一.配置文件
SpringBoot可以使用两种类型的配置文件(文件名固定):
application.properties
application.yml
配置文件的作用就是来修改SpringBoot自动配置的默认值:SpringBoot在底层都给我们配置好了所有的配置信息
yml:YAML(YAML Ain't a Markup Language):新型配置文件.以前的配置文件大都使用到的是"xxx.xml"文件,YML以数据为中心,更适合做配置文件;
二.YML语法
1.基本语法
k:(空格)v --表示一对键值对(空格必须有);
以空格的缩进来控制层级关系: 只要是左对齐的一列数据,都是同一层级的,且属性和值都是大小写敏感的
2.值的写法
字面量: 普通的值(数字,字符串,布尔): key: value,字符串不用加引号:
""字符串:不会转义字符串中的特殊字符,特殊字符会作为本身想要表示的意思
"zhangsan \n lisi" 输出: zhangsan 换行 lisi
' '字符串: 特殊字符不会进行转义,特殊字符最终只是一个普通的字符串数据
对象,Map(属性和值)(键值对):
k: v: //在下一行来写对象的属性和值的关系,要用空格控制好缩进
k: v
friends:
lastName: zhangsan
age: 20
行内写法:
friends: {lastName: zhangsan,age: 18}
数组(List,set):
用- 值来表示数组中的一个元素
pets:
- cat
- dog
- pig
行内写法:
pets: [cat,dog,pig]
3.配置自定义类
1 package com.skykuqi.springboot.helloworld.entity;
2
3 import org.springframework.boot.context.properties.ConfigurationProperties;
4 import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
5
6 import java.util.Date;
7 import java.util.List;
8 import java.util.Map;
9
10 /**
11 * @author : S K Y
12 * @version :0.0.1
13 */
14 /*将yml配置文件中配置的每一个属性的值映射到属性文件中*/
15 @Component
16 @ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "person")
17 public class Person {
18 private String lastName;
19 private Integer age;
20 private Boolean boss;
21 private Date birth;
22
23 private Map<String, Object> maps;
24 private List<Object> lists;
25 private Dog dog;
26
27 public String getLastName() {
28 return lastName;
29 }
30
31 public void setLastName(String lastName) {
32 this.lastName = lastName;
33 }
34
35 public Integer getAge() {
36 return age;
37 }
38
39 public void setAge(Integer age) {
40 this.age = age;
41 }
42
43 public Boolean getBoss() {
44 return boss;
45 }
46
47 public void setBoss(Boolean boss) {
48 this.boss = boss;
49 }
50
51 public Date getBirth() {
52 return birth;
53 }
54
55 public void setBirth(Date birth) {
56 this.birth = birth;
57 }
58
59 public Map<String, Object> getMaps() {
60 return maps;
61 }
62
63 public void setMaps(Map<String, Object> maps) {
64 this.maps = maps;
65 }
66
67 public List<Object> getLists() {
68 return lists;
69 }
70
71 public void setLists(List<Object> lists) {
72 this.lists = lists;
73 }
74
75 public Dog getDog() {
76 return dog;
77 }
78
79 public void setDog(Dog dog) {
80 this.dog = dog;
81 }
82
83 @Override
84 public String toString() {
85 return "Person{" +
86 "lastName='" + lastName + '\'' +
87 ", age=" + age +
88 ", boss=" + boss +
89 ", birth=" + birth +
90 ", maps=" + maps +
91 ", lists=" + lists +
92 ", dog=" + dog +
93 '}';
94 }
95 }
1 package com.skykuqi.springboot.helloworld.entity;
2
3 import org.springframework.boot.context.properties.ConfigurationProperties;
4 import org.springframework.boot.context.properties.NestedConfigurationProperty;
5 import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
6
7 /**
8 * @author : S K Y
9 * @version :0.0.1
10 */
11 @Component
12 @ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "dog")
13 public class Dog {
14 private String name;
15 private Integer age;
16
17 public String getName() {
