上一个打印时间的简单例子
#include <iostream>
#include <chrono>
#include <thread>
int main()
{
using namespace std::literals::chrono_literals;
auto start = std::chrono::high_resolution_clock::now();
std::this_thread::sleep_for(1s);
auto end = std::chrono::high_resolution_clock::now();
std::chrono::duration<float> duration = end - start;
std::cout << duration.count() << "s" << std::endl;
std::cin.get();
}
执行后输出显示1s。
另一个更加使用的情况是这样的
#include <iostream>
#include <chrono>
#include <thread>
struct Timer
{
std::chrono::time_point<std::chrono::steady_clock> start, end;
std::chrono::duration<float> duration;
Timer()
{
start = std::chrono::high_resolution_clock::now();
}
~Timer()
{
end = std::chrono::high_resolution_clock::now();
duration = end - start;
float ms = duration.count() * 1000.0f;
std::cout << "Timer took " << ms << "ms" << std::endl;
}
};
void Function()
{
Timer timer;
for (int i = 0; i < 100; i++)
std::cout << "Hello" << std::endl;
}
int main()
{
Function();
std::cin.get();
}
我们创建一个Timer的struct,计算打印100次要多少时间。
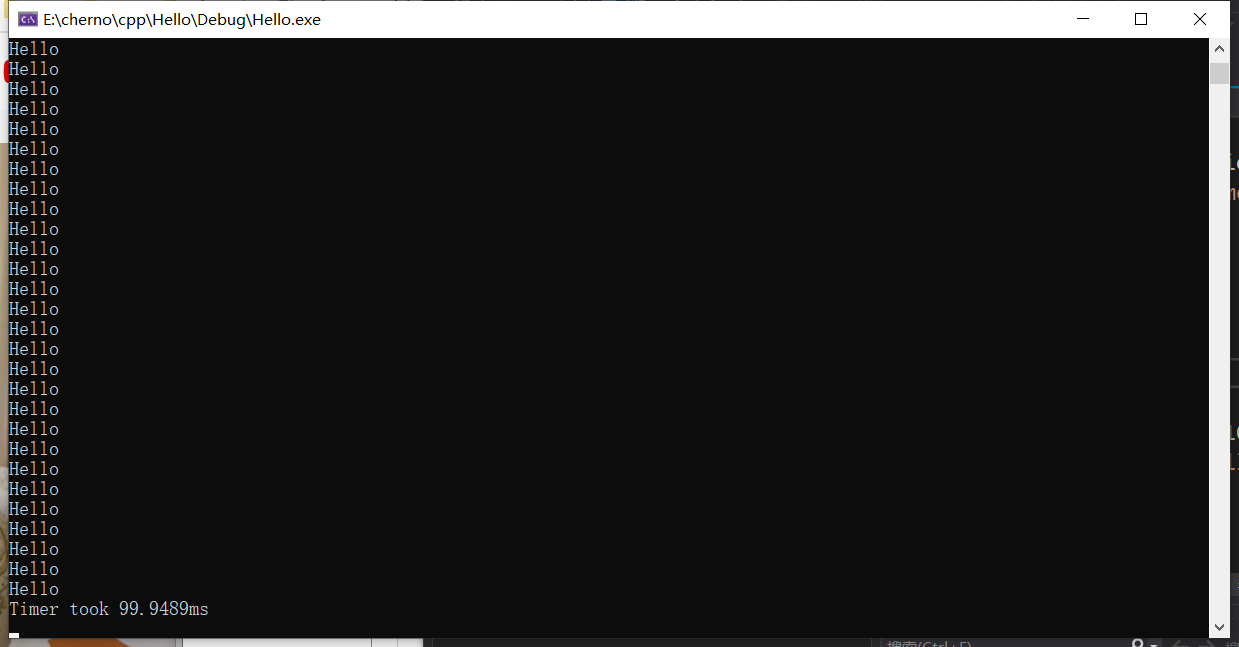
我们可以把每次打印的std::endl去掉
for (int i = 0; i < 100; i++)
std::cout << "Hello\n";
这样来打印,可以显著提高时间,因为std::endl总是要花时间的。
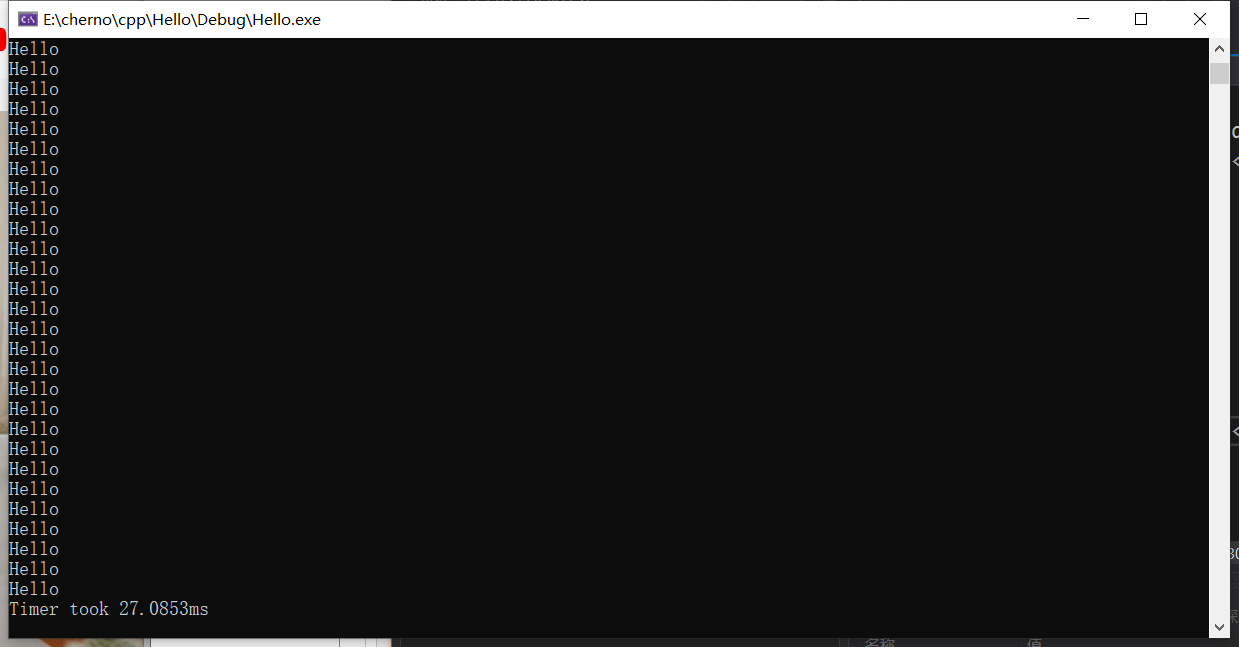
总之,这是一个非常粗糙的关于时间计算的例子,不过可以帮助理解。
来源:https://www.cnblogs.com/EvansPudding/p/12542500.html