| 作业描述 | 详情 |
|---|---|
| 这个作业属于哪个课程 | 2020年面向对象程序设计 |
| 这个作业要求在哪 | 面向对象程序设计寒假作业2 |
| 这个作业目标 | 1. 使用git,建立github仓库 2.优化架构 3.优化命名规范 4.制作编译脚本 5.进行单元测试 6.添加功能 |
| 作业正文 | 博客地址 |
| 其他参考文献 | Python基础之os.system函数 C++ main()函数及其参数 C++中头文件(.h)和源文件(.cpp)的编写 代码命名 Git忽略提交 git教程 |
实践题
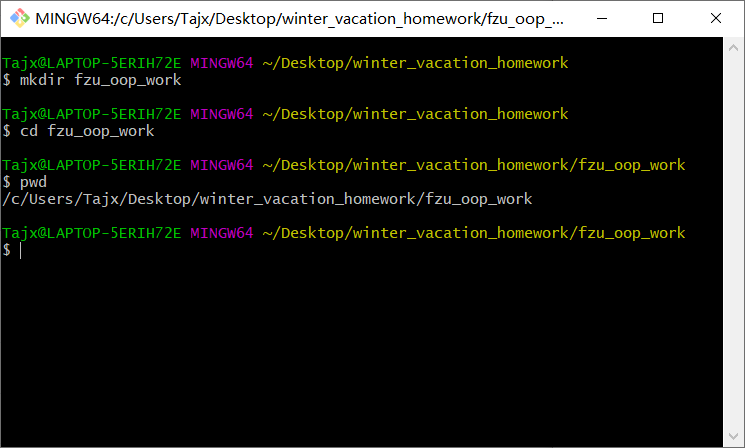
新建一个github仓库,使用git,或者github desktop把接下去的编程题的代码及测试脚本传到这个仓库。
请使用.gitignore文件忽略不要上传的文件。用法自行百度。
- 根据廖老师的教程进行安装git
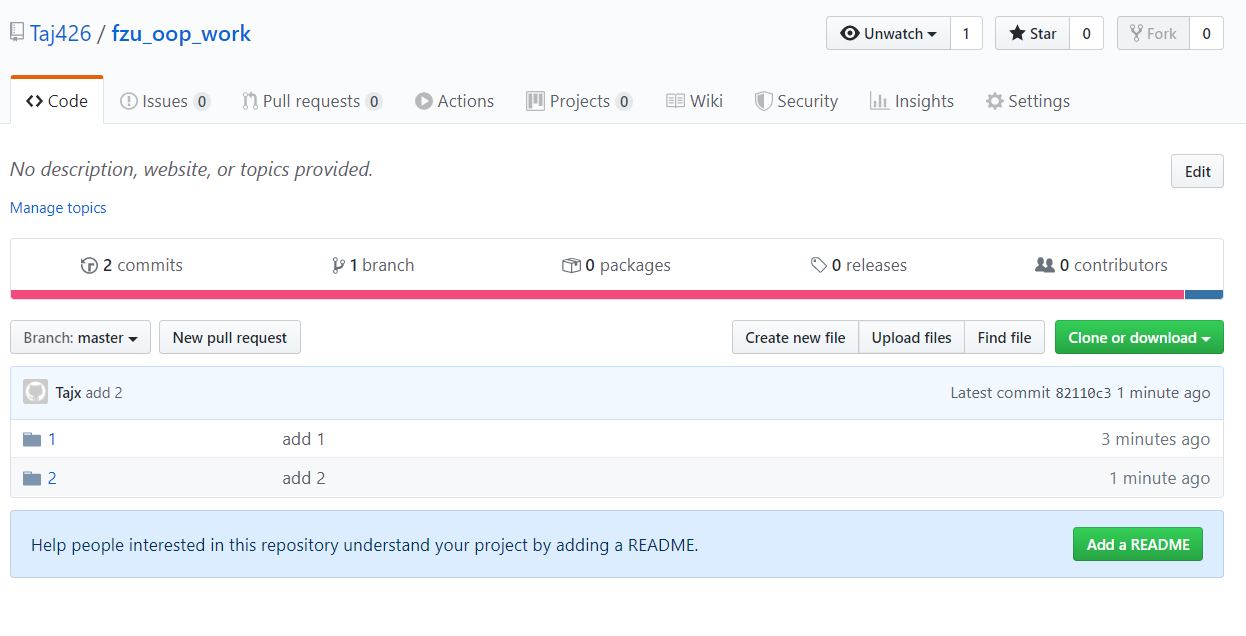
- 在github上创建仓库fzu_oop_work
- 在本地创建代码仓库

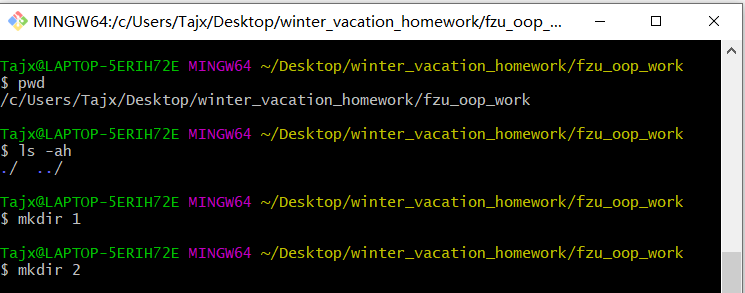
- 创建子目录1,2,分别上传上次和本次的作业

- git add . 提交该目录下的所以文件到暂存区,在git commit -m “”
- 编写.gitignore并提交
- 关联远程库
- git push推送到远程

编程题
继续完成作业一的编程题。
优化架构,一般要求每个函数长度不超过15行。
优化规范,尤其是命名规范。
制作一个编译脚本,运行该脚本可以编译你的代码,可选的脚本语言,python(2.7),windows批处理,powershell,shell。
进行单元测试,即测试每一个函数,并制作一个测试脚本,运行该脚本可以进行测试,并显示测试结果。
在作业一编程题的基础上添加以下功能:
- 通过命令行读取一个文件,然后运行这个文件。如我的程序叫lang,
lang 1.txt代表我要运行1.txt这个文本中的代码。 - 假设我的
1.txt内容如下:
整数 钱包 等于 零 钱包 增加 四 钱包 减少 三 看看 钱包
- 输入
lang 1.txt后,命令行输出一。
- 通过命令行读取一个文件,然后运行这个文件。如我的程序叫lang,
一开始对于变量如何存储不太懂,后面向某位廖姓大佬请教后,发现可以直接写一个变量类来搞
- 分为3个类,变量库,数字库,以及主体部分加一个异常处理函数
优化了架构(个人觉得)
头文件(main.h)
#ifndef LANG_H
#define LANG_H
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
class VarRepository {
public:
std::map<std::string, int>var;
