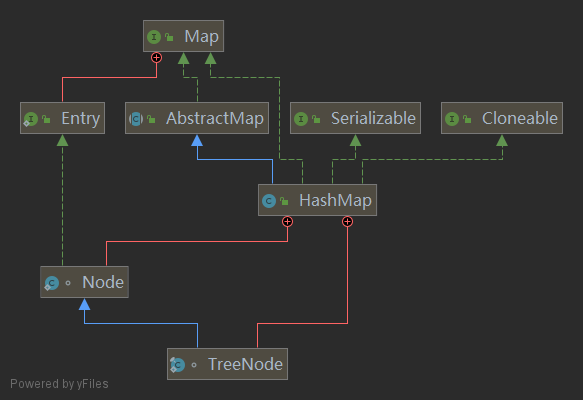
HashMap
属性
public class HashMap<K,V> extends AbstractMap<K,V>
implements Map<K,V>, Cloneable, Serializable {
/*--------------常量--------------*/
// 默认hash桶初始长度16
static final int DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY = 1 << 4; // aka 16
// hash桶最大容量2的30次幂
static final int MAXIMUM_CAPACITY = 1 << 30;
// 默认加载因子为0.75f
static final float DEFAULT_LOAD_FACTOR = 0.75f;
// 链表的数量大于等于8个并且桶的数量大于等于64时链表树化
static final int TREEIFY_THRESHOLD = 8;
// hash表某个节点链表的数量小于等于6时树拆分
static final int UNTREEIFY_THRESHOLD = 6;
// 树化时最小桶的数量
static final int MIN_TREEIFY_CAPACITY = 64;
/*--------------实例变量--------------*/
// hash桶,长度必须为2的n次幂
transient Node<K,V>[] table;
// 存放具体元素的集
transient Set<Map.Entry<K,V>> entrySet;
// 键值对的数量
transient int size;
// HashMap被改变的次数,用于fail-fast机制的实现
transient int modCount;
// 扩容的阀值,当键值对的数量超过这个阀值会产生扩容,threshold = table.length * loadFactor
int threshold;
// 负载因子, 用于计算哈希表元素数量的阈值
final float loadFactor;
}
Constructor
public HashMap() {
// 默认构造函数,赋值加载因子为默认的0.75f, hash桶在put时初始化
this.loadFactor = DEFAULT_LOAD_FACTOR; // all other fields defaulted
}
public HashMap(int initialCapacity) {
this(initialCapacity, DEFAULT_LOAD_FACTOR);
}
// 同时指定初始化容量以及加载因子,用的很少,一般不会修改loadFactor
public HashMap(int initialCapacity, float loadFactor) {
// 初始化容量处理
if (initialCapacity < 0)
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Illegal initial capacity: " +
initialCapacity);
if (initialCapacity > MAXIMUM_CAPACITY)
initialCapacity = MAXIMUM_CAPACITY;
// 加载因子判断
if (loadFactor <= 0 || Float.isNaN(loadFactor))
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Illegal load factor: " +
loadFactor);
this.loadFactor = loadFactor;
// 设置阈值为初始化容量的2的n次方的值
this.threshold = tableSizeFor(initialCapacity);
}
// 新建一个哈希表,同时将另一个map m 里的所有元素加入表中
public HashMap(Map<? extends K, ? extends V> m) {
this.loadFactor = DEFAULT_LOAD_FACTOR;
putMapEntries(m, false);
}
// 用来保证hash桶数量一定为2的n次方,哈希桶的实际容量 length。 返回值一般会>=cap
static final int tableSizeFor(int cap) {
// 经过下面的 或 和位移 运算, n最终各位都是1。‘|’为同为0时为0, 其他为1;
