一、JDBC实现查询分析
如果不使用mybatis,使用原生的API来进行JDBC查询时的实现如下:
public static List<Map<String,Object>> jdbcQuery(){
Connection connection = null;
ResultSet rs = null;
PreparedStatement stmt = null;
List<Map<String,Object>> resultList = new ArrayList<Map<String,Object>>();
try {
//1、加载JDBC驱动
Class.forName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver").newInstance();
String url = "jdbc:mysql://127.0.0.1:3306/mysql?characterEncoding=UTF-8";
//2、获取数据库连接
connection = DriverManager.getConnection(url,"root","123456");
String sql = "select * from user where id = ? ";
//3、创建Statement对象(每一个Statement为一次数据库执行请求)
stmt = connection.prepareStatement(sql);
//4、设置传入参数
stmt.setInt(1, 1);
//5、执行SQL语句
rs = stmt.executeQuery();
//6、处理查询结果(将查询结果转换成List<Map>格式)
ResultSetMetaData rsmd = rs.getMetaData();
int num = rsmd.getColumnCount();
while(rs.next()){
Map map = new HashMap();
for(int i = 0;i < num;i++){
String columnName = rsmd.getColumnName(i+1);
map.put(columnName,rs.getString(columnName));
}
resultList.add(map);
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
try {
//7、关闭结果集
if (rs != null) {
rs.close();
rs = null;
}
//7、关闭执行
if (stmt != null) {
stmt.close();
stmt = null;
}
if (connection != null) {
connection.close();
connection = null;
}
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
return resultList;
}
从上面代码可以看出使用原生的JDBC方式,总共需要7步来实现,而mybatis就是把这7步封装起来
二、mybatis实现查询
使用mybatis来查询数据的实现
public static void main(String[] args) {
InputStream inputStream= Resources.getResourceAsStream("conf/mybatis-config.xml");
SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(inputStream);
SqlSession sqlSession = sqlSessionFactory.openSession();
User user = sqlSession.selectOne("com.test.dao.User.selectOne", 1);
}
mybatis-config.xml的配置如下
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<!DOCTYPE configuration
PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Config 3.0//EN"
"http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-config.dtd">
<configuration>
<!-- 环境配置:事务管理器和数据源配置 -->
<environments default="development">
<environment id="development">
<transactionManager type="JDBC" />
<dataSource type="POOLED">
<property name="driver" value="${jdbc.driver}" />
<property name="url" value="${jdbc.url}" />
<property name="username" value="${jdbc.username}" />
<property name="password" value="${jdbc.password}" />
</dataSource>
</environment>
</environments>
<!-- 映射器 -->
<mappers>
<mapper resource="com/test/dao/mapper/User.xml" />
</mappers>
</configuration>
三、mybatis架构
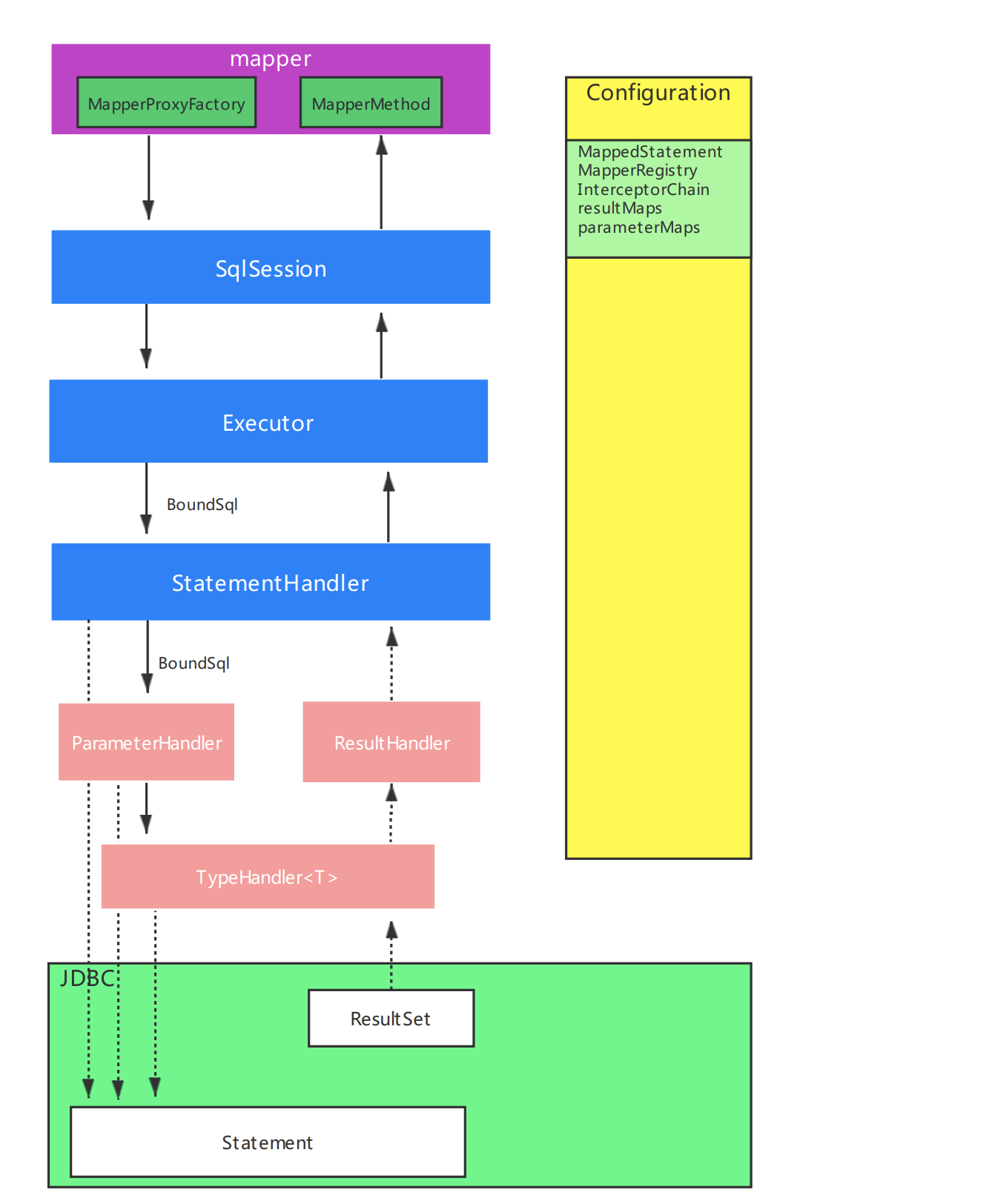
1、mapper接口
mybatis-spring通过代理的方式来生成mapper接口的实现类,具体可以参考:Mybatis-spring自动注入机制
MapperProxy
public class MapperProxy<T> implements InvocationHandler, Serializable {
@Override
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable {
try {
if (Object.class.equals(method.getDeclaringClass())) {
return method.invoke(this, args);
} else if (isDefaultMethod(method)) {
return invokeDefaultMethod(proxy, method, args);
}
} catch (Throwable t) {
throw ExceptionUtil.unwrapThrowable(t);
}