bool IsExist(std::string name);
void Create(std::string name, int val);
void Add(std::string name, int val);
void Reduce(std::string name, int val);
};//存储变量
class NumRepository {
private:
std::string base_num[11] = {"零", "一", "二", "三", "四", "五", "六", "七", "八", "九", "十"};
public:
std::map<std::string, int>chs2num;
std::map<int, std::string>num2chs;
void MakeTable();
};//生成映射表
class Body {
public:
VarRepository Var;
NumRepository Num;
std::string part[5];
int cnt;
void Look(std::string name);
bool Parse(std::string line);
void Clear();
int GetNum(std::string num);
void Choose();
void Define();
void Add();
void Reduce();
};//进行语句解析及后续操作
void Exception(int type);
#endif
异常处理(Exception.cpp)
与上次基本一样,只是放在另一个cpp文件中
#include "main.h"
void Exception(int types) {
if (types == 1)
puts("请正确输入指令");
else if (types == 2)
puts("请勿重复定义相同的变量名");
else if (types == 3)
puts("请输入正确的数字");
else if (types == 4)
puts("这玩意还没被定义过");
else if (types == 5)
puts("请不要用关键词作为变量名");
else if (types == 6)
puts("相加的数字过大");
else if (types == 7)
puts("相减的数字过大");
}
变量库(VarRepository.cpp)
用map容器进行存储,实现多变量
#include "main.h"
bool VarRepository::IsExist(std::string name) {
return var.count(name) != 0;
}
void VarRepository::Create(std::string name, int val) {
if (IsExist(name)) {
Exception(2);