18 return name;
19 }
20
21 public void setName(String name) {
22 this.name = name;
23 }
24
25 public Integer getAge() {
26 return age;
27 }
28
29 public void setAge(Integer age) {
30 this.age = age;
31 }
32
33 @Override
34 public String toString() {
35 return "Dog{" +
36 "name='" + name + '\'' +
37 ", age=" + age +
38 '}';
39 }
40 }
1 person:
2 lastName: zhangsan
3 age: 22
4 boss: true
5 birth: 2019/11/25
6 maps: {k1: 12,k2: 21}
7 lists:
8 - lisi
9 - zhaoliu
10 - wnangwu
11 dog:
12 name: 小狗
13 age: 3
1 package com.skykuqi.springboot.helloworld;
2
3 import com.skykuqi.springboot.helloworld.entity.Person;
4 import javafx.application.Application;
5 import org.junit.Test;
6 import org.junit.runner.RunWith;
7 import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
8 import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest;
9 import org.springframework.test.context.junit4.SpringJUnit4ClassRunner;
10 import org.springframework.test.context.junit4.SpringRunner;
11
12 /**
13 * @author : S K Y
14 * @version :0.0.1
15 * SpringBoot单元测试
16 * 可以在测试期间类似编码一样进行自动注入到容器的功能,目录结构必须和原路径相同
17 */
18 @RunWith(SpringRunner.class)
19 @SpringBootTest
20 public class HelloWorldMainApplicationTests {
21 @Autowired
22 Person person;
23
24 @Test
25 public void testPerson() {
26 System.out.println(person);
27 }
28 }
1 <!--配置文件的处理器,编写自定义的属性则会出现提示--> 2 <dependency> 3 <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> 4 <artifactId>spring-boot-configuration-processor</artifactId> 5 <optional>true</optional> 6 </dependency>
4.除了使用@ConfigurationProperties注解,我们还可以使用@Value注解来完成
1 package com.skykuqi.springboot.helloworld.entity;
2
3 import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value;
4 import org.springframework.boot.context.properties.ConfigurationProperties;
5 import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
6
7 import java.util.Date;
8 import java.util.List;
9 import java.util.Map;
10
11 /**
12 * @author : S K Y
13 * @version :0.0.1
14 */
15 /*将yml配置文件中配置的每一个属性的值映射到属性文件中*/
16 @Component
17 //@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "person")
18 public class Person {
19 @Value("${person.lastName}")
20 private String lastName;
21 @Value("#{11*2}")
22 private Integer age;
23 @Value("false")
24 private Boolean boss;
25 private Date birth;
26
27 private Map<String, Object> maps;
28 private List<Object> lists;
29 private Dog dog;
30
31 public String getLastName() {
32 return lastName;
33 }
34
35 public void setLastName(String lastName) {
36 this.lastName = lastName;
37 }
38
39 public Integer getAge() {
40 return age;
41 }
42
43 public void setAge(Integer age) {
44 this.age = age;
45 }
46
47 public Boolean getBoss() {
48 return boss;
49 }
50
51 public void setBoss(Boolean boss) {
52 this.boss = boss;
53 }
54
55 public Date getBirth() {
56 return birth;
57 }
58
59 public void setBirth(Date birth) {
60 this.birth = birth;
61 }
62
63 public Map<String, Object> getMaps() {
64 return maps;
65 }
66
67 public void setMaps(Map<String, Object> maps) {
68 this.maps = maps;