int n = cap - 1;
n |= n >>> 1;
n |= n >>> 2;
n |= n >>> 4;
n |= n >>> 8;
n |= n >>> 16;
// 判断n是否越界,返回 2的n次方作为 table(哈希桶)的阈值
return (n < 0) ? 1 : (n >= MAXIMUM_CAPACITY) ? MAXIMUM_CAPACITY : n + 1;
}
扰动函数
// 可以看出HashMap的key可以为null
static final int hash(Object key) {
int h;
// key.hashCode():返回散列值也就是hashcode
// ^ :按位异或
// >>>:无符号右移,忽略符号位,空位都以0补齐
return (key == null) ? 0 : (h = key.hashCode()) ^ (h >>> 16);
}
内部类 Node
// 单链表
static class Node<K,V> implements Map.Entry<K,V> {
final int hash;// 存放的hash()的值
final K key;
V value;
Node<K,V> next;
Node(int hash, K key, V value, Node<K,V> next) {
this.hash = hash;
this.key = key;
this.value = value;
this.next = next;
}
}
内部类 TreeNode
// 红黑树
static final class TreeNode<K,V> extends LinkedHashMap.Entry<K,V> {
TreeNode<K,V> parent; // 父节点
TreeNode<K,V> left; // 左节点
TreeNode<K,V> right; // 右节点
TreeNode<K,V> prev; // 双向链表前节点
boolean red; //节点颜色
TreeNode(int hash, K key, V val, Node<K,V> next) {
super(hash, key, val, next);//最终为调用HashMap.Node的构造器
}
}
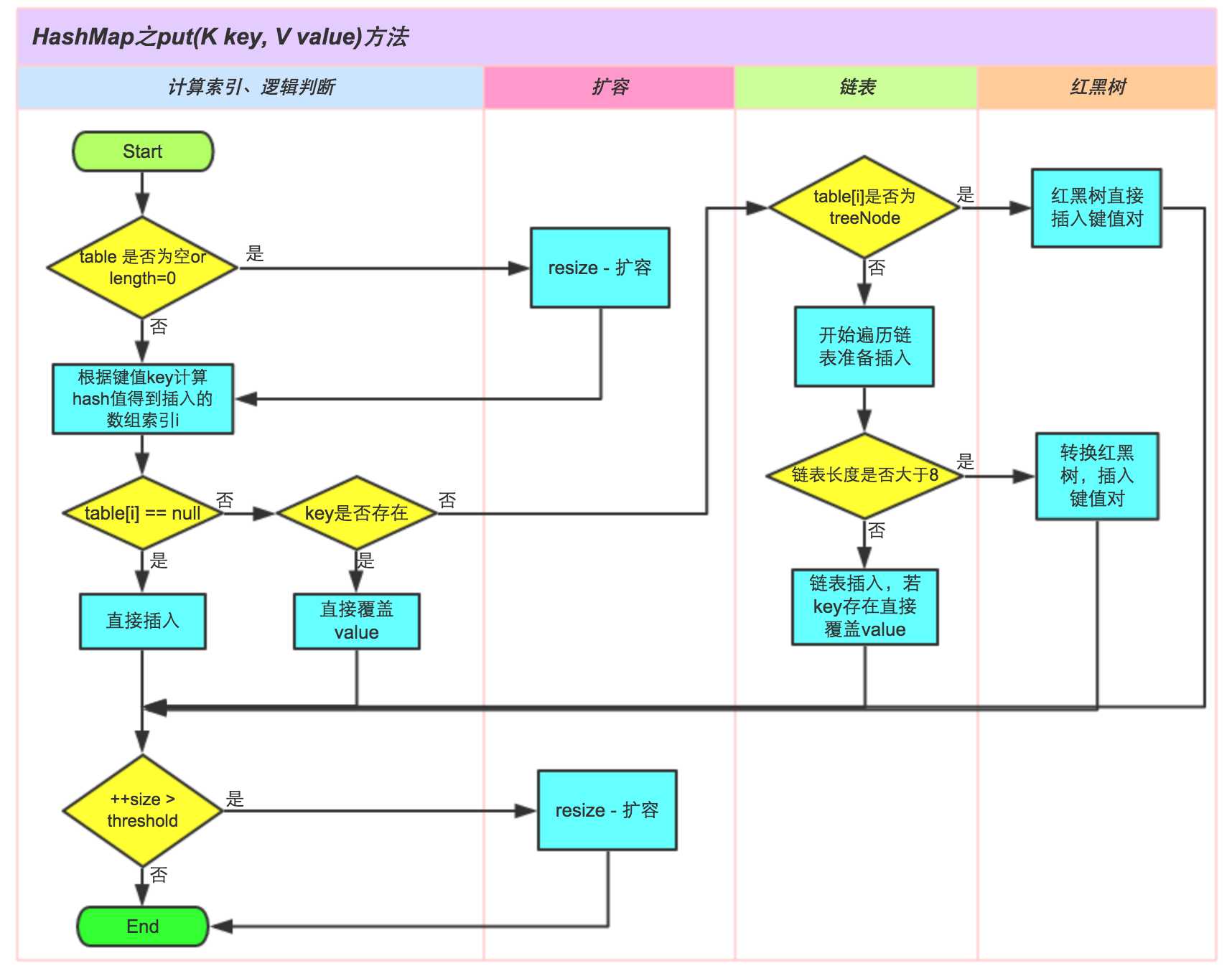
put
图片来源见参考
public V put(K key, V value) {
return putVal(hash(key), key, value, false, true);
}
@Override
public V putIfAbsent(K key, V value) {
return putVal(hash(key), key, value, true, true);
}
//onlyIfAbsent代表是否不覆盖,false为覆盖
final V putVal(int hash, K key, V value, boolean onlyIfAbsent, boolean evict) {
//tab存放 当前的hash桶, p用作临时链表节点
Node<K,V>[] tab; Node<K,V> p; int n, i;
//当table为空时,这里初始化table,不是通过构造函数初始化,而是在插入时通过扩容初始化,有效防止了初始化HashMap没有数据插入造成空间浪费可能造成内存泄露的情况
if ((tab = table) == null || (n = tab.length) == 0)
n = (tab = resize()).length;
//没有发生哈希碰撞。 直接构建一个新节点Node存放
if ((p = tab[i = (n - 1) & hash]) == null)//index = (n - 1) & hash
tab[i] = newNode(hash, key, value, null);
else {//发生了哈希冲突
Node<K,V> e; K k;
//如果头节点的hash值与key相等,直接覆盖
if (p.hash == hash &&
((k = p.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k))))
e = p;
//当前节点为红黑树节点,转为红黑树插入
else if (p instanceof TreeNode)
e = ((TreeNode<K,V>)p).putTreeVal(this, tab, hash, key, value);
else {
//当前节点为链表,循环遍历判定是否存在相同的key