return ;
}
if (name == "看看" || name == "增加" || name == "减少" || name == "整数") {\
Exception(5);
return ;
}
var[name] = val;
}
void VarRepository::Add(std::string name, int val) {
int now = var[name];
now += val;
if (now > 99) {
Exception(6);
return ;
}
var[name] = now;
}
void VarRepository::Reduce(std::string name, int val) {
int now = var[name];
now -= val;
if (now < 0) {
Exception(7);
return ;
}
var[name] = now;
}
数字库(NumRepository.cpp)
#include "main.h"
void NumRepository::MakeTable() {
for (int i = 0; i <= 10; ++i)
chs2num[base_num[i]] = i; // deal with 0 ~ 10
for (int i = 1; i <= 9; ++i) {
std::string a = base_num[10];
a += base_num[i];
chs2num[a] = 10 + i;
}// deal with 11 ~ 19
for (int i = 2; i <= 9; ++i) {
std::string a = base_num[i];
a += base_num[10];
chs2num[a] = i * 10;
}// deal with multiples of 10
for (int i = 2; i <= 9; ++i) {
std::string a = base_num[i];
a += base_num[10];
int num = i * 10;
for (int j = 1; j <= 9; ++j)
chs2num[a + base_num[j]] = num + j;
}
for (auto it : chs2num) {
num2chs[it.second] = it.first;
}// deal with num to chs
}
主体(body.cpp)
#include "main.h"
void Body::Look(std::string name) {
if (!Var.IsExist(name)) {
Exception(4);
return ;
}
std::cout << Num.num2chs[Var.var[name]] << "\n";
}
bool Body::Parse(std::string line) {
