1、实例,原型对象,构造函数之间的关系
如图:借用__proto__一级一级实现原型链(一般最后为Object.prototype.__proto__ = null)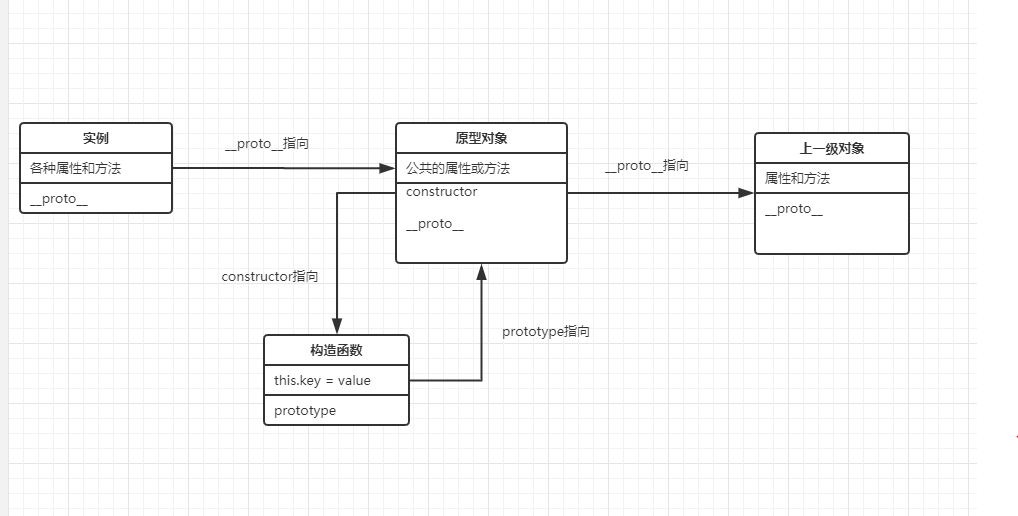
2、原型链继承:将父类构造函数的实例变成子类的原型
代码:
<script>
function Parent() {
this.parentName = 'zzz';
}
Parent.prototype.getParent = () => {
return 'parent'
};
function Child() {
this.childName = '233';
}
Child.prototype = new Parent();
Child.prototype.getChild = () => {
return 'Child'
};
let child = new Child();
console.log(child);
</script>
结构如下: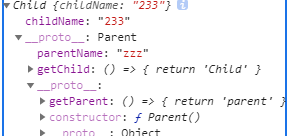
作用:父类的方法和属性存在于原型两种,可以调用;缺点:父类中存在引用类型时,原型链调用会共享一个引用类型
2、es6语法实现继承
代码:
<script>
class Parent {
constructor() {
this.parentName = 'zzz';
}
getParent() {
return 'parent';
}
}
class Child extends Parent {
constructor() {
super(); //调用父类
this.childName = '233';
}
getChild() {
return 'child';
}
}
let child = new Child();
console.log(child);
</script>
结构如下:
作用:方法存在于原型链中,构造函数定义的实例属性被复制到子类中
修改代码为:
<script>
class Parent {
constructor() {
this.parentName = {
name: 'parentname',
age: {
number: 22
}
}
}
getParent() {
return 'parent';
}
}
class Child extends Parent {
constructor() {
super(); //调用父类
this.childName = '233';
}
getChild() {
return 'child';
}
}
let parent = new Parent();
let child = new Child();
parent.parentName.age.number = 2020;
console.log(parent);
console.log(child);
</script>
得出结果为:引用类型的复制为深拷贝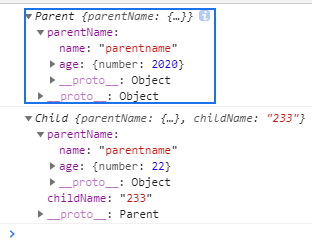
3、利用call,apply的构造函数式继承
代码:
function Child() {
Parent.call(this);
this.childName = '233';
}
结构如下: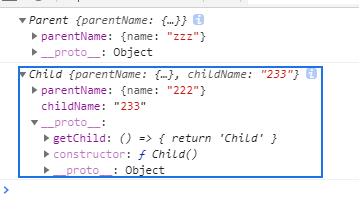
作用:
会继承父类构造函数里的属性和方法,但不会继承父类的原型中的属性和方法
4、组合继承(混合原型链继承和构造函数继承)
关键代码:
function Child() {
Parent.call(this);
this.childName = '233';
}
Child.prototype = new Parent();
作用:会继承父类及父类原型上的属性方法,缺点是调用了两次构造函数
5、寄生式组合继承
关键代码:
function objectCreate(obj) {
function F() {};
F.prototype = obj;
return new F();
} //寄生
function Child() {
Parent.call(this);
this.childName = '233';
}
Child.prototype = objectCreate(Parent.prototype);
Child.prototype.constructor = Child;
作用:解决组合式继承两次调用的问题
来源:https://www.cnblogs.com/Zxq-zn/p/12289779.html