final MapperMethod mapperMethod = cachedMapperMethod(method);
return mapperMethod.execute(sqlSession, args);
}
}
MapperMethod
public Object execute(SqlSession sqlSession, Object[] args) {
Object result;
switch (command.getType()) {
case INSERT: {
Object param = method.convertArgsToSqlCommandParam(args);
result = rowCountResult(sqlSession.insert(command.getName(), param));
break;
}
case UPDATE: {
Object param = method.convertArgsToSqlCommandParam(args);
result = rowCountResult(sqlSession.update(command.getName(), param));
break;
}
case DELETE: {
Object param = method.convertArgsToSqlCommandParam(args);
result = rowCountResult(sqlSession.delete(command.getName(), param));
break;
}
case SELECT:
if (method.returnsVoid() && method.hasResultHandler()) {
//调用sqlSession来执行查询操作
executeWithResultHandler(sqlSession, args);
result = null;
} else if (method.returnsMany()) {
result = executeForMany(sqlSession, args);
} else if (method.returnsMap()) {
result = executeForMap(sqlSession, args);
} else if (method.returnsCursor()) {
result = executeForCursor(sqlSession, args);
} else {
Object param = method.convertArgsToSqlCommandParam(args);
result = sqlSession.selectOne(command.getName(), param);
if (method.returnsOptional() &&
(result == null || !method.getReturnType().equals(result.getClass()))) {
result = Optional.ofNullable(result);
}
}
break;
case FLUSH:
result = sqlSession.flushStatements();
break;
default:
throw new BindingException("Unknown execution method for: " + command.getName());
}
if (result == null && method.getReturnType().isPrimitive() && !method.returnsVoid()) {
throw new BindingException("Mapper method '" + command.getName()
+ " attempted to return null from a method with a primitive return type (" + method.getReturnType() + ").");
}
return result;
}
private void executeWithResultHandler(SqlSession sqlSession, Object[] args) {
MappedStatement ms = sqlSession.getConfiguration().getMappedStatement(command.getName());
if (!StatementType.CALLABLE.equals(ms.getStatementType())
&& void.class.equals(ms.getResultMaps().get(0).getType())) {
throw new BindingException("method " + command.getName()
+ " needs either a @ResultMap annotation, a @ResultType annotation,"
+ " or a resultType attribute in XML so a ResultHandler can be used as a parameter.");
}
Object param = method.convertArgsToSqlCommandParam(args);
if (method.hasRowBounds()) {
RowBounds rowBounds = method.extractRowBounds(args);
sqlSession.select(command.getName(), param, rowBounds, method.extractResultHandler(args));
} else {
sqlSession.select(command.getName(), param, method.extractResultHandler(args));
}
}
2、Configuration
Configuration类是mybatis的一个基础配置类,它贯穿了sql执行的整个生命周期,它的主要作用有以下几点
- mybatis的全局配置属性,例如是否使用缓存
- 配置拦截器InterceptorChain
- 保存mapper接口与代理类的关系MapperRegistry
- 配置类型转换处理器TypeHandlerRegistry
- 保存mapper.xml解析后的sql语句mappedStatements
- 等等其他配置
3、SqlSession
SqlSession主要是来承接各种sql的增删改查功能的,不过它不具体实现增删改查,增删改查最终是交给了Executor去执行,可以只看注释
DefaultSqlSession
@Override
public <E> List<E> selectList(String statement, Object parameter, RowBounds rowBounds) {
