word.txt
hello spark wordhello scala sparkhi java flinkhi hello kafkahello kafka spark flink spark
package com.wedoctor.sparkcoreimport org.apache.log4j.{Level, Logger}import org.apache.spark.rdd.RDDimport org.apache.spark.{SparkConf, SparkContext}object WordCount {Logger.getLogger("org").setLevel(Level.ERROR)def main(args: Array[String]): Unit = {val conf: SparkConf = new SparkConf().setMaster("local[*]").setAppName(this.getClass.getSimpleName)val sc: SparkContext = new SparkContext(conf)val lineData: RDD[String] = sc.textFile("d://word.txt")val value: RDD[String] = lineData.flatMap(_.split(' '))val wordWithOne: RDD[(String, Int)] = value.map((_,1))val resultData: RDD[(String, Int)] = wordWithOne.reduceByKey(_+_)val resultData2 = wordWithOne.groupByKey().mapValues(_.sum)resultData2.sortBy(-_._2).foreach(println)sc.stop()}}
一 groupByKey
/*** Group the values for each key in the RDD into a single sequence. Allows controlling the* partitioning of the resulting key-value pair RDD by passing a Partitioner.* The ordering of elements within each group is not guaranteed, and may even differ* each time the resulting RDD is evaluated.** @note This operation may be very expensive. If you are grouping in order to perform an* aggregation (such as a sum or average) over each key, using `PairRDDFunctions.aggregateByKey`* or `PairRDDFunctions.reduceByKey` will provide much better performance.** @note As currently implemented, groupByKey must be able to hold all the key-value pairs for any* key in memory. If a key has too many values, it can result in an `OutOfMemoryError`.*/def groupByKey(partitioner: Partitioner): RDD[(K, Iterable[V])] = self.withScope {// groupByKey shouldn't use map side combine because map side combine does not// reduce the amount of data shuffled and requires all map side data be inserted// into a hash table, leading to more objects in the old gen.val createCombiner = (v: V) => CompactBuffer(v)val mergeValue = (buf: CompactBuffer[V], v: V) => buf += vval mergeCombiners = (c1: CompactBuffer[V], c2: CompactBuffer[V]) => c1 ++= c2val bufs = combineByKeyWithClassTag[CompactBuffer[V]](createCombiner, mergeValue, mergeCombiners, partitioner, mapSideCombine = false)bufs.asInstanceOf[RDD[(K, Iterable[V])]]}
默认的HashPartitioner:key的hashcode % 分区数量
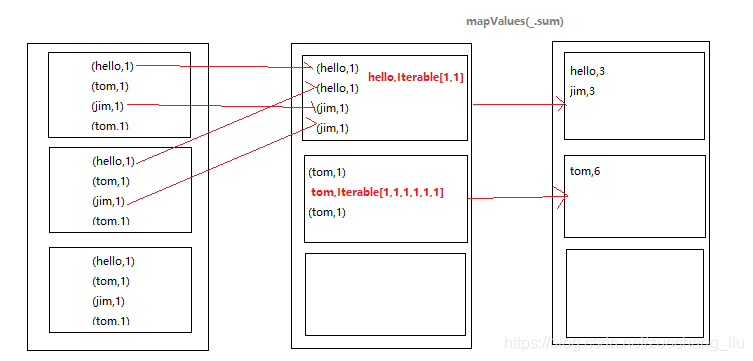
二 reduceByKey
/*** Merge the values for each key using an associative and commutative reduce function. This will* also perform the merging locally on each mapper before sending results to a reducer, similarly* to a "combiner" in MapReduce. Output will be hash-partitioned with the existing partitioner/* parallelism level.*/def reduceByKey(func: (V, V) => V): RDD[(K, V)] = self.withScope {reduceByKey(defaultPartitioner(self), func)}
默认的HashPartitioner:key的hashcode % 分区数量
但是会在分区内进行聚合
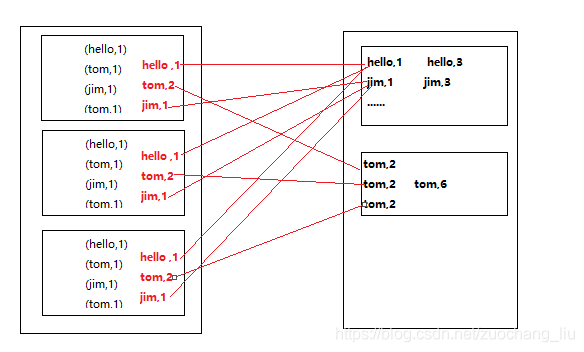
三 总结
reduceByKey会传一个聚合函数, 相当于 groupByKey + mapValues
reduceByKey 会有一个分区内聚合,而groupByKey没有 最核心的区别
结论:reduceByKey有分区内聚合,更高效,优先选择使用reduceByKey。
本文分享自微信公众号 - 大数据私房菜(datagogogo)。
如有侵权,请联系 support@oschina.cn 删除。
本文参与“OSC源创计划”,欢迎正在阅读的你也加入,一起分享。
来源:oschina
链接:https://my.oschina.net/u/4631230/blog/4538491