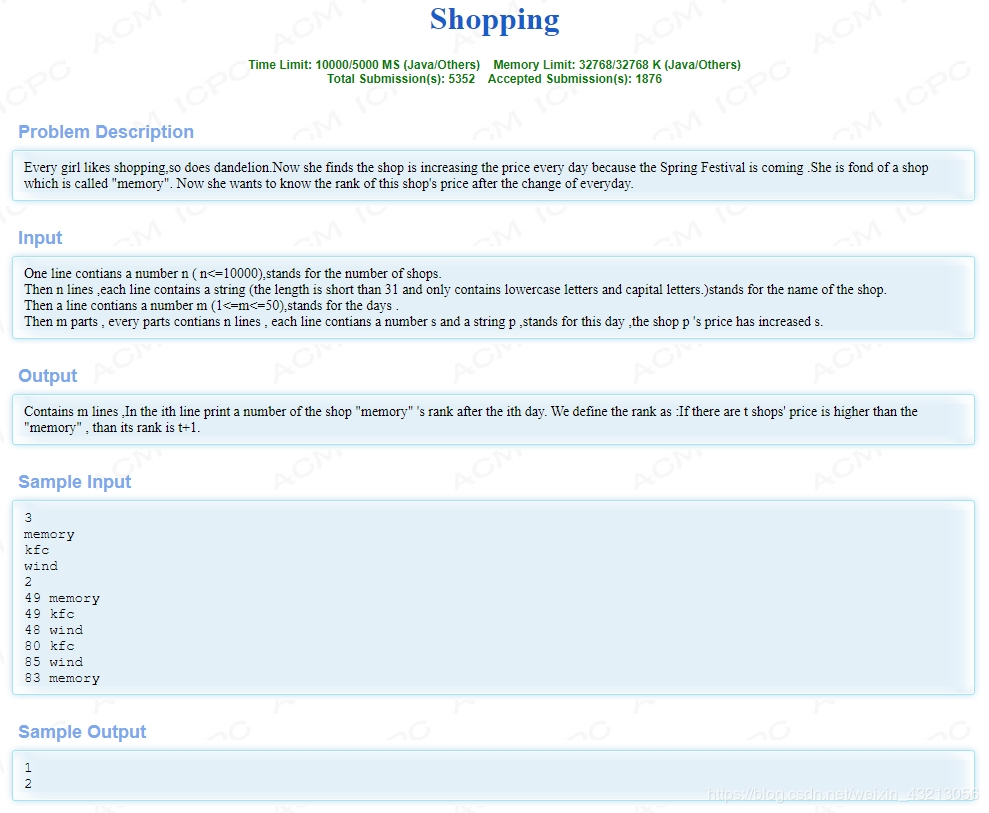
//#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#include <iostream>
#include <stack>
#include <string>
#include <queue>
#include <stack>
#include <set>
#include <list>
#include <map>
using namespace std;
int main() {
int n, m, p;
map<string, int> shop;
while (cin >> n){
string s;
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++) cin >> s;
cin >> m;
while(m--){
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++){
cin >> p >> s;
shop[s] += p;
}
int rank = 1;
map<string, int>::iterator it;
for(auto it: shop){
if(it . second > shop["memory"])
rank ++;
}
cout << rank << endl;
}
shop.clear();
}
return 0;
}
二、常用函数
1、sort()
复杂度O(nlogn)
它的排序范围是[first, last),包括first,不包括last。
//#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#include <iostream>
#include <stack>
#include <string>
#include <queue>
#include <stack>
#include <set>
#include <list>
#include <map>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
bool my_less(int i, int j) {return (i < j);} // 自定义升序
bool my_greater(int i, int j){return (i > j);} // 自定义降序
int main(){
vector<int> a = {3, 7, 2, 5, 6, 8, 5, 4};
sort(a.begin(), a.begin() + 4); // 对前四个排序
sort(a.begin(), a.end()); // 默认升序排列
