beautiful soup的基本使用
练习的文档
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8"/>
<title>python Beautiful soup 测试</title>
<link href="images/bitbug_favicon.ico" rel="icon"/>
<link href="css/in-css.css" rel="stylesheet" type="text/css"/>
<link href="css/theme-style.css" rel="stylesheet" type="text/css"/>
<script src="js/jquery-1.8.3.min.js" type="text/javascript"></script>
<script src="js/in-js.js" type="text/javascript"></script>
<script src="js/jquery.min.js" type="text/javascript"></script>
<p class="world">hello world</p>
<p class="python">hello python</p>
<a href="http://example.com/elsie" class="sister" id="link1">Elsie</a>
<a href="http://example.com/lacie" class="brother" id="link2">Lacie</a>
</head>基本使用
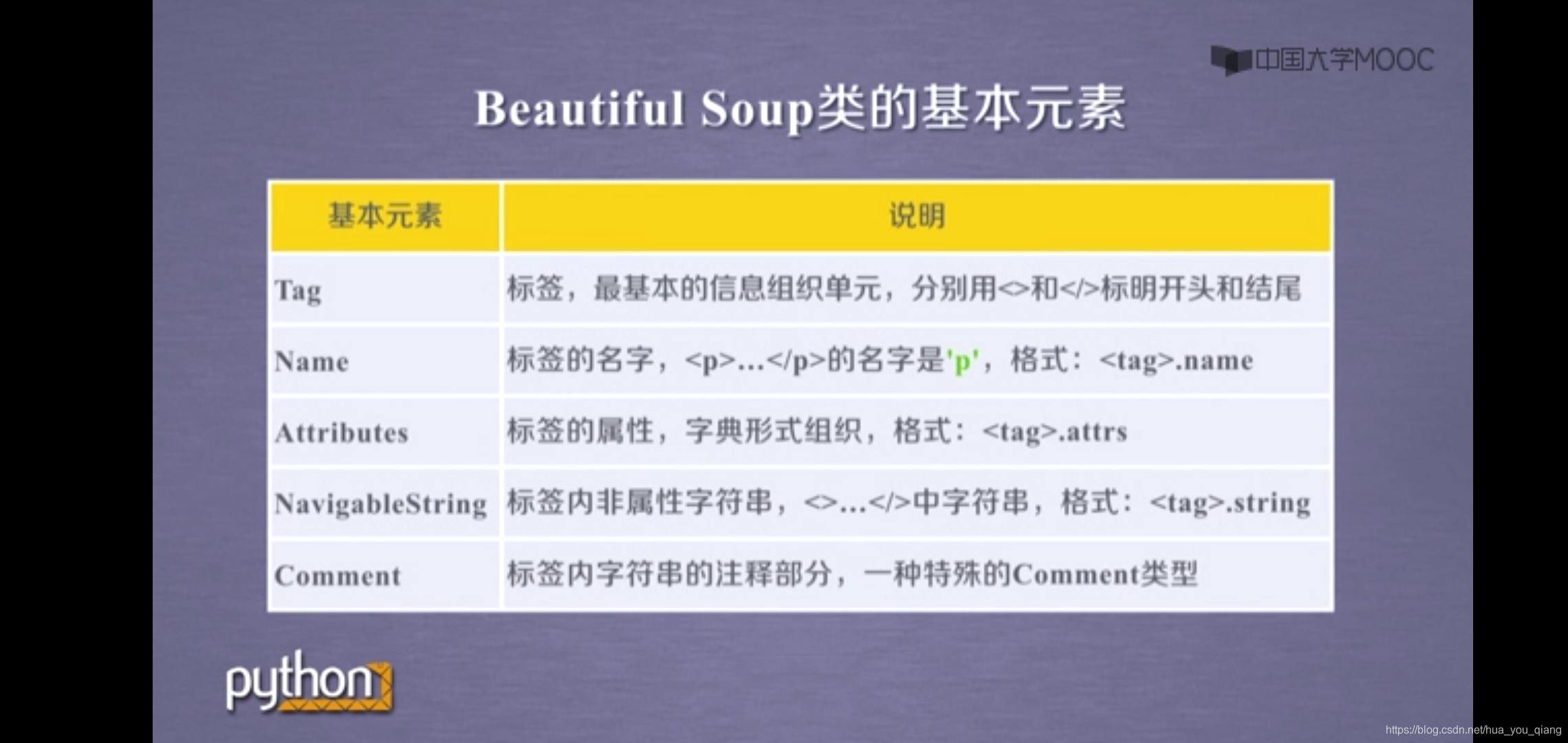
BeautifulSoup 的理解

先做“一锅汤”,我们使用‘lxml’作为我们的解析器。
解析器类型:
| 解析器 | 使用方法 | 优势 | 劣势 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Python标准库 | BeautifulSoup(markup,“html.parser”) | Python的内置标准库: 1. 执行速度适中文 2. 档容错能力强 | Python 2.7.3 or 3.2.2)前的版本中文档容错能力差 |
| lxml HTML 解析器 | BeautifulSoup(markup,“lxml”) | 1. 速度快 2. 文档容错能力强 | 需要安装C语言库 |
| lxml XML 解析器 | 1. BeautifulSoup(markup,[“lxml-xml”]) 2. BeautifulSoup(markup,“xml”) | 1. 速度快 2. 唯一支持XML的解析器 | 需要安装C语言库 |
| html5lib | BeautifulSoup(markup,“html5lib”) | 1. 最好的容错性 2. 以浏览器的方式解析文档 3. 生成HTML5格式的文档 | 1. 速度慢 2. 不依赖外部扩展 |
soup = BeautifulSoup(doc, 'lxml')结构化打印输出
print(soup.prettify())
# 输出结果
"""
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8"/>
<title>
python Beautiful soup 测试
</title>
<link href="images/bitbug_favicon.ico" rel="icon"/>
<link href="css/in-css.css" rel="stylesheet" type="text/css"/>
<link href="css/theme-style.css" rel="stylesheet" type="text/css"/>