69 }
70
71 public List<Object> getLists() {
72 return lists;
73 }
74
75 public void setLists(List<Object> lists) {
76 this.lists = lists;
77 }
78
79 public Dog getDog() {
80 return dog;
81 }
82
83 public void setDog(Dog dog) {
84 this.dog = dog;
85 }
86
87 @Override
88 public String toString() {
89 return "Person{" +
90 "lastName='" + lastName + '\'' +
91 ", age=" + age +
92 ", boss=" + boss +
93 ", birth=" + birth +
94 ", maps=" + maps +
95 ", lists=" + lists +
96 ", dog=" + dog +
97 '}';
98 }
99 }
5.@Value和@ConfigurationProperties获取值比较
功能上:@ConfigurationProperties可以批量注入配置文件中的属性,@Value必须一个一个指定
松散语法:@ConfigurationProperties支持松散绑定lastName last-name last_name 等都可以绑定到当前的属性
Spel(Spring 表达式): @Value支持Spring表达式
JSR303校验:@ConfigurationProperties支持JSR303数据校验
复杂类型封装(map):@ConfigurationProperties之处,@Value不支持
6.如果说我们只是在某个业务逻辑中只是需要获取一下配置文件中的某项值,那么我们只需要使用@Value:
1 @Value("${person.lastName}")
2 private String name;
3
4 @RequestMapping("/helloWithName")
5 public String helloWithName() {
6 return "Hello " + name;
7 }
--如果专门配置了一个JavaBean来和配置文件进行映射,我们就直接使用@ConfigurationProperties
三.@PropertySource和@ImportResource注解的使用
@PropertySource:加载指定的配置文件,我们在使用@ConfigurationProperties注解来进行注入的时候,默认有一个要求,就是当前的配置属性需要写在默认的配置文件中(即application为文件名的配置文件,全局配置文件),如果我们把所有的配置信息都写在全局配置文件中,将会造成配置文件过大的问题,不宜阅读与维护,我们创建一个person.properties文件,而后使用@PropertySource注解完成我们的注入:
1 @Component
2 @ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "person")
3 @PropertySource(value = {"classpath:person.properties"})
4 //@Validated
5 public class Person {}
@ImportSource:导入Spring的配置文件,让配置文件的内容生效,在传统的开发中我们想要在Spring的配置文件中加入一个组件需要这样做:
1 <?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> 2 <beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" 3 xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" 4 xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd"> 5 <bean id="helloService" class="com.skykuqi.springboot.helloworld.service.HelloService"> 6 7 </bean> 8 </beans>
1 package com.skykuqi.springboot.helloworld;
2
3 import com.skykuqi.springboot.helloworld.entity.Person;
4 import javafx.application.Application;
5 import org.junit.Test;
6 import org.junit.runner.RunWith;
7 import org.junit.runners.JUnit4;
8 import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
9 import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest;
10 import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
11 import org.springframework.test.context.junit4.SpringRunner;
12
13 /**
14 * @author : S K Y
15 * @version :0.0.1
16 * SpringBoot单元测试
17 * 可以在测试期间类似编码一样进行自动注入到容器的功能,目录结构必须和原路径相同
18 */
19 @RunWith(SpringRunner.class)
20 @SpringBootTest
21 public class HelloWorldMainApplicationTests {
22 @Autowired
23 Person person;
24
25 @Autowired
26 ApplicationContext context;
27
28 @Test
29 public void testPerson() {
30 System.out.println(person);
31 }
32 @Test
33 public void testBeansXml(){
34 boolean helloService = context.containsBean("helloService");
35 System.out.println(helloService);
36 }
37 }
