搜索:
BFS:广度优先
每一层遍历的节点都与根节点距离相同。设 di 表示第 i 个节点与根节点的距离,推导出一个结论:对于先遍历的节点 i 与后遍历的节点 j,有 di <= dj。利用这个结论,可以求解最短路径等 最优解 问题:第一次遍历到目的节点,其所经过的路径为最短路径。应该注意的是,使用 BFS 只能求解无权图的最短路径。
在程序实现 BFS 时需要考虑以下问题:
- 队列:用来存储每一轮遍历得到的节点;
- 标记:对于遍历过的节点,应该将它标记,防止重复遍历。
1) 每一层遍历的节点都与根节点距离相同:决定了什么时候path++:就是每遍历一层之前保留queue.size,这个size就是这一层的大小
2) 什么时候置flag?已经从队列中poll了之后
3) 最优解问题:因为每次遍历的都是和根节点距离相同的节点,所以最先到达终点的一定是最短路径
1091. 二进制矩阵中的最短路径(m)(经典BFS+visited)
重点:注意只有{0}一个数的情况
public int shortestPathBinaryMatrix(int[][] grid) {
if(grid[0][0]==1 || grid[grid.length-1][grid[0].length-1]==1)
return -1;
if (grid.length == 1 && grid[0][0] == 0) {
return 1;
}
// 顺时针
int[][] xOy = {{-1,0},{-1,-1},{0,-1},{1,-1},{1,0},{1,1},{0,1},{-1,1}};
// int[][] xOy = {{1, 0}, {1, 1}, {1,-1}, {0, 1}, {0, -1}, {-1, 0},{-1, -1}, {-1, 1}};
int n = grid.length;
boolean[][] visited = new boolean[n][n];
visited[0][0] = true;
Queue<int[]> queue = new LinkedList<>();
queue.add(new int[] {0,0});
int pathLength = 0;
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
// 这一层节点的个数
int size = queue.size();
pathLength++;
while (size-- > 0) {
int[] node = queue.poll();
int x = node[0];
int y = node[1];
// grid[x][y] = 1;
for (int[] d : xOy) {
int nx = x + d[0];
int ny = y + d[1];
if (nx == n-1 && ny == n-1) {
