1311. 获取你好友已观看的视频 - BFS
思路:
找到第level层的好友,是一层一层寻找所以使用BFS,然后再计数就行了
"""
BFS
"""
from collections import defaultdict, Counter
class Solution:
def watchedVideosByFriends(self, watchedVideos, friends, id: int, level: int):
mat = defaultdict(list)
# 先建图
for ind, num in enumerate(friends):
mat[ind] += num
Q, vis = [(id, 0)], {id}
# BFS找level层的朋友是谁
while len(Q) != 0:
node, deepth = Q.pop(0)
if deepth == level:
Q = [i[0] for i in Q] + [node]
break
for i in mat[node]:
if i not in vis:
vis.add(i)
Q.append((i, deepth+1))
res = []
for i in Q:
res += watchedVideos[i]
r = sorted(Counter(res).items(), key=lambda x: (x[1], x[0]))
return [i[0] for i in r]
LCP 3. 机器人大冒险
思路:
第一反映应该是模拟,当然没有这么简单,就超时了。
那么转去判断是否能够到达障碍处,这样需要判断的最多也只有1k+。
如果能够到达某处,必然是走了x轮,y步之后的结果,那么去除掉x轮走过的路,只判断这y步能否走的即可。
class Solution:
def robot(self, command: str, obstacles, x: int, y: int) -> bool:
tx, ty, res = 0, 0, []
# 记录一次command能到达的位置,如果能走到某处,去除掉x轮之后的位置必定在这里面。
for i in command:
if i == 'R':
tx += 1
if i == 'U':
ty += 1
res.append([tx, ty])
res.append([0, 0])
sorted(res)
# 判断是否能走到终点,gl表示走的轮数
gl = min(x // tx, y // ty)
if [x - gl * tx, y - gl * ty] not in res:
return False
for ox, oy in obstacles:
# 走几轮可以到这?
l = min(ox // tx, oy // ty)
# 障碍物的轮数大于目标的,那么肯定碰不到
if l > gl:
continue
# 轮数相同但是在目标位置后面也碰不着
if l == gl:
if res.index([ox - l * tx, oy - l * ty]) > res.index([x - gl * tx, y - gl * ty]):
continue
if [ox - l * tx, oy - l * ty] in res:
return False
return True
1306. 跳跃游戏 III - DFS

思路:
因为都到某个下标后都有两条路可以走 -> 想到使用DFS的模板
class Solution:
def canReach(self, arr, start: int) -> bool:
vis = set()
def DFS(node, res):
if not arr[node]:
return True
for i in [-1, 1]:
tnode = node + i * arr[node]
if judge(tnode) and tnode not in vis:
vis.add(tnode)
if DFS(tnode, res + [tnode]):
return True
vis.remove(tnode)
return False
# 判断是否出界
def judge(num):
if -1 < num < len(arr):
return True
return False
return DFS(start, [start])
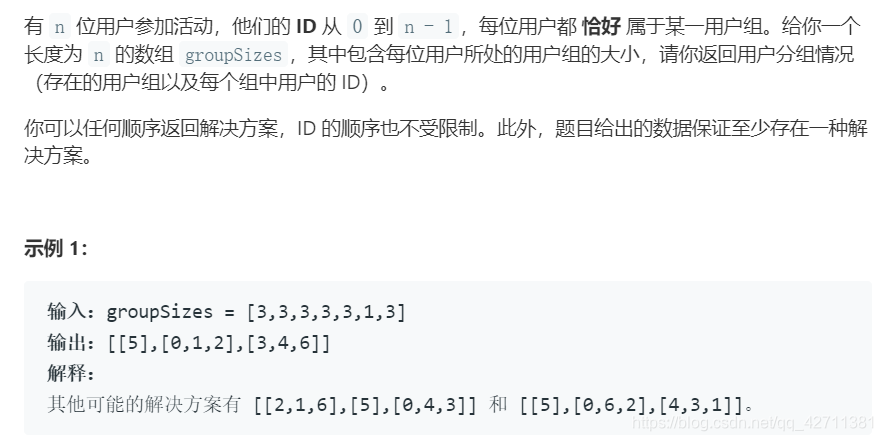
1282. 用户分组
思路:
相同组大小的先放到一起,然后再根据组大小进行切割。
from collections import defaultdict
class Solution:
def groupThePeople(self, groupSizes):
res = defaultdict(list)
r = []
# 组大小相同的放在一起
for ind, group in enumerate(groupSizes):
res[group].append(ind)
# 根据组的大小进行切割
for k, v in res.items():
r += [v[i-k:i] for i in range(1, len(v)+1) if i % k == 0]
return sorted(r, key=lambda x:len(x))
1296. 划分数组为连续数字的集合
"""
通过频率来判断是否可以划分
"""
from collections import Counter
class Solution:
def isPossibleDivide(self, nums, k: int) -> bool:
# d记录所有数字出现频率
d = Counter(nums)
if len(nums) % k:
return False
for i in sorted(nums):
if d[i] <= 0:
continue
for j in range(k):
if i+j not in d or d[i+j] <= 0:
return False
d[i+j] -= 1
return True
1297. 子串的最大出现次数 - 滑动窗口
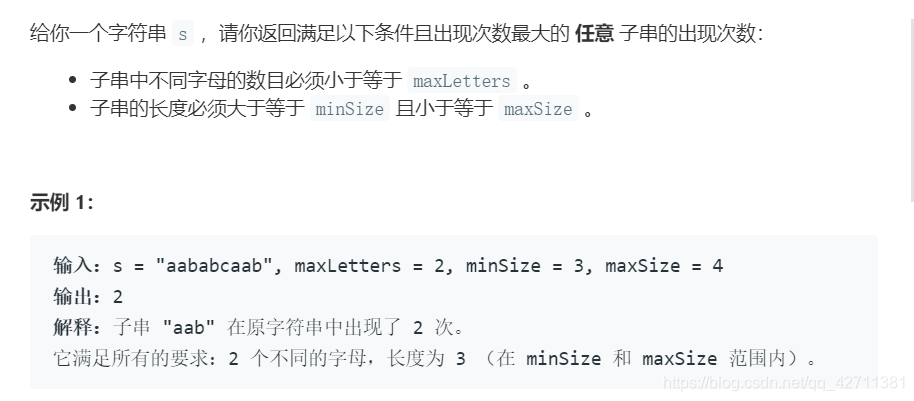
思路:
滑动窗口,窗口大小为minSize。maxSize完全就是一个迷惑项,因为但是maxSize长度的子串出现的地方,minSize长度子串必然出现,反之却不是。
from collections import Counter
class Solution:
def maxFreq(self, s: str, maxLetters: int, minSize: int, maxSize: int) -> int:
res = []
# 先把符合条件的全部搜集起来
for i in range(0, len(s)-minSize+1):
ts = s[i:i+minSize]
if len(set(ts)) > maxLetters:
continue
else:
res.append(ts)
if not res:
return 0
# 返回出现次数最多的
return sorted(Counter(res).items(), key=lambda x:x[1], reverse=True)[0][1]
来源:https://www.cnblogs.com/NFii/p/12365345.html