--测试我们的testBeansXml方法,发现我们自己编写的配置文件也不能自动识别,想让Spring的配置文件生效,那么我们需要将@ImportResource注解标注在我们的主配置类上:
1 @SpringBootApplication
2 @ImportResource(locations = {"classpath:beans.xml"})
3 public class HelloWorldMainApplication {
4 }
SpringBoot中推荐给容器中添加组件的方式(全注解的方式):
1.配置类:Spring配置类========>Spring配置文件:
1 package com.skykuqi.springboot.helloworld.config;
2
3 import com.skykuqi.springboot.helloworld.service.HelloService;
4 import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
5 import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
6
7 /**
8 * @author : S K Y
9 * @version :0.0.1
10 */
11 @Configuration //使用该注解通知SpringBoot这是一个配置类,用来替代之前的Spring配置文件
12 public class MyAppConfig {
13 /*在之前的配置文件中我们利用<bean/>标签来添加组件,在配置类中,我们使用@Bean注解来完成;
14 *
15 * 该注解将当前方法的返回值添加到Spring容器中,容器中这个组件的默认id就是方法名*/
16 @Bean
17 public HelloService helloService() {
18 return new HelloService();
19 }
20 }
四.配置文件占位符
我们在配置文件中可以使用Spring提供的随机数:${random.value},${random.int|long|int(10)|int[1024,65536]},此外我们还可以使用属性来匹配占位符:
1 person:
2 lastName: ${person.age}_zhangsan_${random.uuid}
3 age: ${random.int[2,22]}
4 boss: true
5 birth: 2019/11/25
6 maps: {k1: 12,k2: 21}
7 lists:
8 - lisi
9 - zhaoliu
10 - wnangwu
11 dog:
12 name: 小狗
13 age: 3
五.Profile(Spring多环境支撑)
在我们的日常开发中,在开发环境和正式的运行环境中,会有着一些环境上的差异,例如数据库环境,Spring可以使用@Profile注解来配置多环境:
1.我们在编写配置文件时,可以在配置文件命名时加上环境标识: application-{profile}.properties:
application-test.properties application-run.properties 默认使用的无标识后缀的默认配置文件中
a.我们可以在默认的配置文件中使用spring.profiles.active来指定当前的环境;
2.yml支持多文档块方式:
1 person:
2 lastName: ${person.age}_zhangsan_${random.uuid}
3 age: ${random.int[2,22]}
4 boss: true
5 birth: 2019/11/25
6 maps: {k1: 12,k2: 21}
7 lists:
8 - lisi
9 - zhaoliu
10 - wnangwu
11 dog:
12 name: 小狗
13 age: 3
14 # 我们可以使用---来划分文档块
15 spring:
16 profiles:
17 active: run
18 ---
19 server:
20 port: 8081
21 spring:
22 profiles: test
23 ---
24 server:
25 port: 80
26 spring:
27 profiles: run
3.此外我们还可以使用命令行方式来激活指定的配置文件: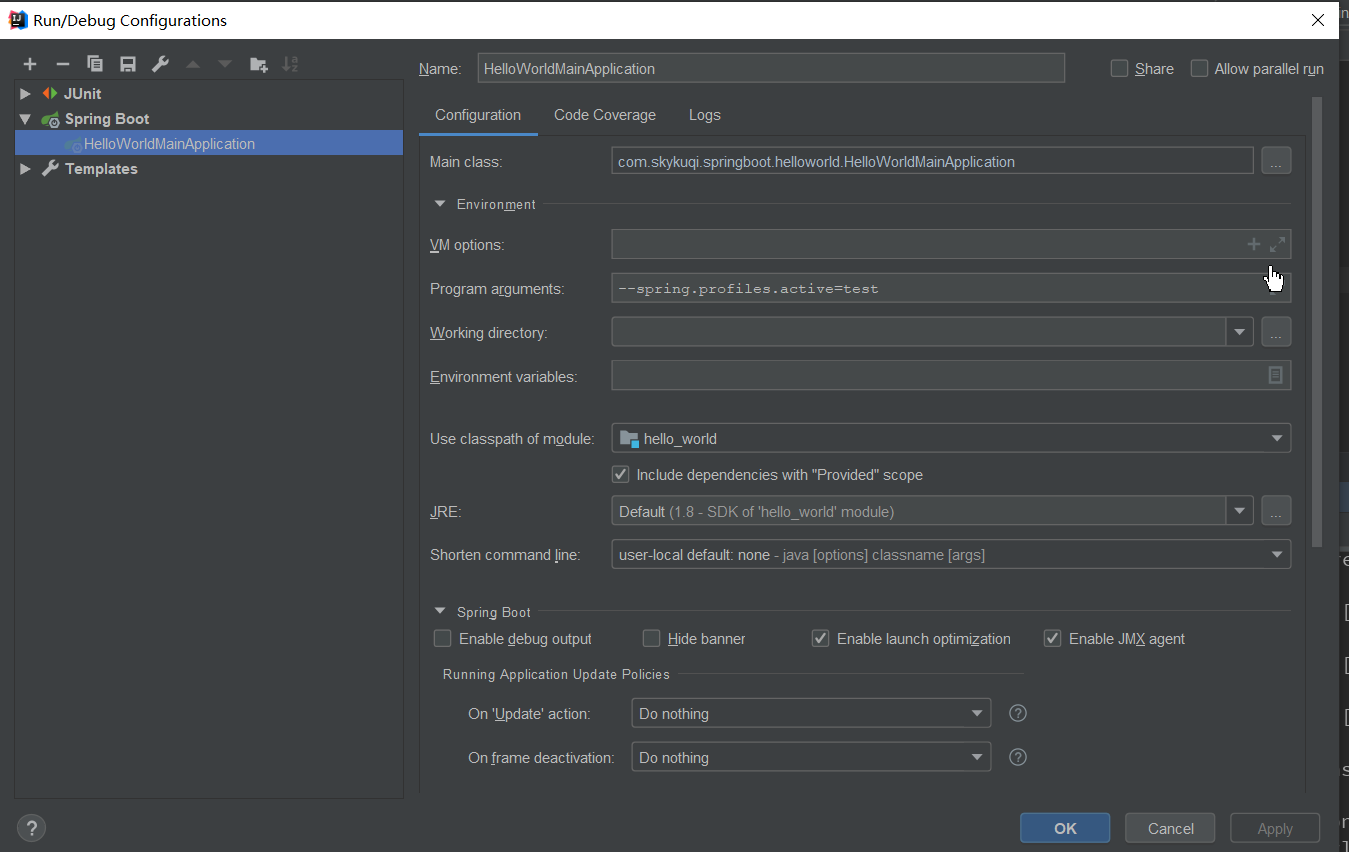
4.我们在打包完成之后也可以在运行jar包时指定环境参数: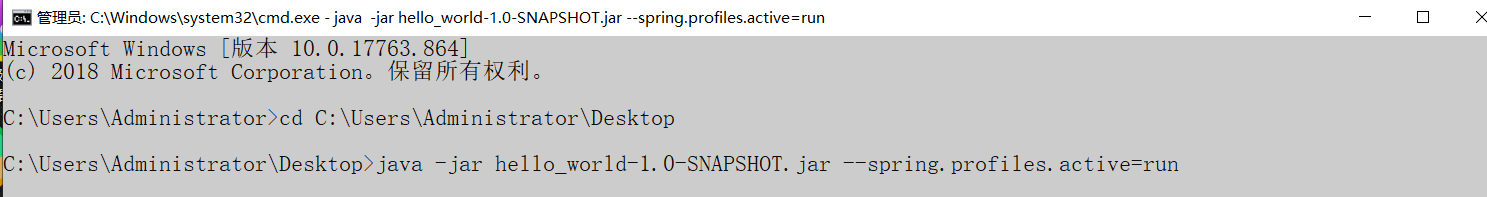
5.除了配置命令行参数外我们还可以配置虚拟机参数(命令行参数优先级高于JVM虚拟机参数):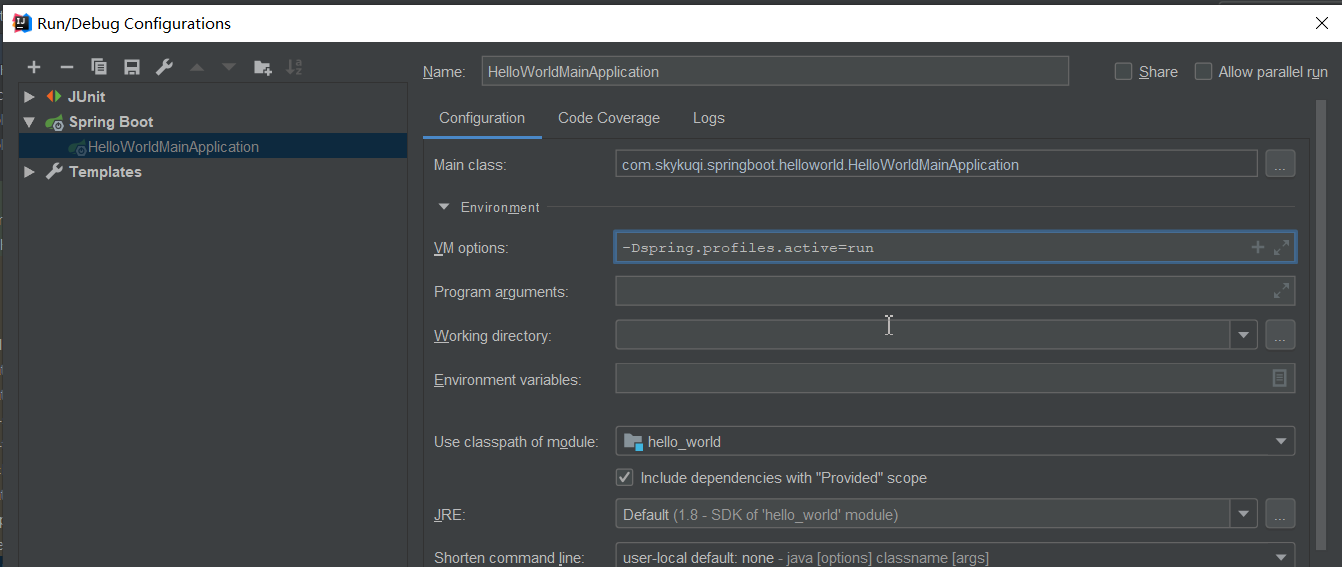
六.配置文件加载位置
SpringBoot启动会扫描以下位置的application.properties或者application.yml文件作为Spring boot的默认配置文件,优先级高低如下:
-file:./config/
-file:./
-classpath:/config/
-classpath:/
我们也可以通过配置spring.config.location来改变默认配置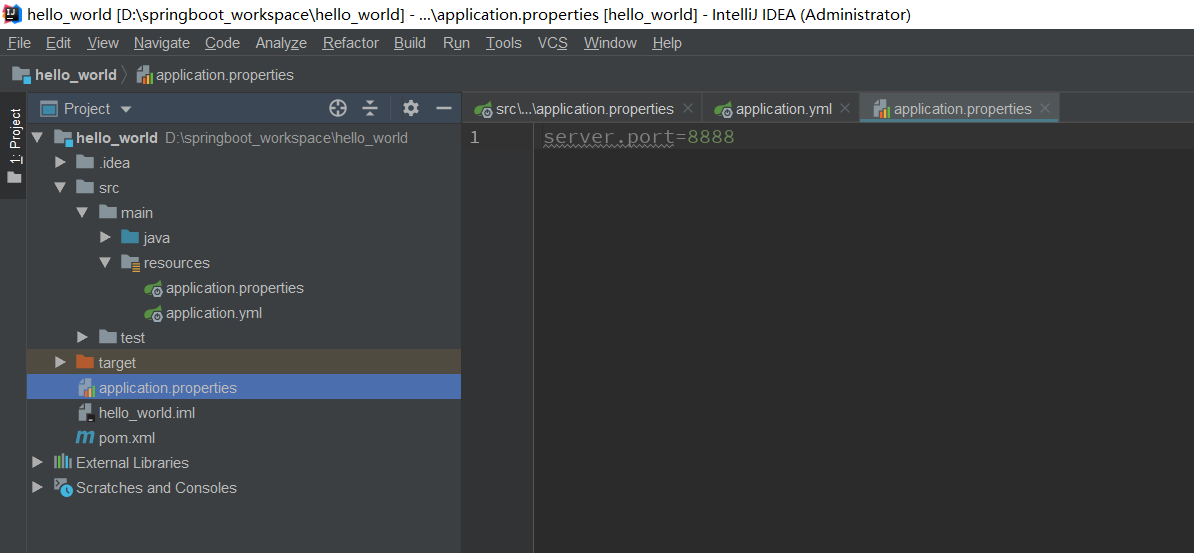
--低优先级的配置文件中的重复配置不会生效,但是在高优先级中没有定义的配置可以生效,实现互补配置
七.外部配置的加载顺序
SpringBoot如果想要进行一些配置,不止可以写在配置文件中,还可以引入外部配置,具体参照Spring官网文档说明.其中列举(按照优先级从高到低):
1.命令行参数
java -jar XXX.jar --server.port=80
2.jar包外部的application-{profile}.properties或application.yml(带spring.profile)配置文件;
3.jar内部的application-{profile}.properties或application.yml(带spring.profile)配置文件;
4.jar包外部的application.properties或application.yml(不带spring.profile)配置文件;
5.jar包内部的application.properties或application.yml(不带spring.profile)配置文件;
6.优先加载带profile的,再来加载不带profile,都是由jar包外向jar包内传送:
java -jar hello_world-1.0-SNAPSHOT.jar --server.port=8087 --server.context-path=/hello 多个配置用空格分开