return pathLength+1;
}
if (nx < 0 || nx >= n || ny < 0 || ny >= n || visited[nx][ny] || grid[nx][ny] == 1){
continue;
}
visited[nx][ny] = true;
queue.add(new int[] {nx,ny});
}
}
}
return -1;
}
279. 完全平方数(m)
思路:
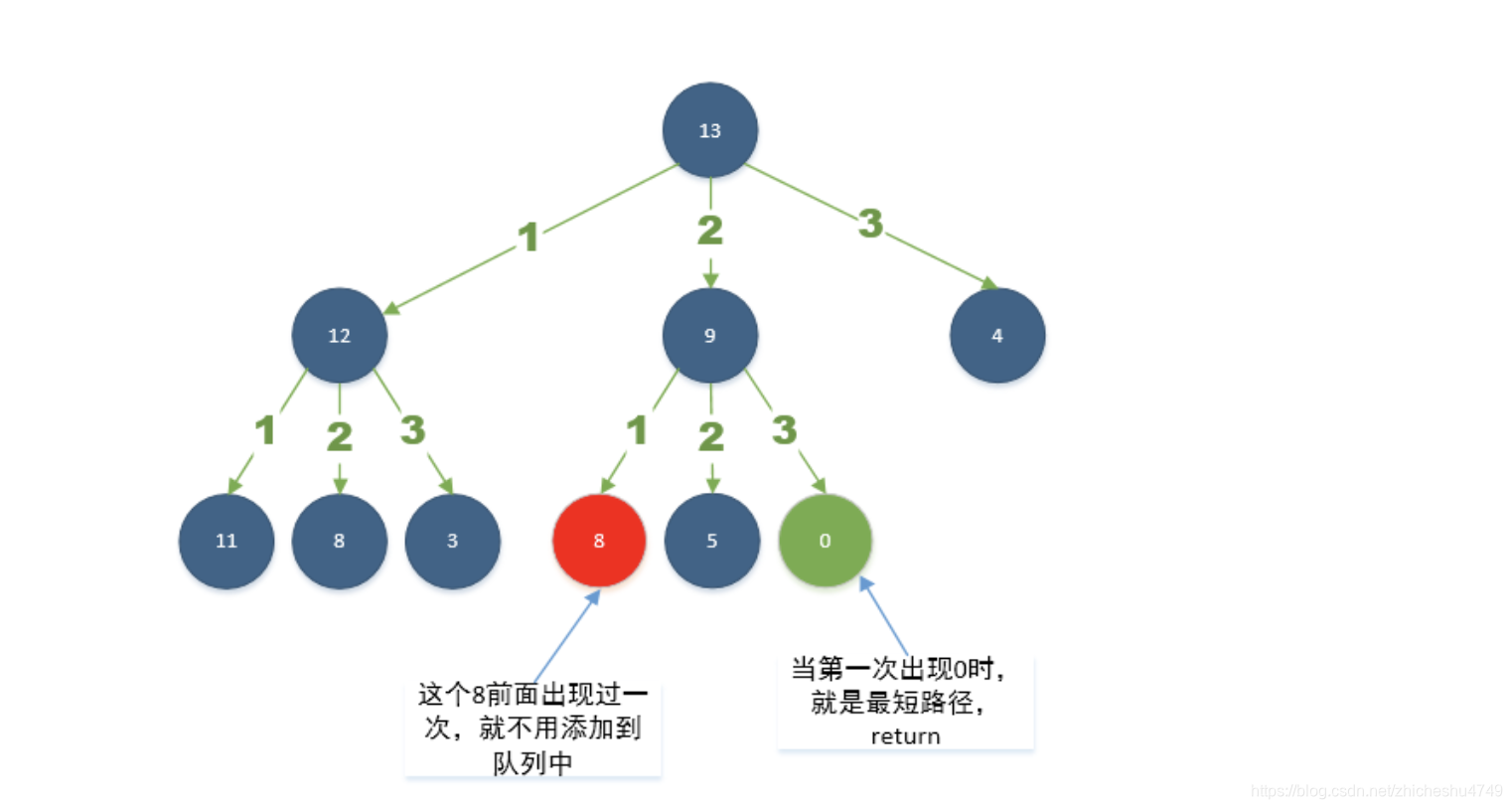
可以将每个整数看成图中的一个节点,如果两个整数之差为一个平方数,那么这两个整数所在的节点就有一条边。
要求解最小的平方数数量,就是求解从节点 n 到节点 0 的最短路径。
本题也可以用动态规划求解,在之后动态规划部分中会再次出现。
完全平方数的规律:1,4,9,16.。。中间刚好相差(3,5,7,9....),即n^2-(n-1)^2 = 2n-1
public int numSquares(int n) {
List<Integer> list = generateSquares(n);
Queue<Integer> queue = new LinkedList<>();
boolean[] visited = new boolean[n+1];
queue.add(n);
visited[n] = true;
int level = 0;
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
int size = queue.size();
level++;
while (size-- > 0) {
int cur = queue.poll();
for (int i: list
) {
int next = cur - i;
// 因为LinkedList是按顺序读,我们存的时候就是(1,4,9...)
if (next < 0) {
break;
}
if (next == 0) {
return level;
}
visited[next] = true;
queue.add(next);
}
}
}
return n;
}
/**
* 生成小于 n 的平方数序列
* @return 1,4,9,...
*/
private List<Integer> generateSquares(int n) {
List<Integer> squares = new ArrayList<>();
int square = 1;
int diff = 3;
while (square <= n) {
squares.add(square);
square += diff;
diff += 2;
}
return squares;
}
127. 单词接龙(m)(重点!!)
