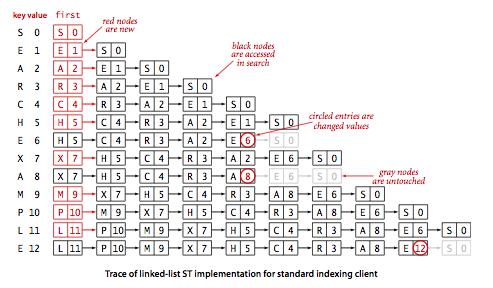
符号表是一种存储键值对的数据结构,支持两种操作,
- 插入(put) 将新的键值对存入表中
- 查询(get) 给定键得到相应的值
规则
重复的键
每一个键只能对应着一个值(表中不允许存在重复的键)
当存入的的键值对和表中已有的键冲突时,新的值会替代旧的值
空键
键不能为空,使用空键会产生一个运行异常。
空值
规定不允许有空值,当键不存在时get()返回空,任何不在表中的键关联的值都是空
删除操作
在表中删除有两种方法:
- 延迟删除,也就是将键对应的值置为空(null) put(key,null)
及时删除,delete(key)
实现
符号表分为有序和无序两种
无序链表的顺序查找

public class SequentialSearchST<K, V> {
private class Node {
K key;
V val;
Node next;
public Node(K key, V val, Node next) {
this.key = key;
this.val = val;
this.next = next;
}
}
private Node first;
public V get(K key) {
for (Node x = first; x != null; x = x.next) {
if (key.equals(x.key)) {
return x.val;
}
}
return null;
}
public int size() {
int cut = 0;
Node cur = this.first;
while (cur != null) {
cut++;
cur = cur.next;
}
return cut;
}
public void put(K key, V value) {
for (Node x = first; x != null; x = x.next) {
if (key.equals(x.key)) {
x.val = value;//命中更新节点
return;
}
first = new Node(key, value, first);//未命中,建立新节点
}
}
public void delete(K key) {
if (first == null) {
return;
}
if (first.key.equals(key)) {
first = first.next;
}
Node pre = first;
Node cur = first.next;
while (cur != null) {
if (cur.key.equals(key)) {
pre.next = cur.next;
return;
}
pre = pre.next;
cur = cur.next;
}
}
}
有序数组的二分查找
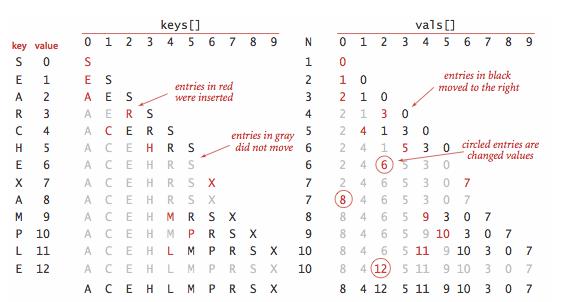
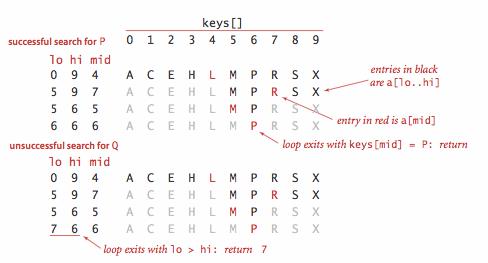
- 使用一对平行数组,一个存储键,一个存储值
- 二分查找的 rank() 方法至关重要,当键在表中时,它能够知道该键的位置;当键不在表中时,它也能知道在何处插入新键。
- 二分查找最多需要 logN+1 次比较,使用二分查找实现的符号表的查找操作所需要的时间最多是对数级别的。但是插入操作需要移动数组元素,是线性级别的。
public class BinarySearchST<K extends Comparable<K>, V> {
private K[] keys;
private V[] vals;
private int N;
public BinarySearchST(int capacity) {
keys = (K[]) new Comparable[capacity];
vals = (V[]) new Object[capacity];
}
public K min() {
return keys[0];
}
public K max() {
return keys[N - 1];
}
public int size() {
return N;
}
public V get(K key) {
if (isEmpty()) {
return null;
}
int i = rank(key);
if (i < N && keys[i].compareTo(key) == 0) {
return vals[i];
} else {
return null;
}
}
private boolean isEmpty() {
return N == 0;
}
private int rank(K key) {
int lo = 0, hi = N - 1;
while (lo <= hi) {
int mid = lo + (hi - lo) / 2;
int cmp = key.compareTo(keys[mid]);
if (cmp < 0) {
hi = mid - 1;
} else if (cmp > 0) {
lo = mid + 1;
} else {
return mid;
}
}
//如果未命中
//未命中时,lo大于查询值(后一个) hi小于查询值(前一个)
return lo;
}
public void put(K key, V value) {
int i = rank(key);
if (i < N && keys[i].compareTo(key) == 0) {
vals[i] = value;
return;
}
//腾位置
for (int j = N; j > i; j--) {
keys[j] = keys[j - 1];
vals[j] = vals[j - 1];
}
keys[i] = key;
vals[i] = value;
N++;
}
}
上面是非递归实现
递归实现:
public int rank(Key key, int lo, int hi) {
if (lo > hi) return lo;
int mid = (lo + hi) / 2;
int cmp = key.compareTo(key[mid]);
if (cmp > 0) return rank(key, mid + 1, hi);
else if (cmp < 0) return rank(key, lo, mid-1);
else return mid;
}
未命中时
- lo大于查询值(后一个)
- hi小于查询值(前一个)