for (int i = 0; i < line.length(); ++i) {
if (line[i] != ' ') {
while(line[i] != ' ' && i < line.length()) {
part[cnt] += line[i];
i++;
}
cnt++;
}
}
if (cnt <= 1) {
Exception(1);
return false;
}
return true;
}
void Body::Clear() {
cnt = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < 5; ++i)
part[i] = "";
}
int Body::GetNum(std::string num) {
if (Num.chs2num.count(num))
return int(Num.chs2num[num]);
return -1;
}
void Body::Define() {
int GetedNum = GetNum(part[3]);
if (GetedNum == -1) {
Exception(3);
return ;
}
Var.Create(part[1], GetedNum);
}
void Body::Add() {
if (cnt != 3) {
Exception(1);
return ;
}
if (!Var.IsExist(part[0])) {
Exception(4);
return ;
}
int GetedNum = GetNum(part[2]);
if (GetedNum == -1) {
Exception(3);
return ;
}
Var.Add(part[0], GetedNum);
}
void Body::Reduce() {
if (cnt != 3) {
Exception(1);
return ;
}
if (!Var.IsExist(part[0])) {
Exception(4);
return ;
}
int GetedNum = GetNum(part[2]);
if (GetedNum == -1) {
Exception(3);
return ;
}
Var.Reduce(part[0], GetedNum);
}
void Body::Choose() {
if (part[0] == "整数")
Define();
else if (part[0] == "看看")
Look(part[1]);
else if (part[1] == "增加")
Add();
else if (part[1] == "减少")
Reduce();
else
Exception(1);
}
主函数(main.cpp)
#include "main.h"
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