sort(a.begin(), a.end(), less<int>());
sort(a.begin(), a.end(), my_less);
sort(a.begin(), a.end(), greater<int>());
sort(a.begin(), a.end(), my_greater);
for(int i = 0; i < a.size(); i++){
cout << a[i] << " ";
}
return 0;
}
sort()还可以对结构体进行排序
struct Student{
char name[256];
int score;
}
bool cmp(struct Student* a, struct Student* b){
return a -> score > b -> score;
}
vector<struct struct*> list;
sort(list.begin(), list.end(), cmp);
2、next_permulation()
STL提供求下一个排列组合的函数next_permulation()。例如3个字符a、b、c组成的序列,next_permulation()能按字典序返回六个组合,即abc,acb,bac,bca,cab,cba。
bool next_permulation(first,last);
返回值:如果没有下一个排列组合,返回false,否则返回true,每次执行next_permulation()会把新的排列放到原来的空间里。
hdu 1027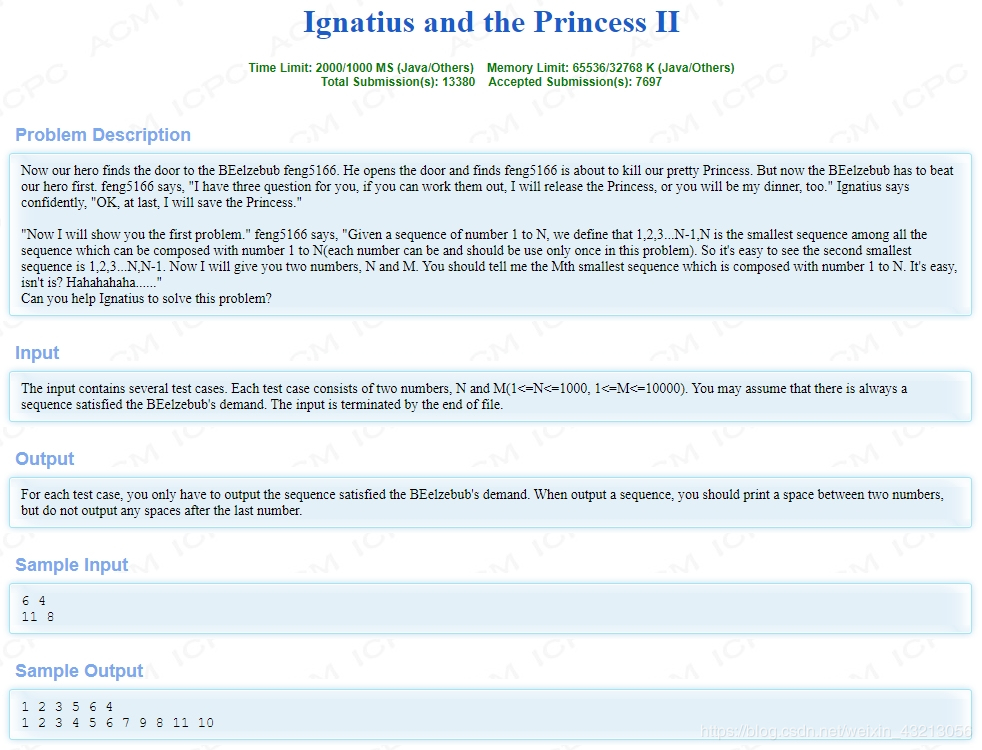
//#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#include <iostream>
#include <stack>
#include <string>
#include <queue>
#include <stack>
#include <set>
#include <list>
#include <map>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
int a[1001];
int main(){
int n, m;
while(cin >> n >> m){
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++) a[i] = i;
int b = 1;
do{
if(b == m) break;
b++;
}while(next_permutation(a + 1, a + 1 + n));
for(int i = 1; i < n; i++){
cout << a[i] << " ";
}
cout << a[n] << endl;
}
return 0;
}