java -jar hello_world-1.0-SNAPSHOT.jar --spring.config.location=D:\springboot_workspace\hello_world\src\main\resources\application.properties 引用外部配置文件
八.自动配置原理
配置文件能配置的属性参照Spring配置模板.
1.当SpringBoot应用启动的时候,在主配置的@SpringBootApplication中配置了@EnableAutoConfiguration
2.@EnableAutoConfiguration注解中利用@Import(EnableAutoConfigurationImportSelector.class)选择器来给SpringBoot中导入一些组件;
3.EnableAutoConfigurationImportSelector的父类AutoConfigurationImportSelector中使用public String[] selectImports(AnnotationMetadata annotationMetadata) {}方法来插入组件内容:
1 @Override
2 public String[] selectImports(AnnotationMetadata annotationMetadata) {
3 if (!isEnabled(annotationMetadata)) {
4 return NO_IMPORTS;
5 }
6 try {
7 AutoConfigurationMetadata autoConfigurationMetadata = AutoConfigurationMetadataLoader
8 .loadMetadata(this.beanClassLoader);
9 AnnotationAttributes attributes = getAttributes(annotationMetadata);
10 List<String> configurations = getCandidateConfigurations(annotationMetadata,
11 attributes);
12 configurations = removeDuplicates(configurations);
13 configurations = sort(configurations, autoConfigurationMetadata);
14 Set<String> exclusions = getExclusions(annotationMetadata, attributes);
15 checkExcludedClasses(configurations, exclusions);
16 configurations.removeAll(exclusions);
17 configurations = filter(configurations, autoConfigurationMetadata);
18 fireAutoConfigurationImportEvents(configurations, exclusions);
19 return configurations.toArray(new String[configurations.size()]);
20 }
21 catch (IOException ex) {
22 throw new IllegalStateException(ex);
23 }
24 }
4.代码第十行:List<String> configurations = getCandidateConfigurations(annotationMetadata,attributes);中获取到了当前的候选配置;在该方法中调用了SpringFactoriesLoader.loadFactoryNames(getSpringFactoriesLoaderFactoryClass(), getBeanClassLoader());方法
1 public static List<String> loadFactoryNames(Class<?> factoryClass, ClassLoader classLoader) {
2 String factoryClassName = factoryClass.getName();
3 try {
4 Enumeration<URL> urls = (classLoader != null ? classLoader.getResources(FACTORIES_RESOURCE_LOCATION) :
5 ClassLoader.getSystemResources(FACTORIES_RESOURCE_LOCATION));
6 List<String> result = new ArrayList<String>();
7 while (urls.hasMoreElements()) {
8 URL url = urls.nextElement();
9 Properties properties = PropertiesLoaderUtils.loadProperties(new UrlResource(url));
10 String factoryClassNames = properties.getProperty(factoryClassName);
11 result.addAll(Arrays.asList(StringUtils.commaDelimitedListToStringArray(factoryClassNames)));
12 }
13 return result;
14 }
15 catch (IOException ex) {
16 throw new IllegalArgumentException("Unable to load [" + factoryClass.getName() +
17 "] factories from location [" + FACTORIES_RESOURCE_LOCATION + "]", ex);
18 }
19 }
5.代码第4-5行表示的意思是在类路径下获取资源,即扫描所有jar包类路径下的public static final String FACTORIES_RESOURCE_LOCATION = "META-INF/spring.factories";把扫描到的这些文件的内容包装成properties对象.而后我们在这个properties对象中(代码第9行);
6.回到protected List<String> getCandidateConfigurations(AnnotationMetadata metadata,AnnotationAttributes attributes) {}方法,其中调用loadFactoryNames方法的参数就是EnableAutoConfiguration.class;即从properties中获取到这个类的类名对应的值,然后把他们添加在容器中.
