在前端开发中,经常会遇到一些通过遍历循环来获取想要的内容的情形,而且这种情形在开发中无所不在,那么本篇博文就来分享一个比较常用又经典的知识点:forEach() 的使用。
forEach() 是前端开发中操作数组的一种方法,主要功能是遍历数组,其实就是for循环的升级版,该语句需要有一个回调函数作为参数。回调函数的形参依次为:1、value:遍历数组的内容;2、index:对应数组的索引,3、array:数组自身。
在Vue项目中,标签里的循环使用v-for,方法里面的循环使用forEach。
forEach() 方法主要是用于调用数组的每个元素,并将元素传递给回调函数。需要注意的是: forEach() 方法对于空数组是不会执行回调函数的。
forEach:即Array.prototype.forEach,只有数组才有的方法,相当于for循环遍历数组。用法:arr.forEach(function(item,index,array){...}),其中回调函数有3个参数,item为当前遍历到的元素,index为当前遍历到的元素下标,array为数组本身。forEach方法不会跳过null和undefined元素。比如数组[1,undefine,null,,2]中的四个元素都将被遍历到,注意与map的区别。
array.forEach(function(currentValue, index, array), thisValue)
例子:array.forEach(function(item,index,array){ ... })
①forEach()的continue和break:forEach() 自身不支持continue和break语句的,但是可以通过some和every来实现。
②forEach()与map的区别: forEach()没有返回值,性质上等同于for循环,对每一项都执行function函数。即map是返回一个新数组,原数组不变,而forEach是改变原数组。
③forEach()与for循环的对比:for循环步骤多比较复杂,forEach循环比较简单好用,不易出错。
let array = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7];
array.forEach(function (item, index) {
console.log(item); //输出数组的每一个元素
var array=[1, 2, 3, 4, 5];
array.forEach(function(item, index, array){
console.log(array); //输出结果:修改了原数组元素,为每个元素都乘以4
<el-checkbox v-for="(item) in searchContent"
<span>{{item.value}}{{item.checked}}</span>
this.jurisdiction = true;
this.$http.get(“/user/resources", {
params: {userId: this.userId}
a.searchContent = response.body;
a.searchContent.forEach(function (b) {
a.selectedCheck.push(b.id);
var userList = new Array();
if (response.data.userList != null && response.data.userList.length > 0) {
response.data.userList.forEach((item, index) => {
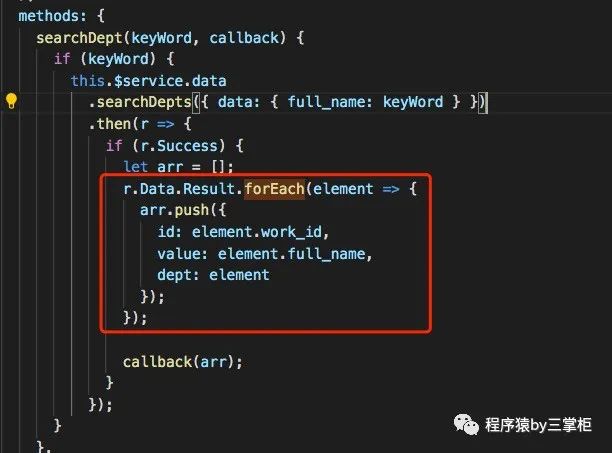
searchDept(keyWord, callback) {
.searchDepts({ data: { full_name: keyWord } })
r.Data.Result.forEach(element => {
value: element.full_name,

以上就是本章全部内容,欢迎关注三掌柜的微信公众号“iOS开发by三掌柜”,三掌柜的新浪微博“三掌柜666”,欢迎关注!


本文分享自微信公众号 - iOS开发by三掌柜(sanzhanggui777)。
如有侵权,请联系 support@oschina.cn 删除。
本文参与“OSC源创计划”,欢迎正在阅读的你也加入,一起分享。
来源:oschina
链接:https://my.oschina.net/sanzhanggui/blog/4885420