Bolt提供了四种通信模型,分别是Oneway ,Sync ,Future ,Callback asynchronous
4.1 Oneway
oneway单向通话
特点
- 不关心返回值
- 发送请求就立即返回
com.alipay.remoting.BaseRemoting#oneway
protected void oneway(final Connection conn, final RemotingCommand request) {
try {
conn.getChannel().writeAndFlush(request).addListener(new ChannelFutureListener() {
@Override
public void operationComplete(ChannelFuture f) throws Exception {
if (!f.isSuccess()) {
logger.error("Invoke send failed. The address is {}",
RemotingUtil.parseRemoteAddress(conn.getChannel()), f.cause());
}
}
});
} catch (Exception e) {
if (null == conn) {
logger.error("Conn is null");
} else {
logger.error("Exception caught when sending invocation. The address is {}",
RemotingUtil.parseRemoteAddress(conn.getChannel()), e);
}
}
}
4.2 Sync
Sync同步请求
特点
- 需要获取返回值
- 如果在超时时间内未返回,触发超时错误
protected RemotingCommand invokeSync(final Connection conn, final RemotingCommand request,
final int timeoutMillis) throws RemotingException,
InterruptedException {
final InvokeFuture future = createInvokeFuture(request, request.getInvokeContext());
conn.addInvokeFuture(future);
final int requestId = request.getId();
try {
conn.getChannel().writeAndFlush(request).addListener(new ChannelFutureListener() {
@Override
public void operationComplete(ChannelFuture f) throws Exception {
if (!f.isSuccess()) {
conn.removeInvokeFuture(requestId);
future.putResponse(commandFactory.createSendFailedResponse(
conn.getRemoteAddress(), f.cause()));
logger.error("Invoke send failed, id={}", requestId, f.cause());
}
}
});
} catch (Exception e) {
conn.removeInvokeFuture(requestId);
future.putResponse(commandFactory.createSendFailedResponse(conn.getRemoteAddress(), e));
logger.error("Exception caught when sending invocation, id={}", requestId, e);
}
RemotingCommand response = future.waitResponse(timeoutMillis);
if (response == null) {
conn.removeInvokeFuture(requestId);
response = this.commandFactory.createTimeoutResponse(conn.getRemoteAddress());
logger.warn("Wait response, request id={} timeout!", requestId);
}
return response;
}
上面的代码是客户端发送请求的代码,InvokeFuture的实现类是DefaultInvokeFuture,内部用CountDownLatch来实现同步,初始化时CountDownLatch默认值是1.
private final CountDownLatch countDownLatch = new CountDownLatch(1);
当调用putResponse时,countDownLatch计数减1
@Override
public void putResponse(RemotingCommand response) {
this.responseCommand = (ResponseCommand) response;
this.countDownLatch.countDown();
}
然后触发waitResponse返回
@Override
public ResponseCommand waitResponse(long timeoutMillis) throws InterruptedException {
this.countDownLatch.await(timeoutMillis, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS);
return this.responseCommand;
}
服务器正常返回了,在哪里触发的putResponse呢?
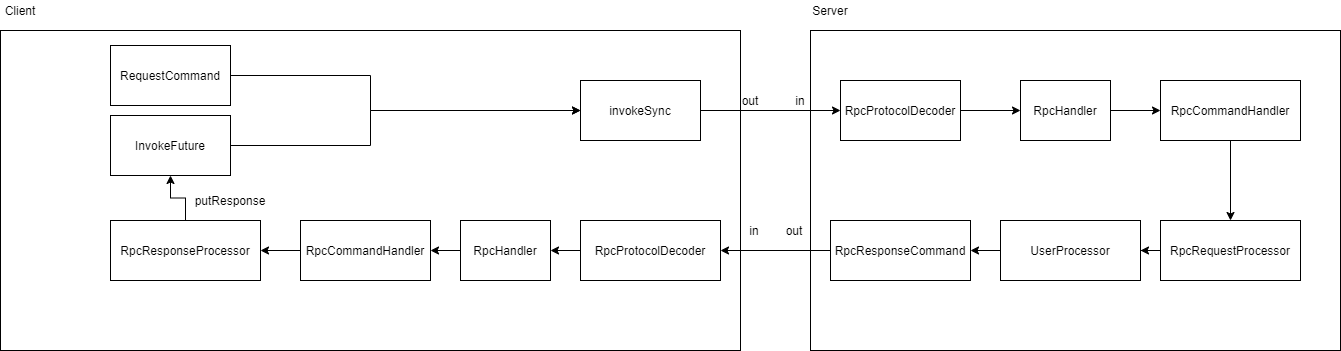
在RpcResponseProcessor类中可以追踪到putResponse
com.alipay.remoting.rpc.protocol.RpcResponseProcessor#doProcess
public void doProcess(RemotingContext ctx, RemotingCommand cmd) {
Connection conn = ctx.getChannelContext().channel().attr(Connection.CONNECTION).get();
InvokeFuture future = conn.removeInvokeFuture(cmd.getId());
ClassLoader oldClassLoader = null;
try {
if (future != null) {
if (future.getAppClassLoader() != null) {
oldClassLoader = Thread.currentThread().getContextClassLoader();
Thread.currentThread().setContextClassLoader(future.getAppClassLoader());
}
future.putResponse(cmd);
future.cancelTimeout();
try {
future.executeInvokeCallback();
} catch (Exception e) {
logger.error("Exception caught when executing invoke callback, id={}",