for (int binCount = 0; ; ++binCount) {
//遍历到尾部,追加新节点到尾部
if ((e = p.next) == null) {
p.next = newNode(hash, key, value, null);
//链表的数量大于等于8个并且桶的数量大于等于64时链表转换为红黑树
if (binCount >= TREEIFY_THRESHOLD - 1) // -1 for 1st
treeifyBin(tab, hash);
break;
}
//如果找到了要覆盖的节点
if (e.hash == hash &&
((k = e.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k))))
break;
p = e;
}
}
//如果e不是null,说明有需要覆盖的节点
if (e != null) {
//旧值
V oldValue = e.value;
if (!onlyIfAbsent || oldValue == null)
//覆盖值
e.value = value;
//这是一个空实现的函数,用作LinkedHashMap重写使用。
afterNodeAccess(e);
//返回旧值
return oldValue;
}
}
//如果执行到了这里,说明插入了一个新的节点,所以会修改modCount & size,以及返回null。
//map调整次数加1
++modCount;
//更新size,并判断是否需要扩容。
if (++size > threshold)
resize();
//这是一个空实现的函数,用作LinkedHashMap重写使用。
afterNodeInsertion(evict);
return null;
}
扩容函数
final Node<K,V>[] resize() {
//oldTab 为当前表的哈希桶
Node<K,V>[] oldTab = table;
//当前哈希桶的容量 length
int oldCap = (oldTab == null) ? 0 : oldTab.length;
//当前的阈值
int oldThr = threshold;
//初始化新的容量和阈值为0
int newCap, newThr = 0;
//如果当前容量大于0
if (oldCap > 0) {
//如果当前容量已经到达上限
if (oldCap >= MAXIMUM_CAPACITY) {
//则设置阈值是2的31次方-1
threshold = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
//同时返回当前的哈希桶,不再扩容
return oldTab;
}//否则新的容量为旧的容量的两倍。
else if ((newCap = oldCap << 1) < MAXIMUM_CAPACITY &&
oldCap >= DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY)//如果旧的容量大于等于默认初始容量16
//那么新的阈值也等于旧的阈值的两倍
newThr = oldThr << 1; // double threshold
}//如果当前表是空的,但是有阈值。代表是初始化时指定了容量、阈值的情况
else if (oldThr > 0) // initial capacity was placed in threshold
newCap = oldThr;//那么新表的容量就等于旧的阈值
else {}//如果当前表是空的,而且也没有阈值。代表是初始化时没有任何容量/阈值参数的情况 // zero initial threshold signifies using defaults
newCap = DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY;//此时新表的容量为默认的容量 16
newThr = (int)(DEFAULT_LOAD_FACTOR * DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY);//新的阈值为默认容量16 * 默认加载因子0.75f = 12
}
if (newThr == 0) {//如果新的阈值是0,对应的是 当前表是空的,但是有阈值的情况
float ft = (float)newCap * loadFactor;//根据新表容量 和 加载因子 求出新的阈值
//进行越界修复
newThr = (newCap < MAXIMUM_CAPACITY && ft < (float)MAXIMUM_CAPACITY ?