7.总结:将类路径下的META-INF/spring.factories里面配置的所有EnableAutoConfiguration的值加入到了容器中:
1 # Auto Configure 2 org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.EnableAutoConfiguration=\ 3 org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.admin.SpringApplicationAdminJmxAutoConfiguration,\ 4 org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.aop.AopAutoConfiguration,\ 5 org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.amqp.RabbitAutoConfiguration,\ 6 org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.batch.BatchAutoConfiguration,\ 7 org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.cache.CacheAutoConfiguration,\ 8 org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.cassandra.CassandraAutoConfiguration,\ 9 org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.cloud.CloudAutoConfiguration,\ 10 org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.context.ConfigurationPropertiesAutoConfiguration,\ 11 org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.context.MessageSourceAutoConfiguration,\ 12 org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.context.PropertyPlaceholderAutoConfiguration,\ 13 org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.couchbase.CouchbaseAutoConfiguration,\ 14 org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.dao.PersistenceExceptionTranslationAutoConfiguration,\ 15 org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.cassandra.CassandraDataAutoConfiguration,\ 16 org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.cassandra.CassandraRepositoriesAutoConfiguration,\ 17 org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.couchbase.CouchbaseDataAutoConfiguration,\ 18 org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.couchbase.CouchbaseRepositoriesAutoConfiguration,\ 19 org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.elasticsearch.ElasticsearchAutoConfiguration,\ 20 org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.elasticsearch.ElasticsearchDataAutoConfiguration,\ 21 org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.elasticsearch.ElasticsearchRepositoriesAutoConfiguration,\ 22 org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.jpa.JpaRepositoriesAutoConfiguration,\ 23 org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.ldap.LdapDataAutoConfiguration,\ 24 org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.ldap.LdapRepositoriesAutoConfiguration,\ 25 org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.mongo.MongoDataAutoConfiguration,\ 26 org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.mongo.MongoRepositoriesAutoConfiguration,\ 27 org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.neo4j.Neo4jDataAutoConfiguration,\ 28 org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.neo4j.Neo4jRepositoriesAutoConfiguration,\ 29 org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.solr.SolrRepositoriesAutoConfiguration,\ 30 org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.redis.RedisAutoConfiguration,\ 31 org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.redis.RedisRepositoriesAutoConfiguration,\ 32 org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.rest.RepositoryRestMvcAutoConfiguration,\ 33 org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.web.SpringDataWebAutoConfiguration,\ 34 org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.elasticsearch.jest.JestAutoConfiguration,\ 35 org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.freemarker.FreeMarkerAutoConfiguration,\ 36 org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.gson.GsonAutoConfiguration,\ 37 org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.h2.H2ConsoleAutoConfiguration,\ 38 org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.hateoas.HypermediaAutoConfiguration,\ 39 org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.hazelcast.HazelcastAutoConfiguration,\ 40 org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.hazelcast.HazelcastJpaDependencyAutoConfiguration,\ 41 org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.info.ProjectInfoAutoConfiguration,\ 42 org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.integration.IntegrationAutoConfiguration,\ 43 org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.jackson.JacksonAutoConfiguration,\ 44 org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.jdbc.DataSourceAutoConfiguration,\ 45 org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.jdbc.JdbcTemplateAutoConfiguration,\ 46 org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.jdbc.JndiDataSourceAutoConfiguration,\ 47 org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.jdbc.XADataSourceAutoConfiguration,\ 48 org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.jdbc.DataSourceTransactionManagerAutoConfiguration,\ 49 org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.jms.JmsAutoConfiguration,\ 50 org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.jmx.JmxAutoConfiguration,\ 51 org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.jms.JndiConnectionFactoryAutoConfiguration,\ 52 org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.jms.activemq.ActiveMQAutoConfiguration,\ 53 org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.jms.artemis.ArtemisAutoConfiguration,\ 54 org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.flyway.FlywayAutoConfiguration,\ 55 org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.groovy.template.GroovyTemplateAutoConfiguration,\ 56 org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.jersey.JerseyAutoConfiguration,\ 57 org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.jooq.JooqAutoConfiguration,\ 58 org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.kafka.KafkaAutoConfiguration,\ 59 org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.ldap.embedded.EmbeddedLdapAutoConfiguration,\ 60 org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.ldap.LdapAutoConfiguration,\ 61 org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.liquibase.LiquibaseAutoConfiguration,\ 62 org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.mail.MailSenderAutoConfiguration,\ 63 org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.mail.MailSenderValidatorAutoConfiguration,\ 64 org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.mobile.DeviceResolverAutoConfiguration,\ 65 org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.mobile.DeviceDelegatingViewResolverAutoConfiguration,\ 66 org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.mobile.SitePreferenceAutoConfiguration,\ 67 org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.mongo.embedded.EmbeddedMongoAutoConfiguration,\ 68 org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.mongo.MongoAutoConfiguration,\ 69 org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.mustache.MustacheAutoConfiguration,\ 70 org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.orm.jpa.HibernateJpaAutoConfiguration,\ 71 org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.reactor.ReactorAutoConfiguration,\ 72 org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.security.SecurityAutoConfiguration,\ 73 org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.security.SecurityFilterAutoConfiguration,\ 74 org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.security.FallbackWebSecurityAutoConfiguration,\ 75 org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.security.oauth2.OAuth2AutoConfiguration,\ 76 org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.sendgrid.SendGridAutoConfiguration,\ 77 org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.session.SessionAutoConfiguration,\ 78 org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.social.SocialWebAutoConfiguration,\ 79 org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.social.FacebookAutoConfiguration,\ 80 org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.social.LinkedInAutoConfiguration,\ 81 org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.social.TwitterAutoConfiguration,\ 82 org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.solr.SolrAutoConfiguration,\ 83 org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.thymeleaf.ThymeleafAutoConfiguration,\ 84 org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.transaction.TransactionAutoConfiguration,\ 85 org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.transaction.jta.JtaAutoConfiguration,\ 86 org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.validation.ValidationAutoConfiguration,\ 87 org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.DispatcherServletAutoConfiguration,\ 88 org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.EmbeddedServletContainerAutoConfiguration,\ 89 org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.ErrorMvcAutoConfiguration,\ 90 org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.HttpEncodingAutoConfiguration,\ 91 org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.HttpMessageConvertersAutoConfiguration,\ 92 org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.MultipartAutoConfiguration,\ 93 org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.ServerPropertiesAutoConfiguration,\ 94 org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.WebClientAutoConfiguration,\ 95 org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.WebMvcAutoConfiguration,\ 96 org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.websocket.WebSocketAutoConfiguration,\ 97 org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.websocket.WebSocketMessagingAutoConfiguration,\ 98 org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.webservices.WebServicesAutoConfiguration
--每一个这样的XXXAutoConfiguration类都是容器中的一个组件,都加入到容器中,用他们来做自动配置.
