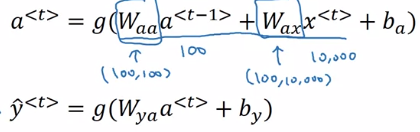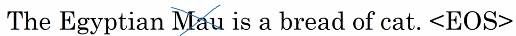Coursera - Sequence Models - Andrew Ng 学习随笔
Part 1 Recurrent Nerual Network
- 应用广泛:Speech Recognition / Music Generation / Sentiment Classification / DNA Sequence Analysis / Machine Translation / Video Activity Recognition / Name Entity Recognition
- Notation, 以Name Entity Recognition为例, Representing words可以采用one-hot, 但是维度过大, 且十分稀疏 - Problems, 句子的***输入输出长度不一定相等且句子中相同词汇需要共享特征提取的过程***, 所以native的DNN (比如全连接层) 则不适合这种工作

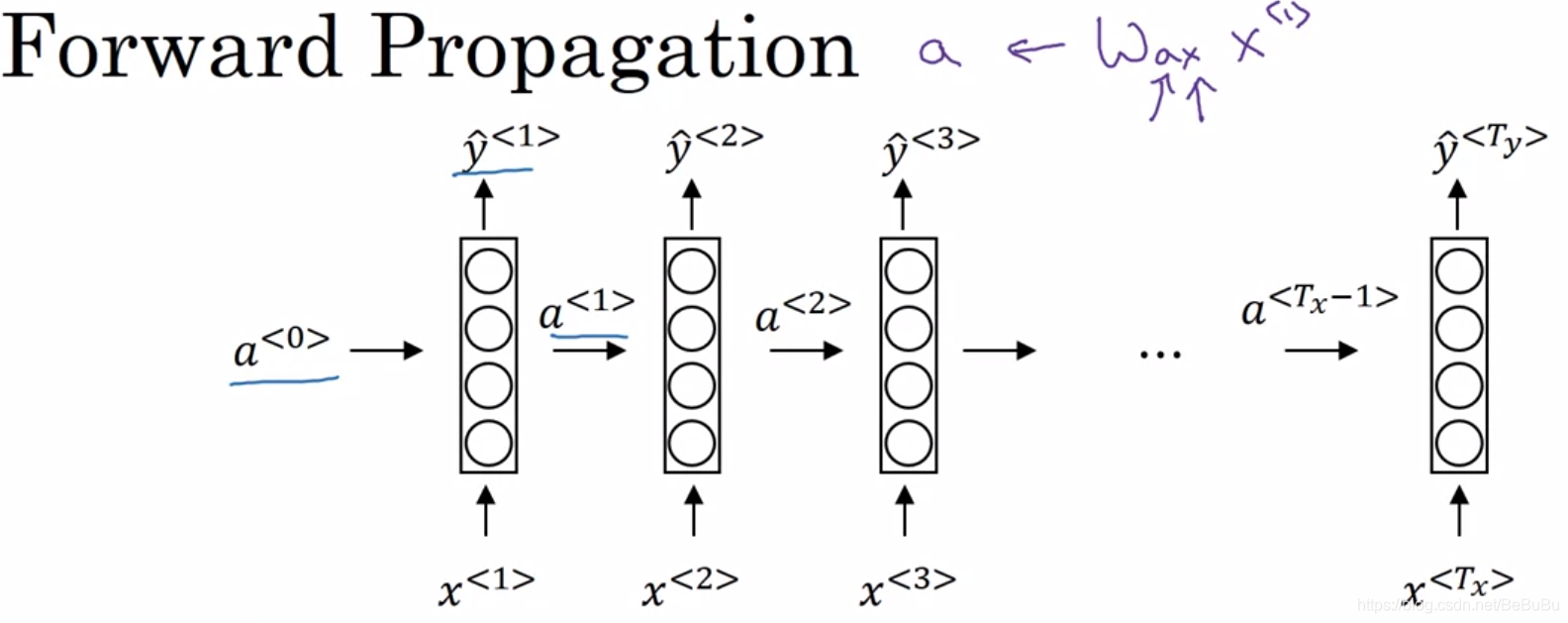
- Recurrent Nerual Network:
-
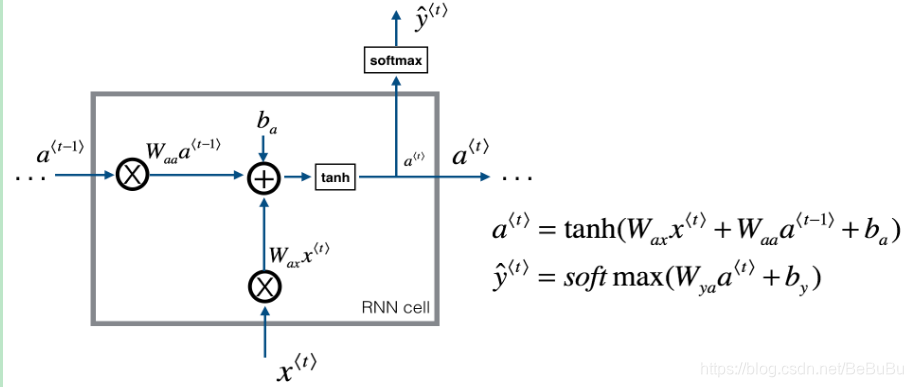
- (当输入和输出长度相同时)

