集合–Collection
集合是长度可变的容器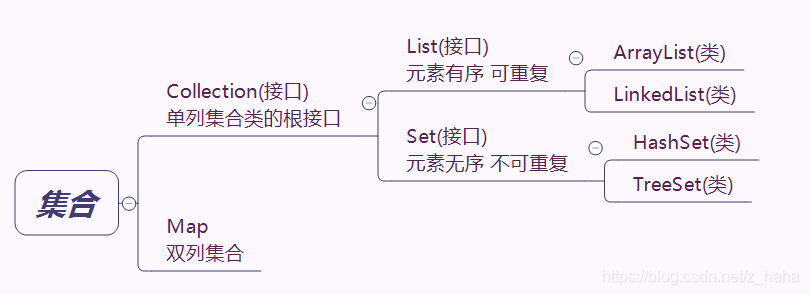
Collection 使用示例
public static void main(String[] args) {
//Collection是所有单列集合的父接口
//因此在Collection中定义了单列集合(List和Set)通用的一些方法
//这些方法可用于操作所有的单列集合
//创建集合
Collection<String> collection = new ArrayList<>();
//添加元素
collection.add("test1");
collection.add("test2");
System.out.println(collection);
//判断元素是否在集合内
boolean if_contain = collection.contains("test1");
if(if_contain == true){
System.out.println("test1存在于集合中");
}
//删除集合中的元素
collection.remove("test1");
System.out.println(collection);
//查看集合中的元素个数
System.out.println("元素个数: " + collection.size());
//将集合转换为Obeject数组
Object[] objects = collection.toArray();
for(int i = 0;i<objects.length;++i){
System.out.println(objects[i]);
}
//清空集合
collection.clear();
//判断集合是否为空
boolean if_empty = collection.isEmpty();
if(if_contain == true){
System.out.println("集合为空");
}
}
输出结果
Iterator迭代器
顾名思义,主要是用来遍历元素的
使用示例
public static void main(String[] args) {
//创建集合
Collection<String> collection = new ArrayList<>();
//添加元素
collection.add("test1");
collection.add("test2");
//构造迭代器
//迭代器的泛型是取出来的元素的类型
Iterator<String> iterator = collection.iterator();
//遍历元素
while(iterator.hasNext()){
String string = iterator.next();
System.out.println(string);
}
}
输出结果
注意迭代器在使用第一个next之前,索引的地方是在第0个元素之前
遍历元素也可以使用增强版的for循环
结构
for(数据类型 变量 : 集合/数组){
}
使用示例
public static void main(String[] args) {
//创建迭代器
Collection<String> collection = new ArrayList<>();
//添加元素
collection.add("test1");
collection.add("test2");
for(String str : collection){
System.out.println(str);
}
}
输出结果
泛型的使用
泛型类和泛型方法的使用
public class test_class<TEST> {
//这里的TEST表示任意类型都可以
public TEST a;
public void Set(TEST test){
this.a = test;
}
public TEST Get(){
return a;
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
test_class<String> stringtest_class = new test_class<String>();
stringtest_class.Set("ceshi");
System.out.println(stringtest_class.Get());
}
输出结果
泛型接口的使用
public interface test_interface<T> {
public abstract T fun();
}
- 定义类时确定类型
public class test_class implements test_interface<String> {
@Override
public String fun(String str) {
return str;
}
}
- 在创建对象时确定类型
public class test_class<T> implements test_interface<T> {
@Override
public T fun(T t) {
return t;
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
test_class<String> str = new test_class<>();
System.out.println(str.fun("ceshi"));
}
当不知道使用什么类型来接受数据的时候可以使用通配符接收数据
通配符也可以用来设置泛型的上限和下限
类型名称 <? extends 某类 > 对象名称
只接收某类及其子类
类型名称 <? super 某类 > 对象名称
只接收某类及其基类
使用示例
public class Main {
//可接受任意
public static void test(Collection <?> collection){}
//可接受Number及其子类
public static void test_extends(Collection<? extends Number> collection){}
//可接受Number及其基类
public static void test_super(Collection<? super Number> collection){}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Collection<Integer> integers = new ArrayList<>();
Collection<Number> numbers = new ArrayList<>();
Collection<String> strings = new ArrayList<>();
test(integers);
test(numbers);
test(strings);
//Number是Integer的基类
test_extends(integers);
test_extends(numbers);
test_extends(strings);//报错
test_super(integers);//报错
test_super(strings);//报错
test_super(numbers);
}
}
来源:CSDN
作者:z_haha
链接:https://blog.csdn.net/z_haha/article/details/104403668