try {
MappedStatement ms = configuration.getMappedStatement(statement);
return executor.query(ms, wrapCollection(parameter), rowBounds, Executor.NO_RESULT_HANDLER);
} catch (Exception e) {
throw ExceptionFactory.wrapException("Error querying database. Cause: " + e, e);
} finally {
ErrorContext.instance().reset();
}
}
4、Executor
Executor是sql的执行器,来完成增删改查的功能,具体流程为一下几点(本系列文章都是按查询sql来分析源码的)
BaseExecutor
@Override
public <E> List<E> query(MappedStatement ms, Object parameter, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler, CacheKey key, BoundSql boundSql) throws SQLException {
ErrorContext.instance().resource(ms.getResource()).activity("executing a query").object(ms.getId());
if (closed) {
throw new ExecutorException("Executor was closed.");
}
if (queryStack == 0 && ms.isFlushCacheRequired()) {
clearLocalCache();
}
List<E> list;
try {
queryStack++;
//1、从一级缓存中获取数据,如果有,就直接返回了,不再查询数据库
list = resultHandler == null ? (List<E>) localCache.getObject(key) : null;
if (list != null) {
handleLocallyCachedOutputParameters(ms, key, parameter, boundSql);
} else {
//2、如果缓存中查不到,则从数据库查询
list = queryFromDatabase(ms, parameter, rowBounds, resultHandler, key, boundSql);
}
} finally {
queryStack--;
}
if (queryStack == 0) {
for (DeferredLoad deferredLoad : deferredLoads) {
deferredLoad.load();
}
// issue #601
deferredLoads.clear();
if (configuration.getLocalCacheScope() == LocalCacheScope.STATEMENT) {
// issue #482
clearLocalCache();
}
}
return list;
}
private <E> List<E> queryFromDatabase(MappedStatement ms, Object parameter, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler, CacheKey key, BoundSql boundSql) throws SQLException {
List<E> list;
localCache.putObject(key, EXECUTION_PLACEHOLDER);
try {
//3、调用内部方法从数据库查询
list = doQuery(ms, parameter, rowBounds, resultHandler, boundSql);
} finally {
localCache.removeObject(key);
}
//4、将从数据库中查询得到的数据放入缓存中
localCache.putObject(key, list);
if (ms.getStatementType() == StatementType.CALLABLE) {
localOutputParameterCache.putObject(key, parameter);
}
return list;
}
SimpleExecutor
@Override
public <E> List<E> doQuery(MappedStatement ms, Object parameter, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler, BoundSql boundSql) throws SQLException {
Statement stmt = null;
try {
//5、从MappedStatement中获取Configuration
Configuration configuration = ms.getConfiguration();
//6、生成StatementHandler对象
StatementHandler handler = configuration.newStatementHandler(wrapper, ms, parameter, rowBounds, resultHandler, boundSql);
//7、StatementHandler生成PrepareStatement、使用ParameterHandler处理参数
stmt = prepareStatement(handler, ms.getStatementLog());
//8、StatementHandler执行查询、结果对象处理
return handler.query(stmt, resultHandler);
} finally {
closeStatement(stmt);
}
}
Executor执行流程中会涉及几个重要的功能
- 1、mybatis一级缓存、二级缓存,推荐阅读Mybatis缓存机制
- 2、mybatis插件机制,推荐阅读Mybatis插件机制
5、StatementHandler
StatementHandler的主要功能有
- 将statement进行预处理,相当于connection.prepareStatement(sql)功能,生成PrepareStatement。
- 将动态sql设置参数(调用ParameterHandler的setParameters)
- 调用ResultSetHandler来处理结果集,转换成List