- (当输入和输出长度相同时)
-
- Backpropagation through time BPTT, 循环结构展开,将所有时刻(对于句子就是词语的先后)下的损失函数求和对各个时刻的参数进行求和
- 按输出输出数目分类:many2many / one2many(music generation) / many2one / one2one 类型 ;Encoder-Decoder解决长度不一致的问题!
- Language model and sequence generation
-
- Language Model: P(Sentence) = ? 给一个句子,判断在这个世界使用的几率大小. 训练数据: Large corpus of English text:

- Language Model: P(Sentence) = ? 给一个句子,判断在这个世界使用的几率大小. 训练数据: Large corpus of English text:
-
-
- RNN Model: 概率论上就是按照条件概率展开,乘法规则
-
- Sampling novel sequence,将前序输出直接输入到后序,得到的整体输出序列,有句子有词语: Word-level and Character-level (更要求计算力) language model
- Vanishing Gradients with RNNs: 基本的RNN结构无法捕捉长距离的依赖,按时序展开后较深的输出很难反向传播影响之前层的参数. The cats, which …, was/were full.
-
- 相应的Exploding Gradient容易发现(NaN, Not a Number),且可以采用Gradient Clipping去解决.
-
- Gated Recurrent Unit (GRU) - 2014
-
-
- Original RNN Unit:

- Original RNN Unit:
-
-
-
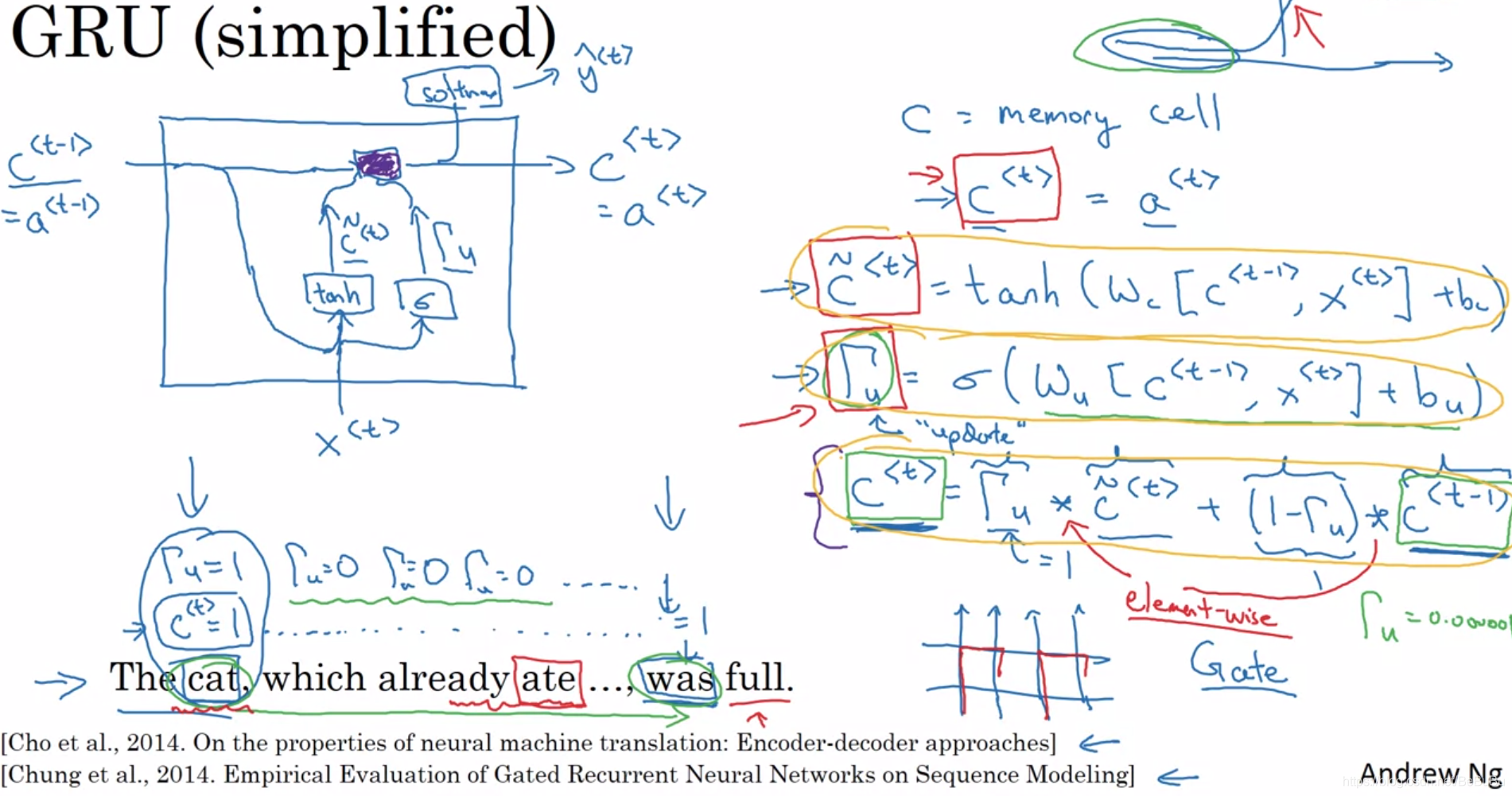
- GRU cell:


- GRU cell:
-
-
-
-
- 个人理解:1) Update Gate: gamma_u意在控制时序上的隐藏层的更新;2) Relevant Gate: gamma_r意在控制用于更新的隐藏层有多少或者是否能被使用(在是否利用前序隐藏层信息和只用当前输入信息间抉择)
-
-
-
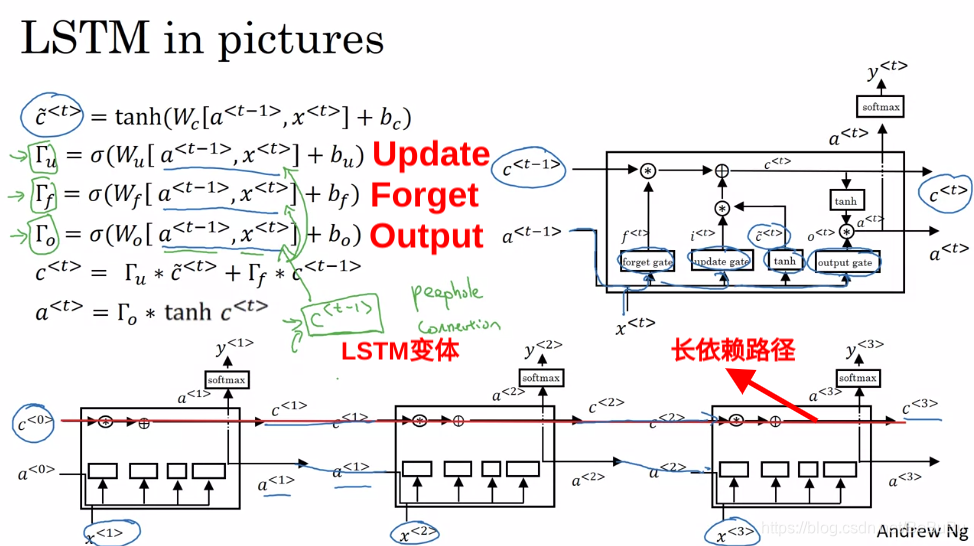
- Long Short Term Memory (LSTM) Unit —— 1997