8.每一个自动配置类进行自动配置功能,以org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.HttpEncodingAutoConfiguration为例解释自动配置原理:
1 /*
2 * Copyright 2012-2016 the original author or authors.
3 *
4 * Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
5 * you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
6 * You may obtain a copy of the License at
7 *
8 * http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
9 *
10 * Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
11 * distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
12 * WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
13 * See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
14 * limitations under the License.
15 */
16
17 package org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web;
18
19 import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.EnableAutoConfiguration;
20 import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.condition.ConditionalOnClass;
21 import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.condition.ConditionalOnMissingBean;
22 import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.condition.ConditionalOnProperty;
23 import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.condition.ConditionalOnWebApplication;
24 import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.HttpEncodingProperties.Type;
25 import org.springframework.boot.context.embedded.ConfigurableEmbeddedServletContainer;
26 import org.springframework.boot.context.embedded.EmbeddedServletContainerCustomizer;
27 import org.springframework.boot.context.properties.EnableConfigurationProperties;
28 import org.springframework.boot.web.filter.OrderedCharacterEncodingFilter;
29 import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
30 import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
31 import org.springframework.core.Ordered;
32 import org.springframework.web.filter.CharacterEncodingFilter;
33
34 /**
35 * {@link EnableAutoConfiguration Auto-configuration} for configuring the encoding to use
36 * in web applications.
37 *
38 * @author Stephane Nicoll
39 * @author Brian Clozel
40 * @since 1.2.0
41 */
42 @Configuration
43 @EnableConfigurationProperties(HttpEncodingProperties.class)
44 @ConditionalOnWebApplication
45 @ConditionalOnClass(CharacterEncodingFilter.class)
46 @ConditionalOnProperty(prefix = "spring.http.encoding", value = "enabled", matchIfMissing = true)
47 public class HttpEncodingAutoConfiguration {
48
49 private final HttpEncodingProperties properties;
50
51 public HttpEncodingAutoConfiguration(HttpEncodingProperties properties) {
52 this.properties = properties;
53 }
54
55 @Bean
56 @ConditionalOnMissingBean(CharacterEncodingFilter.class)
57 public CharacterEncodingFilter characterEncodingFilter() {
58 CharacterEncodingFilter filter = new OrderedCharacterEncodingFilter();
59 filter.setEncoding(this.properties.getCharset().name());
60 filter.setForceRequestEncoding(this.properties.shouldForce(Type.REQUEST));
61 filter.setForceResponseEncoding(this.properties.shouldForce(Type.RESPONSE));
62 return filter;
63 }
64
65 @Bean
66 public LocaleCharsetMappingsCustomizer localeCharsetMappingsCustomizer() {
67 return new LocaleCharsetMappingsCustomizer(this.properties);
68 }
69
70 private static class LocaleCharsetMappingsCustomizer
71 implements EmbeddedServletContainerCustomizer, Ordered {
72
73 private final HttpEncodingProperties properties;
74
75 LocaleCharsetMappingsCustomizer(HttpEncodingProperties properties) {
76 this.properties = properties;
77 }
78
79 @Override
80 public void customize(ConfigurableEmbeddedServletContainer container) {
81 if (this.properties.getMapping() != null) {
82 container.setLocaleCharsetMappings(this.properties.getMapping());
83 }
84 }
85
86 @Override
87 public int getOrder() {
88 return 0;
89 }
90
91 }
92
93 }
a.使用@Configuration注解来表示这是一个配置类
b.@EnableConfigurationProperties(HttpEncodingProperties.class) 启动指定类的@ConfigurationProperties注解
1 /*
2 * Copyright 2012-2016 the original author or authors.
3 *
4 * Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
5 * you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
6 * You may obtain a copy of the License at
7 *
8 * http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
9 *
10 * Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
11 * distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
12 * WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
13 * See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
14 * limitations under the License.
15 */
16
17 package org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web;
18
19 import java.nio.charset.Charset;
20 import java.util.Locale;
21 import java.util.Map;
22
23 import org.springframework.boot.context.properties.ConfigurationProperties;
24
25 /**
26 * Configuration properties for http encoding.
27 *
28 * @author Stephane Nicoll
29 * @author Brian Clozel
30 * @since 1.2.0
31 */
32 @ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "spring.http.encoding")
33 public class HttpEncodingProperties {
34
35 public static final Charset DEFAULT_CHARSET = Charset.forName("UTF-8");
36
37 /**
38 * Charset of HTTP requests and responses. Added to the "Content-Type" header if not
39 * set explicitly.
40 */
41 private Charset charset = DEFAULT_CHARSET;
42
43 /**
44 * Force the encoding to the configured charset on HTTP requests and responses.
45 */
46 private Boolean force;
47
48 /**
49 * Force the encoding to the configured charset on HTTP requests. Defaults to true
50 * when "force" has not been specified.
51 */
52 private Boolean forceRequest;
53
54 /**
55 * Force the encoding to the configured charset on HTTP responses.
56 */
57 private Boolean forceResponse;
58
59 /**
60 * Locale to Encoding mapping.