if (argc != 1) {
freopen(argv[1], "r", stdin);
}
std::string s;
Body my;
my.Clear();
my.Num.MakeTable();
while(std::getline(std::cin, s)) {
if (my.Parse(s)) {
my.Choose();
my.Clear();//每次操作后要对part, cnt 进行清空
}
}
return 0;
}
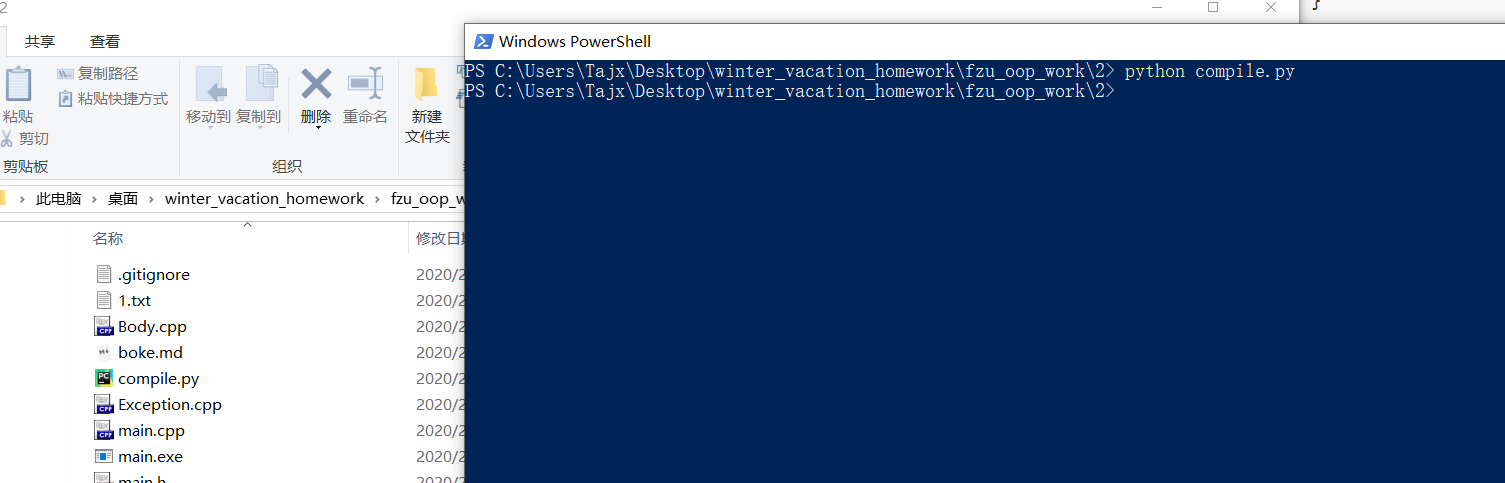
编译脚本(compile.py)
py下的os.system()函数就相当于命令行
在编译过程中,单独编译一个main.cpp 老是报错,一直以为编译器会默认在当前目录下寻找其他相关联的.cpp,结果发现我还是naive啊。
查阅资料后,应该在编译时将相关的.cpp一起编译, 文件输入的先后无影响
脚本代码如下:
import os
file = 'Body.cpp Exception.cpp main.cpp NumRepository.cpp VarRepository.cpp'
os.system('g++ -o main -std=c++11 ' + file)
编译结果:
编译成功,无返回值,目录有main.exe生成
单元测试(test.py)
通过编译test.cpp 等文件来实现
仅仅验证了数字表是否正确。。。
#include "main.h"
Body my;
void CheckChs2Num() {
if (my.Num.chs2num["十"] == 10)
std::cout << "pass\n";
else
std::cout << "error\n";
if (my.Num.chs2num["二十"] == 20)
std::cout << "pass\n";
else
std::cout << "error\n";
if (my.Num.chs2num["零"] == 00)
std::cout << "pass\n";
else
std::cout << "error\n";
if (my.Num.chs2num["五十五"] == 55)
std::cout << "pass\n";
else
std::cout << "error\n";
if (my.Num.chs2num["二十三"] == 23)
std::cout << "pass\n";
else
std::cout << "error\n";
if (my.Num.chs2num["十七"] == 17)
std::cout << "pass\n";
else
std::cout << "error\n";
}
void CheckNum2Chs() {
if (my.Num.num2chs[11] == "十一")