cmd.getId(), e);
}
} else {
logger
.warn("Cannot find InvokeFuture, maybe already timeout, id={}, from={} ",
cmd.getId(),
RemotingUtil.parseRemoteAddress(ctx.getChannelContext().channel()));
}
} finally {
if (null != oldClassLoader) {
Thread.currentThread().setContextClassLoader(oldClassLoader);
}
}
}
4.3 Future
Future异步请求,与同步请求不同,Futrue直接返回InvokeFuture对象,让线程继续执行。直到调用InvokeFuture.get方法时,如果response已经返回,则可以直接获取结果,否则才会阻塞线程。
protected InvokeFuture invokeWithFuture(final Connection conn, final RemotingCommand request, final int timeoutMillis) {
final InvokeFuture future = createInvokeFuture(request, request.getInvokeContext());
conn.addInvokeFuture(future);
final int requestId = request.getId();
try {
Timeout timeout = TimerHolder.getTimer().newTimeout(new TimerTask() {
@Override
public void run(Timeout timeout) throws Exception {
InvokeFuture future = conn.removeInvokeFuture(requestId);
if (future != null) {
future.putResponse(commandFactory.createTimeoutResponse(conn
.getRemoteAddress()));
}
}
}, timeoutMillis, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS);
future.addTimeout(timeout);
conn.getChannel().writeAndFlush(request).addListener(new ChannelFutureListener() {
@Override
public void operationComplete(ChannelFuture cf) throws Exception {
if (!cf.isSuccess()) {
InvokeFuture f = conn.removeInvokeFuture(requestId);
if (f != null) {
f.cancelTimeout();
f.putResponse(commandFactory.createSendFailedResponse(
conn.getRemoteAddress(), cf.cause()));
}
logger.error("Invoke send failed. The address is {}",
RemotingUtil.parseRemoteAddress(conn.getChannel()), cf.cause());
}
}
});
} catch (Exception e) {
InvokeFuture f = conn.removeInvokeFuture(requestId);
if (f != null) {
f.cancelTimeout();
f.putResponse(commandFactory.createSendFailedResponse(conn.getRemoteAddress(), e));
}
logger.error("Exception caught when sending invocation. The address is {}",
RemotingUtil.parseRemoteAddress(conn.getChannel()), e);
}
return future;
}
4.4 Callback asynchronous
CallBack带回调函数的异步请求,与Future相比可以传入回调函数
protected void invokeWithCallback(final Connection conn, final RemotingCommand request,
final InvokeCallback invokeCallback, final int timeoutMillis) {
final InvokeFuture future = createInvokeFuture(conn, request, request.getInvokeContext(),
invokeCallback);
conn.addInvokeFuture(future);
final int requestId = request.getId();
try {
Timeout timeout = TimerHolder.getTimer().newTimeout(new TimerTask() {
@Override
public void run(Timeout timeout) throws Exception {
InvokeFuture future = conn.removeInvokeFuture(requestId);
if (future != null) {
future.putResponse(commandFactory.createTimeoutResponse(conn
.getRemoteAddress()));
future.tryAsyncExecuteInvokeCallbackAbnormally();
}
}
}, timeoutMillis, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS);
future.addTimeout(timeout);
conn.getChannel().writeAndFlush(request).addListener(new ChannelFutureListener() {
@Override
public void operationComplete(ChannelFuture cf) throws Exception {
if (!cf.isSuccess()) {
InvokeFuture f = conn.removeInvokeFuture(requestId);
if (f != null) {
f.cancelTimeout();
f.putResponse(commandFactory.createSendFailedResponse(
conn.getRemoteAddress(), cf.cause()));
f.tryAsyncExecuteInvokeCallbackAbnormally();
}
logger.error("Invoke send failed. The address is {}",
RemotingUtil.parseRemoteAddress(conn.getChannel()), cf.cause());
}
}
});
} catch (Exception e) {
InvokeFuture f = conn.removeInvokeFuture(requestId);