(int)ft : Integer.MAX_VALUE);
}
//更新阈值
threshold = newThr;
@SuppressWarnings({"rawtypes","unchecked"})
//根据新的容量 构建新的哈希桶
Node<K,V>[] newTab = (Node<K,V>[])new Node[newCap];
//更新哈希桶引用
table = newTab;
//如果以前的哈希桶中有元素
//下面开始将当前哈希桶中的所有节点转移到新的哈希桶中
if (oldTab != null) {
//遍历老的哈希桶
for (int j = 0; j < oldCap; ++j) {
//取出当前的节点 e
Node<K,V> e;
//如果当前桶中有元素,则将链表赋值给e
if ((e = oldTab[j]) != null) {
//将原哈希桶置空以便GC
oldTab[j] = null;
//如果当前链表中就一个元素,(没有发生哈希碰撞)
if (e.next == null)
//直接将这个元素放置在新的哈希桶里。
//注意这里取下标 是用 哈希值 与 桶的长度-1 。 由于桶的长度是2的n次方,这么做其实是等于 一个模运算。但是效率更高
newTab[e.hash & (newCap - 1)] = e;
//当前节点是红黑树
else if (e instanceof TreeNode)
((TreeNode<K,V>)e).split(this, newTab, j, oldCap);
//当前节点为链表
else { // preserve order
//因为扩容是容量翻倍,所以原链表上的每个节点,现在可能存放在原来的下标,即low位, 或者扩容后的下标,即high位。 high位= low位+原哈希桶容量
//低位链表的头结点、尾节点
Node<K,V> loHead = null, loTail = null;
//高位链表的头节点、尾节点
Node<K,V> hiHead = null, hiTail = null;
Node<K,V> next;//临时节点 存放e的下一个节点
do {
next = e.next;
//这里又是一个利用位运算 代替常规运算的高效点: 利用哈希值 与 旧的容量,可以得到哈希值去模后,是大于等于oldCap还是小于oldCap,等于0代表小于oldCap,应该存放在低位,否则存放在高位
if ((e.hash & oldCap) == 0) {
//给头尾节点指针赋值
if (loTail == null)
loHead = e;
else
loTail.next = e;
loTail = e;
}//高位也是相同的逻辑
else {
if (hiTail == null)
hiHead = e;
else
hiTail.next = e;
hiTail = e;
}//循环直到链表结束
} while ((e = next) != null);
//将低位链表存放在原index处,
if (loTail != null) {
loTail.next = null;
newTab[j] = loHead;
}
//将高位链表存放在新index处
if (hiTail != null) {
hiTail.next = null;
newTab[j + oldCap] = hiHead;
}
}
}
}
}
return newTab;
}
remove
public V remove(Object key) {
Node<K,V> e;
return (e = removeNode(hash(key), key, null, false, true)) == null ?