61 */
62 private Map<Locale, Charset> mapping;
63
64 public Charset getCharset() {
65 return this.charset;
66 }
67
68 public void setCharset(Charset charset) {
69 this.charset = charset;
70 }
71
72 public boolean isForce() {
73 return Boolean.TRUE.equals(this.force);
74 }
75
76 public void setForce(boolean force) {
77 this.force = force;
78 }
79
80 public boolean isForceRequest() {
81 return Boolean.TRUE.equals(this.forceRequest);
82 }
83
84 public void setForceRequest(boolean forceRequest) {
85 this.forceRequest = forceRequest;
86 }
87
88 public boolean isForceResponse() {
89 return Boolean.TRUE.equals(this.forceResponse);
90 }
91
92 public void setForceResponse(boolean forceResponse) {
93 this.forceResponse = forceResponse;
94 }
95
96 public Map<Locale, Charset> getMapping() {
97 return this.mapping;
98 }
99
100 public void setMapping(Map<Locale, Charset> mapping) {
101 this.mapping = mapping;
102 }
103
104 boolean shouldForce(Type type) {
105 Boolean force = (type == Type.REQUEST ? this.forceRequest : this.forceResponse);
106 if (force == null) {
107 force = this.force;
108 }
109 if (force == null) {
110 force = (type == Type.REQUEST);
111 }
112 return force;
113 }
114
115 enum Type {
116
117 REQUEST, RESPONSE
118
119 }
120
121 }
c. @ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "spring.http.encoding")注解则表示从配置文件中获取指定的值和bean的属性进行绑定.
9.所有在配置文件中能配置的属性都在properties中封装着,因此我们想知道配置文件可以配置什么就可以参照某个功能对应的这个属性类,上述类所表示的就是解决HTTP的编码自动配置功能,将配置文件中对应的值和HttpEncodingProperties绑定起来.
10.回到HttpEncodingAutoConfiguration类的文件中@ConditionalOnWebApplication在Spring底层中,@Conditional注解,根据不同的条件,如果能满足指定的条件,整个配置类才会生效.而@ConditionalOnWebApplication表示的是判断当前应用是否是Web应用.如果是,则当前的配置类生效.
11.@ConditionalOnClass(CharacterEncodingFilter.class) 用来判断当前项目有没有这个类,该类时SpringMVC中进行乱码解决的过滤器(通常配置在web.xml中让其起作用);
12.@ConditionalOnProperty(prefix = "spring.http.encoding", value = "enabled", matchIfMissing = true)判断配置文件中是否存在某个配置,如果不存在matchIfMissing 表示判断也是成立的.即即使我们配置文件中不配置spring.http.encoding.enabled=true,默认也是生效的.
13.总结:自动配置类就是根据当前不同的条件判断,而后决定这个配置类是否生效,如果一旦生效,在该类中使用@Bean注解将zhCharacterEncodingFilter这个类添加到了Spring容器中,这个组件的某些值需要从properties中获取,而HttpEncodingProperties配置类的属性已经和springBoot的配置文件连接了,而其默认的encoding编码就是public static final Charset DEFAULT_CHARSET = Charset.forName("UTF-8");此外我们还可以配置如下属性:
a.force:即启用强制编码
14.我们能配置的属性都是来源于这个功能的Properties类.一旦这个配置类生效,那么这个类就会 给容器中添加各种组件,这些组件的属性是从对应的properties文件中获取的.
15.精髓:因为SpringBoot启动会加载大量的自动配置类,所以我们可以看我们需要的功能有没有SpringBoot已经写好的自动配置类,然后我们可以看我们的自动配置类中有哪些自动配置的属性.只要我们要使用的组件已经存在,我们就不需要再来配置了.给容器的自动配置类添加组件时,会从properties类之中获取某些属性,我们可以在配置文件中指定这些属性的值;
16.在SpringBoot之中有很多的xxxAutoConfiguration自动配置类来给容器中添加这个组件,也有与之对应的xxxProperties类来封装这个配置文件中相关的属性.
九.@Conditional注解详解
在HttpEncodingAutoConfiguration 类中还存在一个@ConditionalOnMissingBean(CharacterEncodingFilter.class)注解表示的是当缺失这个bean的时候那么进行自动配置.
1.@Conditional注解:当指定的条件成立,那么配置类中的所有内容才生效,但是SpringBoot将这些注解扩展了很多:
@ConditionalOnJava:系统的Java版本是否符合要求;
@ConditionalOnBean:容器中存在指定的Bean
@ConditionalOnMissingBean:容器中不存在指定Bean
@ConditionalOnExpression:是否满足一个指定的SpEL表达式
@ConditionalOnClass:系统中有指定的类
@ConditionalMissingClass:系统中不存在当前的类
@ConditionalOnSingleCandidate:容器中只有一个指定的bean,或者这个bean是首选bean
@ConditionalOnProperty:系统中指定的属性是否为指定的值
@ConditionalOnResources:类路径下是否存在指定的资源文件
@ConditionalOnWebApplication:当前是web环境
@ConditionalNotWebApplicaiton:当前不是web环境
@ConditionalOnJndi:Jndi存在指定项
2.自动配置类在一定的条件下才能生效:
1 @Configuration
2 @ConditionalOnClass({ EnableAspectJAutoProxy.class, Aspect.class, Advice.class })
3 @ConditionalOnProperty(prefix = "spring.aop", name = "auto", havingValue = "true", matchIfMissing = true)
4 public class AopAutoConfiguration {
5 }
3.可以发现只有当我们存在Aspect的jar时,当前的配合类才能生效,因此我们现在的任务就是如何知道哪些自动配置类生效了
我们可以在配置文件中使用debug=true来开启SpringBoot的Debug模式,在控制台中我们就可以看到当前启动了哪一项自动配置类.
来源:https://www.cnblogs.com/skykuqi/p/11928270.html