std::cout << "pass\n";
else
std::cout << "error\n";
if (my.Num.num2chs[21] == "二十一")
std::cout << "pass\n";
else
std::cout << "error\n";
if (my.Num.num2chs[17] == "十七")
std::cout << "pass\n";
else
std::cout << "error\n";
if (my.Num.num2chs[30] == "三十")
std::cout << "pass\n";
else
std::cout << "error\n";
if (my.Num.num2chs[50] == "五十")
std::cout << "pass\n";
else
std::cout << "error\n";
if (my.Num.num2chs[63] == "六十三")
std::cout << "pass\n";
else
std::cout << "error\n";
}
int main() {
my.Num.MakeTable();
my.Clear();
std::cout << "Now is checking num2chs\n";
CheckNum2Chs();
std::cout << "check end\n";
std::cout << "Now is checking chs2num\n";
CheckChs2Num();
std::cout << "check end";
system("pause");
return 0;
}
import os
file = 'Body.cpp Exception.cpp test.cpp NumRepository.cpp VarRepository.cpp'
os.system('g++ -o test -std=c++11 ' + file)
os.system('test.exe')
os.system('del test.exe')
测试结果: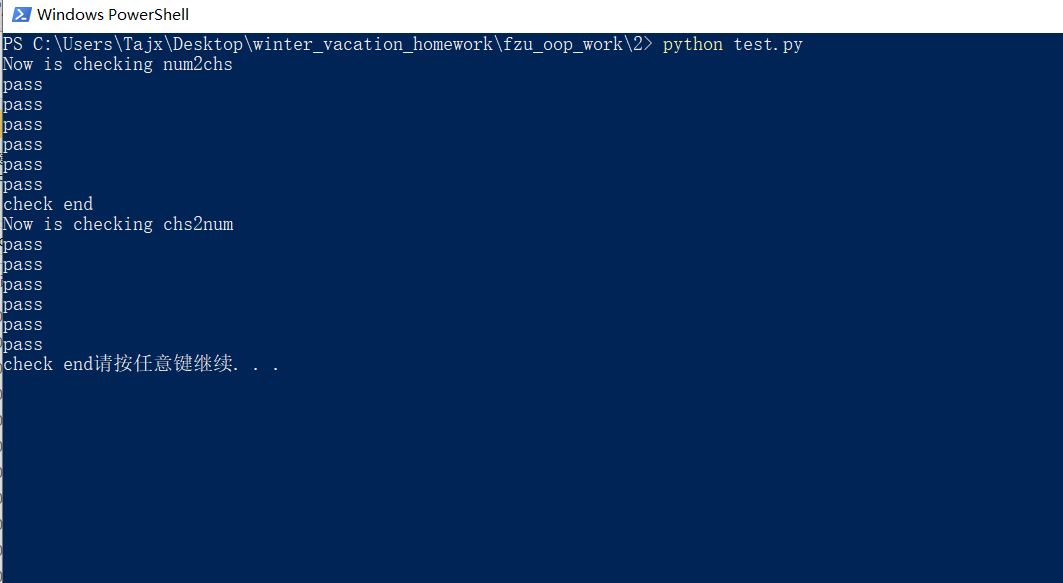
添加功能
命令行的指令会被保留在argv[]里面,如果输入指令main 1.txt,那么argv[1] = '1.txt',基于这个方法,就可以简单的获得文件名,再用freopen()来实现从特定文件中读取文本(代码)
具体实现代码在(main.cpp)中,可以在上面看到,前提是已经编译好main.cpp并且有main.exe文件,给出测试结果:
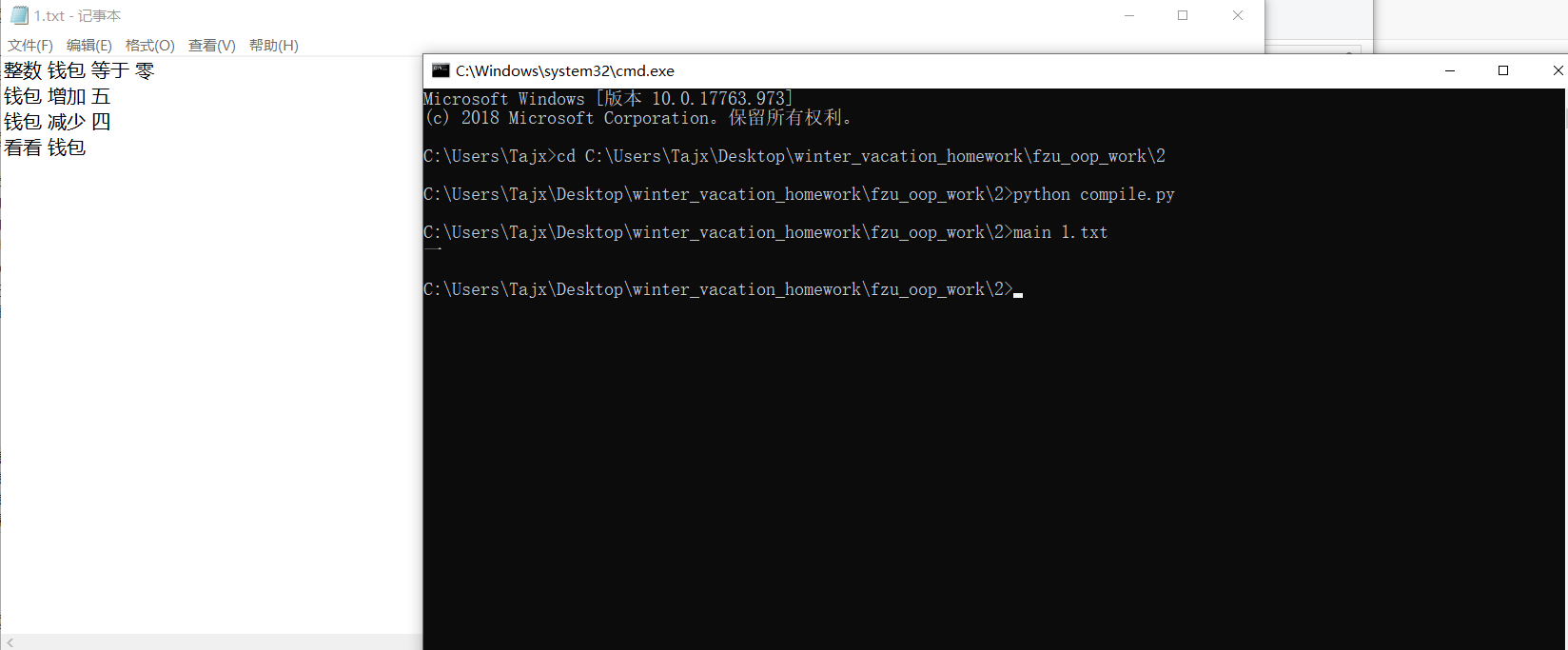
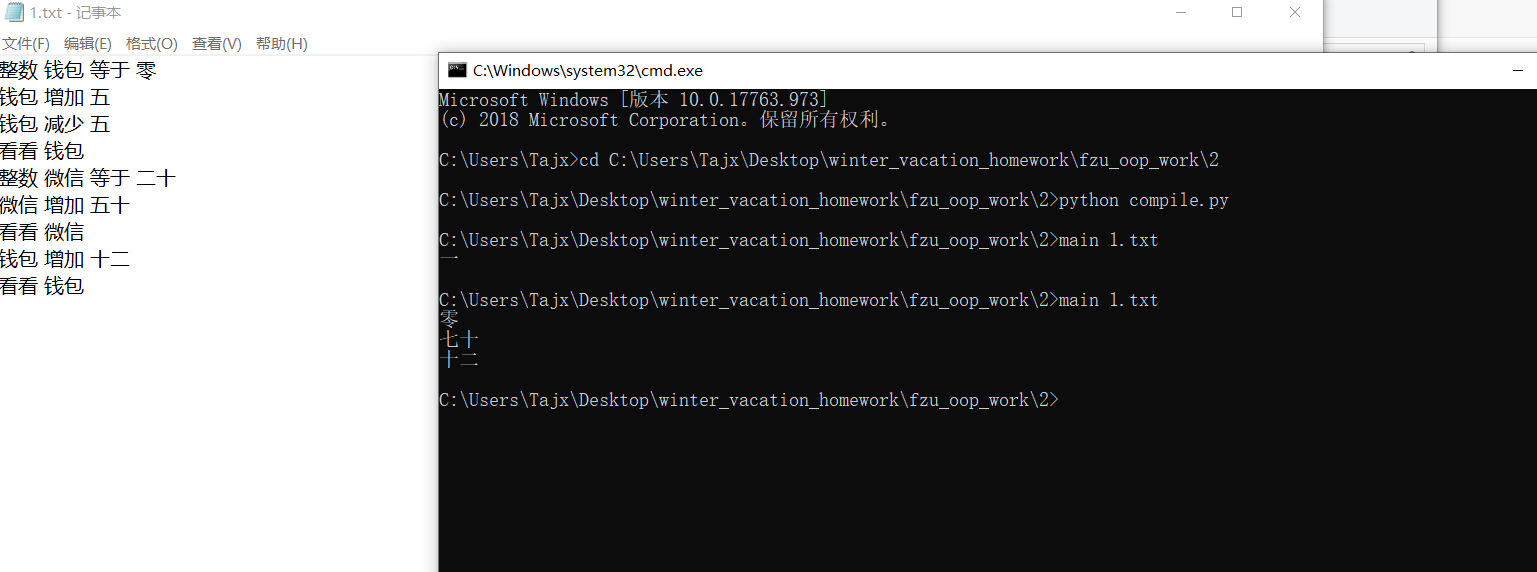
总结
真t喵的累,学的东西也挺多的,摸了摸了。。。
来源:https://www.cnblogs.com/Tajx/p/12250239.html