if (f != null) {
f.cancelTimeout();
f.putResponse(commandFactory.createSendFailedResponse(conn.getRemoteAddress(), e));
f.tryAsyncExecuteInvokeCallbackAbnormally();
}
logger.error("Exception caught when sending invocation. The address is {}",
RemotingUtil.parseRemoteAddress(conn.getChannel()), e);
}
}
回调函数的执行用了观察者模式,InvokeCallbackListener根据reponse的结果执行回调函数的onResponse或onException方法
public void run() {
InvokeCallback callback = future.getInvokeCallback();
// a lot of try-catches to protect thread pool
ResponseCommand response = null;
try {
response = (ResponseCommand) future.waitResponse(0);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
String msg = "Exception caught when getting response from InvokeFuture. The address is "
+ this.remoteAddress;
logger.error(msg, e);
}
if (response == null || response.getResponseStatus() != ResponseStatus.SUCCESS) {
try {
Exception e;
if (response == null) {
e = new InvokeException("Exception caught in invocation. The address is "
+ this.remoteAddress + " responseStatus:"
+ ResponseStatus.UNKNOWN, future.getCause());
} else {
response.setInvokeContext(future.getInvokeContext());
switch (response.getResponseStatus()) {
case TIMEOUT:
e = new InvokeTimeoutException(
"Invoke timeout when invoke with callback.The address is "
+ this.remoteAddress);
break;
case CONNECTION_CLOSED:
e = new ConnectionClosedException(
"Connection closed when invoke with callback.The address is "
+ this.remoteAddress);
break;
case SERVER_THREADPOOL_BUSY:
e = new InvokeServerBusyException(
"Server thread pool busy when invoke with callback.The address is "
+ this.remoteAddress);
break;
case SERVER_EXCEPTION:
String msg = "Server exception when invoke with callback.Please check the server log! The address is "
+ this.remoteAddress;
RpcResponseCommand resp = (RpcResponseCommand) response;
resp.deserialize();
Object ex = resp.getResponseObject();
if (ex instanceof Throwable) {
e = new InvokeServerException(msg, (Throwable) ex);
} else {
e = new InvokeServerException(msg);
}
break;
default:
e = new InvokeException(
"Exception caught in invocation. The address is "
+ this.remoteAddress + " responseStatus:"
+ response.getResponseStatus(), future.getCause());
}
}
callback.onException(e);
} catch (Throwable e) {
logger
.error(
"Exception occurred in user defined InvokeCallback#onException() logic, The address is {}",
this.remoteAddress, e);
}
} else {
ClassLoader oldClassLoader = null;
try {
if (future.getAppClassLoader() != null) {
oldClassLoader = Thread.currentThread().getContextClassLoader();
Thread.currentThread().setContextClassLoader(future.getAppClassLoader());
}
response.setInvokeContext(future.getInvokeContext());
RpcResponseCommand rpcResponse = (RpcResponseCommand) response;
response.deserialize();
try {
callback.onResponse(rpcResponse.getResponseObject());
} catch (Throwable e) {
logger
.error(
"Exception occurred in user defined InvokeCallback#onResponse() logic.",
e);
}
} catch (CodecException e) {
logger
.error(
"CodecException caught on when deserialize response in RpcInvokeCallbackListener. The address is {}.",
this.remoteAddress, e);
} catch (Throwable e) {
logger.error(
"Exception caught in RpcInvokeCallbackListener. The address is {}",
this.remoteAddress, e);
} finally {
if (oldClassLoader != null) {
Thread.currentThread().setContextClassLoader(oldClassLoader);
}
}
} // enf of else
} // end of run
来源:https://www.cnblogs.com/huiyao/p/12417874.html