6、ParameterHandler
ParameterHandler是设置PrepareStatement中的动态参数
DefaultParameterHandler
public void setParameters(PreparedStatement ps) {
ErrorContext.instance().activity("setting parameters").object(mappedStatement.getParameterMap().getId());
List<ParameterMapping> parameterMappings = boundSql.getParameterMappings();
if (parameterMappings != null) {
for (int i = 0; i < parameterMappings.size(); i++) {
ParameterMapping parameterMapping = parameterMappings.get(i);
if (parameterMapping.getMode() != ParameterMode.OUT) {
Object value;
String propertyName = parameterMapping.getProperty();
if (boundSql.hasAdditionalParameter(propertyName)) { // issue #448 ask first for additional params
value = boundSql.getAdditionalParameter(propertyName);
} else if (parameterObject == null) {
value = null;
} else if (typeHandlerRegistry.hasTypeHandler(parameterObject.getClass())) {
value = parameterObject;
} else {
MetaObject metaObject = configuration.newMetaObject(parameterObject);
value = metaObject.getValue(propertyName);
}
TypeHandler typeHandler = parameterMapping.getTypeHandler();
JdbcType jdbcType = parameterMapping.getJdbcType();
if (value == null && jdbcType == null) {
jdbcType = configuration.getJdbcTypeForNull();
}
try {
typeHandler.setParameter(ps, i + 1, value, jdbcType);
} catch (TypeException e) {
throw new TypeException("Could not set parameters for mapping: " + parameterMapping + ". Cause: " + e, e);
} catch (SQLException e) {
throw new TypeException("Could not set parameters for mapping: " + parameterMapping + ". Cause: " + e, e);
}
}
}
}
}
7、ResultSetHandler
ResultSetHandler是结果处理器,主要是将原始的ResultSet数据转换成PO实体对象。
DefaultResultSetHandler
public List<Object> handleResultSets(Statement stmt) throws SQLException {
ErrorContext.instance().activity("handling results").object(mappedStatement.getId());
final List<Object> multipleResults = new ArrayList<>();
int resultSetCount = 0;
ResultSetWrapper rsw = getFirstResultSet(stmt);
List<ResultMap> resultMaps = mappedStatement.getResultMaps();
int resultMapCount = resultMaps.size();
validateResultMapsCount(rsw, resultMapCount);
while (rsw != null && resultMapCount > resultSetCount) {
ResultMap resultMap = resultMaps.get(resultSetCount);
//根据resultMap处理rsw生成java对象
handleResultSet(rsw, resultMap, multipleResults, null);
rsw = getNextResultSet(stmt);
cleanUpAfterHandlingResultSet();
resultSetCount++;
}
String[] resultSets = mappedStatement.getResultSets();
if (resultSets != null) {
while (rsw != null && resultSetCount < resultSets.length) {
ResultMapping parentMapping = nextResultMaps.get(resultSets[resultSetCount]);
if (parentMapping != null) {
String nestedResultMapId = parentMapping.getNestedResultMapId();
ResultMap resultMap = configuration.getResultMap(nestedResultMapId);
handleResultSet(rsw, resultMap, null, parentMapping);
}
rsw = getNextResultSet(stmt);
cleanUpAfterHandlingResultSet();
resultSetCount++;
}
}
return collapseSingleResultList(multipleResults);
}
来源:oschina
链接:https://my.oschina.net/u/2649748/blog/4638862