<script src="js/jquery-1.8.3.min.js" type="text/javascript">
</script>
<script src="js/in-js.js" type="text/javascript">
</script>
<script src="js/jquery.min.js" type="text/javascript">
</script>
</head>
<body>
<p class="world">
hello world
</p>
<p class="python">
hello python
</p>
<a class="sister" href="http://example.com/elsie" id="link1">
Elsie
</a>
<a class="brother" href="http://example.com/lacie" id="link2">
Lacie
</a>
</body>
</html>
"""几个简单的浏览结构化数据的方法
# 找到标题标签
print(soup.title)
# 输出结果
# <title>python Beautiful soup 测试</title>
# 找到链接标签
print(soup.link)
# 打印结果
# <link href="images/bitbug_favicon.ico" rel="icon"/>
# 找到标签的字符串
print(soup.title.string)
# 打印结果
# python Beautiful soup 测试
# 找标签(Tag)的属性(attributes),我们可以用字典的方式去找到标签属性的值。
print(soup.a['class'])
# 或者
print(soup.a.get('class'))
# 打印结果
# ['sister']
# 找到链接地址
print(soup.link['href'])
# 打印结果
# images/bitbug_favicon.ico
有时候我们需要爬取的链接很多,而不是只爬取一条链接,这时我们需要用soup.find_all()
# 爬取所有link标签
for url in soup.find_all('link'):
print(url['href'])
# images/bitbug_favicon.ico
# css/in-css.css
# css/theme-style.css
# 爬取a标签的所有链接
for url in soup.find_all('a'):
print(url['href'])
# 打印结果
# http://example.com/elsie
# http://example.com/lacie
有时候我们需要精确爬取某条链接或者某类链接
print(soup.find_all('a', class_='brother'))
# 打印结果
# [<a class="brother" href="http://example.com/lacie" id="link2">Lacie</a>]
# 如果我们需要这条链接
print(soup.find_all('a', class_='brother')[0]['href'])
# 打印结果
# http://example.com/lacie
# 如果我们需要这里面的文字
print(soup.find_all('a', class_='brother')[0].string)
# 打印结果
# Lacie今天的分享比较简单,到时再更新。
来源:CSDN
作者:华筱攸
链接:https://blog.csdn.net/hua_you_qiang/article/details/104795317