OpenCV 提供了两个变换函数,cv2.warpAffine 和 cv2.warpPerspective,使用这两个函数你可以实现所有类型的变换。cv2.warpAffine 接收的参数是2 × 3 的变换矩阵,而 cv2.warpPerspective 接收的参数是 3 × 3 的变换矩阵。
- 扩展缩放
方法:resize(src, dsize, dst=None, fx=None, fy=None, interpolation=None)
dsize为缩放大小
fx,fy为影响因子
interpolation为插值算法(在缩放时推荐使用 cv2.INTER_AREA,在扩展时推荐使用 cv2.INTER_CUBIC(慢) 和 cv2.INTER_LINEAR。默认情况下所有改变图像尺寸大小的操作使用的插值方法都是 cv2.INTER_LINEAR)
1 import numpy as np
2 import cv2
3
4 img1 = cv2.imread("../image/min.jpg")
5
6 # 方式一
7 img2 = cv2.resize(img1, None, fx=2, fy=2, interpolation=cv2.INTER_CUBIC)
8
9 # 方式二
10 height, width = img1.shape[:2]
11 img3 = cv2.resize(img1, (2*width, 2*height), interpolation=cv2.INTER_LINEAR)
12
13
14 cv2.imshow("img", img1)
15 cv2.imshow("img2", img2)
16 cv2.imshow("img3", img3)
17 cv2.waitKey(0)
18 cv2.destroyAllWindows()
- 平移
若沿(x,y)方向平移(tx,ty),可以使用以下平移矩阵:
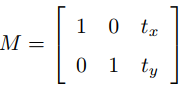
1 import cv2
2 import numpy as np
3
4 img = cv2.imread('../image/min.jpg',0)
5 rows,cols = img.shape
6
7 M = np.float32([[1,0,100],[0,1,50]])
8 dst = cv2.warpAffine(img,M,(cols,rows))
9
10 cv2.imshow('img',dst)
11 cv2.waitKey(0)
12 cv2.destroyAllWindows()
- 仿射变换
import numpy as np
import cv2
def resize_img(img):
# 扩大两倍
# 方法一
# res = cv2.resize(img, None, fx=2, fy=2, interpolation=cv2.INTER_CUBIC)
# 方法二
# height, width = img.shape[:2]
# res = cv2.resize(img, (2 * width, 2 * height), interpolation=cv2.INTER_CUBIC)
# 图像缩小
# 方法二
height, width = img.shape[:2]
res = cv2.resize(img, (width // 2, height // 2), interpolation=cv2.INTER_AREA)
res1 = cv2.resize(res, None, fx=2, fy=2, interpolation=cv2.INTER_CUBIC)
cv2.imshow("normal", img)
cv2.imshow("image", res1)
# 平移
def offset_img(img):
print(img.shape)
rows, cols = img.shape[:2]
M = np.float32([[1, 0, 100], [0, 1, 50]])
print(M)
dst = cv2.warpAffine(img, M, (cols, rows))
cv2.imshow("normal", img)
cv2.imshow("image", dst)
# 旋转
def rotation_img(img):
rows, cols = img.shape[:2]
# 生成旋转矩阵(未缩放,以中心为原点)
M = cv2.getRotationMatrix2D(((cols - 1) / 2.0, (rows - 1) / 2.0), 90, 1)
print(M)
dst = cv2.warpAffine(img, M, (cols, rows))
cv2.imshow("normal", img)
cv2.imshow("image", dst)
# 仿射变换
def affine_img(img):
rows, cols = img.shape[:2]
# 原图像中的三个点位
pts1 = np.float32([[50, 50], [200, 50], [50, 200]])
# 变换后图像对应的三个点位
pts2 = np.float32([[10, 100], [200, 50], [100, 250]])
# 生成变换矩阵
M = cv2.getAffineTransform(pts1, pts2)
print(M)
# 对图像进行仿射变换
dst = cv2.warpAffine(img, M, (cols, rows))
cv2.imshow("normal", img)
cv2.imshow("image", dst)
if __name__ == "__main__":
img = cv2.imread("../image/meixi.jpg")
# print(img)
# resize_img(img)
# offset_img(img)
# rotation_img(img)
affine_img(img)
cv2.namedWindow("normal")
cv2.namedWindow("image")
# cv2.imshow("image", img)
cv2.waitKey(0)
cv2.destroyAllWindows()
来源:oschina
链接:https://my.oschina.net/u/4368331/blog/3459868