重点:
1. 如何比较两个String中是不是有一位字符不同?
所以需要建立一个图(graph),单词是节点,如果两个单词之间只有一位不同则有一条边
2. 如何做visited[]标记数组?因为wordList中是String类型,如何按下标记录标记?
建立graph的时候使用下标而不是单词作为节点
public int ladderLength(String beginWord, String endWord, List<String> wordList) {
if (!wordList.contains(endWord)) {
return 0;
}
// 便于建图
wordList.add(beginWord);
// Queue<String> queue = new LinkedList<>();
Queue<Integer> queue = new LinkedList<>();
List<Integer>[] graph = buildGraph(wordList);
int n = wordList.size();
boolean[] visited = new boolean[n+1];
int end = 0;
for (int i = 0 ; i < wordList.size() ;i ++) {
if (!endWord.equals(wordList.get(i))) {
end++;
}
else {
break;
}
}
queue.add(n-1);
visited[n-1] = true;
int step = 0;
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
int size = queue.size();
step++;
while (size-- > 0) {
int cur = queue.poll();
// graph[cur]是个list<Integer>
for (int next : graph[cur]) {
if (next == end) {
return step+1;
}
if (visited[next]) {
continue;
}
visited[next] = true;
queue.add(next);
}
}
}
return 0;
}
public boolean isConnected(String s1,String s2) {
int diffCnt = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < s1.length() && diffCnt <= 1; i++) {
if (s1.charAt(i) != s2.charAt(i)) {
diffCnt++;
}
}
return diffCnt == 1;
}
public List<Integer>[] buildGraph(List<String> wordList) {
int n = wordList.size();
List<Integer>[] graph = new List[n];
for (int i = 0 ; i < n ; i++) {
graph[i] = new LinkedList<>();
for (int j = 0 ; j < n; j++) {
if (isConnected(wordList.get(i),wordList.get(j))) {
graph[i].add(j);
}
}
}
return graph;
}
DFS(深度优先)
从一个节点出发,使用 DFS 对一个图进行遍历时,能够遍历到的节点都是从初始节点可达的,DFS 常用来求解这种 可达性 问题。
在程序实现 DFS 时需要考虑以下问题:
- 栈:用栈来保存当前节点信息,当遍历新节点返回时能够继续遍历当前节点。可以使用递归栈。
- 标记:和 BFS 一样同样需要对已经遍历过的节点进行标记。
695. 岛屿的最大面积(m)
重点:为了方便起见,本题没有采用visited数组,而是直接将遍历过的置为0。注意找到什么情况需要恢复visited数组,什么情况不需要(本题不需要,剑指offer66题机器人路径规划也不需要),像剑指offer中65题找矩阵中的路径就需要(因为是要找序列)
int[][] direction = {{0,1},{0,-1},{1,0},{-1,0}};
public int maxAreaOfIsland(int[][] grid) {
if (grid == null || grid.length <= 0) {
return 0;
}
// 几行
int m = grid.length;
// 几列
int n = grid[0].length;
int maxArea = 0;
for (int i = 0 ; i < m ; i++) {
for (int j = 0 ; j < n; j++) {
maxArea = Math.max(maxArea,dfs(grid,i,j));
}
}
return maxArea;
}
private int dfs(int[][] grid, int i, int j) {
if (i < 0 || i >= grid.length || j < 0 || j >= grid[0].length || grid[i][j] == 0) {
return 0;
}
// 本来应该是visited数组来标记,但是这里为了方便直接将访问过的置为0
grid[i][j] = 0;
int area = 1;
for (int[] d : direction) {
area += dfs(grid,i+d[0],j+d[1]);
}
return area;
}
来源:CSDN
作者:Nicole_sss
链接:https://blog.csdn.net/zhicheshu4749/article/details/104259877