- Long Short Term Memory (LSTM) Unit —— 1997
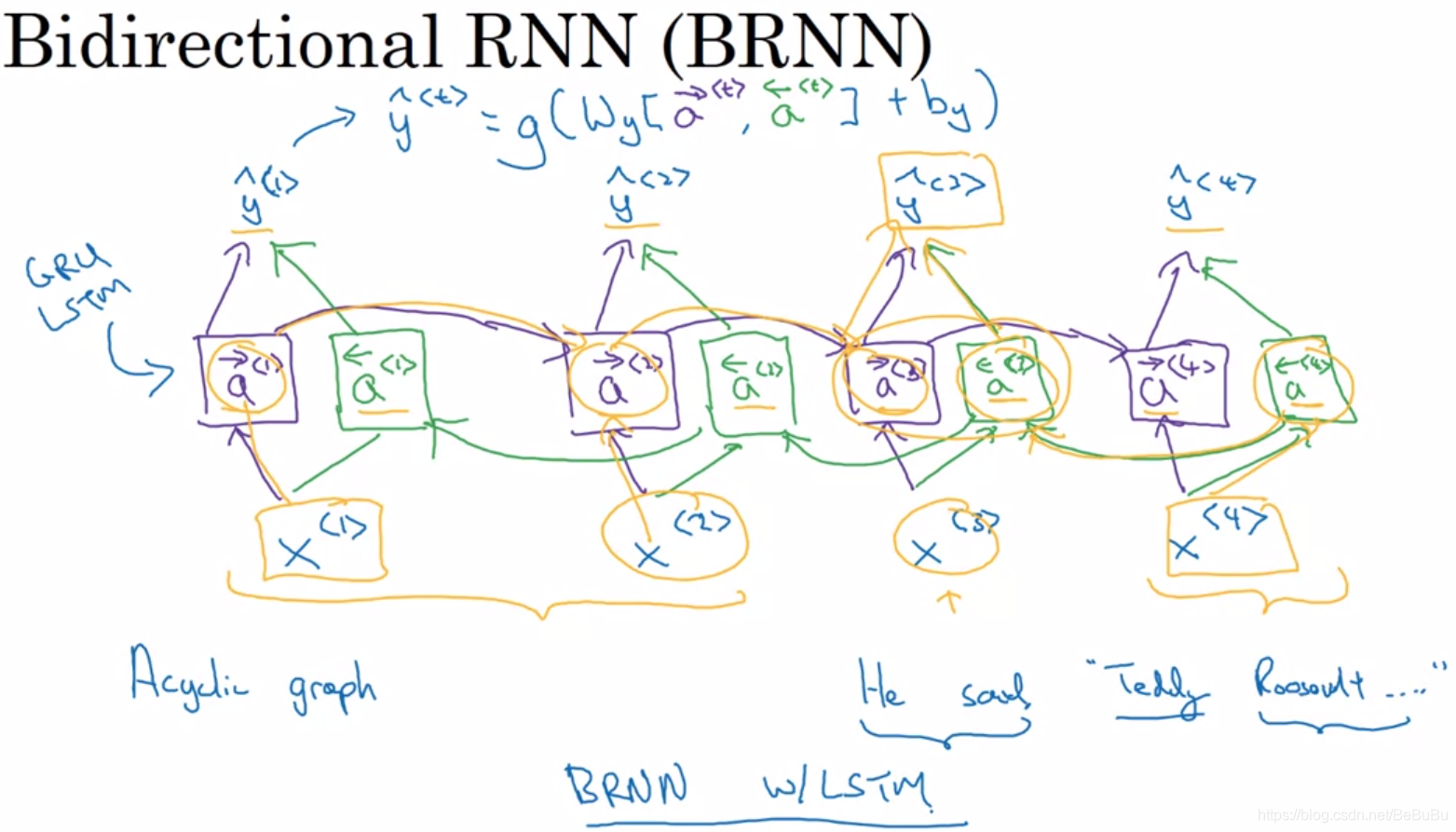
- Bidirectional RNN (BRNN)
-
- Getting information from the future. 缺点:需要整个数据序列才能在任何地方进行预测
-
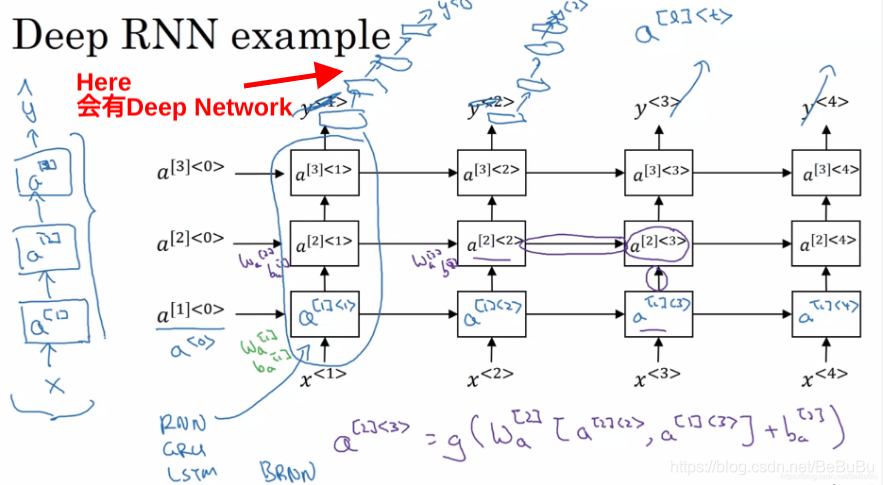
- Deep RNN example (隐藏层多)
-
- 多个隐藏层在时序上展开会是否庞大,一般有三层隐藏层就已经很大了

- 多个隐藏层在时序上展开会是否庞大,一般有三层隐藏层就已经很大了
Part 2 Recurrent Nerual Network
来源:https://blog.csdn.net/BeBuBu/article/details/100789551