null : e.value;
}
@Override
public boolean remove(Object key, Object value) {
return removeNode(hash(key), key, value, true, true) != null;
}
// 如果参数matchValue是true,则必须key 、value都相等才删除。
// 如果参数movable是false,在删除节点时,不移动其他节点
final Node<K,V> removeNode(int hash, Object key, Object value,
boolean matchValue, boolean movable) {
// p 是待删除节点的前置节点
Node<K,V>[] tab; Node<K,V> p; int n, index;
if ((tab = table) != null && (n = tab.length) > 0 &&//如果哈希表不为空
(p = tab[index = (n - 1) & hash]) != null) {//根据hash值算出的index,且不为空
//待删除节点
Node<K,V> node = null, e; K k; V v;
//如果头节点就是待删除节点
if (p.hash == hash &&
((k = p.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k))))
node = p;
else if ((e = p.next) != null) {
if (p instanceof TreeNode)//如果是红黑树
node = ((TreeNode<K,V>)p).getTreeNode(hash, key);
else {//如果是链表
do {//遍历获取待删除节点
if (e.hash == hash &&
((k = e.key) == key ||
(key != null && key.equals(k)))) {
node = e;
break;
}
p = e;
} while ((e = e.next) != null);
}
}
//如果有待删除节点node,且 matchValue为false,或者值也相等
if (node != null && (!matchValue || (v = node.value) == value ||
(value != null && value.equals(v)))) {
if (node instanceof TreeNode)//如果是红黑树,则以红黑树方式移除
((TreeNode<K,V>)node).removeTreeNode(this, tab, movable);
else if (node == p)//如果为头节点
tab[index] = node.next;
else//非头节点
p.next = node.next;
//修改modCount & size
++modCount;
--size;
afterNodeRemoval(node);//LinkedHashMap回调函数
return node;
}
}
return null;
}
get
public V get(Object key) {
Node<K,V> e;
return (e = getNode(hash(key), key)) == null ? null : e.value;
}
@Override
public V getOrDefault(Object key, V defaultValue) {
Node<K,V> e;
return (e = getNode(hash(key), key)) == null ? defaultValue : e.value;
}
final Node<K,V> getNode(int hash, Object key) {
Node<K,V>[] tab; Node<K,V> first, e; int n; K k;
if ((tab = table) != null && (n = tab.length) > 0 &&//如果hash表不为空
(first = tab[(n - 1) & hash]) != null) {//如果下标
if (first.hash == hash && // 判断头节点
((k = first.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k))))
return first;
if ((e = first.next) != null) {
if (first instanceof TreeNode)//如果是红黑树
return ((TreeNode<K,V>)first).getTreeNode(hash, key);
do {//如果是链表,遍历
if (e.hash == hash &&
((k = e.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k))))
return e;
} while ((e = e.next) != null);
}
}
return null;
}
contains
//如果能通过key取出节点就代表存在key
public boolean containsKey(Object key) {
return getNode(hash(key), key) != null;
}
//遍历链表获取值
public boolean containsValue(Object value) {
Node<K,V>[] tab; V v;
if ((tab = table) != null && size > 0) {
for (int i = 0; i < tab.length; ++i) {
for (Node<K,V> e = tab[i]; e != null; e = e.next) {
if ((v = e.value) == value ||
(value != null && value.equals(v)))
return true;
}
}
}
return false;
}
红黑树相关可以参考TreeMap[JDK 1.8]源码学习
总结
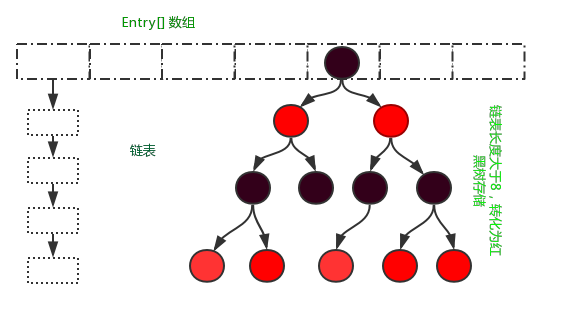
HashMap的存储结构为数组Node[]+单向链表Node+红黑树TreeNode;
默认容量为16,容器hash桶使用懒加载方式,扩容方式为newCap = oldCap << 1;
默认加载因子为0.75f,扩容阀值为容量 * 加载因子,扩容时阀值也为2倍:newThr = oldThr << 1;
当链表长度超过8且hash桶容量小于64时,hash桶扩容;
当链表长度超过8且hash桶容量大于64时,链表红黑树化;
hash计算方式为 hash = key.hashCode() ^ (key.hashCode() >>> 16);
因为hash计算时对null做了特殊处理,HashMap允许key与value为null;
index计算方式为 index = (table.length - 1) & hash;
扩容为创建新容量的hash桶,并复制迁移原hash桶的节点;
扩容时,将单节点以index = (newCap - 1) & hash放入新桶中;将链表以hash & oldCap == 0保留原顺序分为两个节点,符合条件的在原位置index,不相等的放置到index + oldCap;将红黑树也以hash & oldCap == 0的方式分为两个Node,同时Node长度小于等于6的解除红黑树,转为链表,长度大于6的仍然构造为红黑树;
阿里巴巴Java开发手册:
1.5集合处理 14.在集合初始化时,指定集合初始化大小;
参考
Programmer Help × JDK1.8 HashMap Source Code Analysis
来源:oschina
链接:https://my.oschina.net/u/4207994/blog/3109455