你好! 这是我第三天学习 JAVA编程 所整理的一些内容。如果你想学习JAVA编程, 可以仔细阅读这篇文章,了解一下JAVA的switch-for-while-Random。
1.三种循环格式的用法
基本格式
for(初始化语句;判断条件语句;控制条件语句) {
循环体语句;
}
while(判断条件语句) {
循环体语句;
}
do {
循环体语句;
}while((判断条件语句);
continue 忽略一次循环
break 打破循环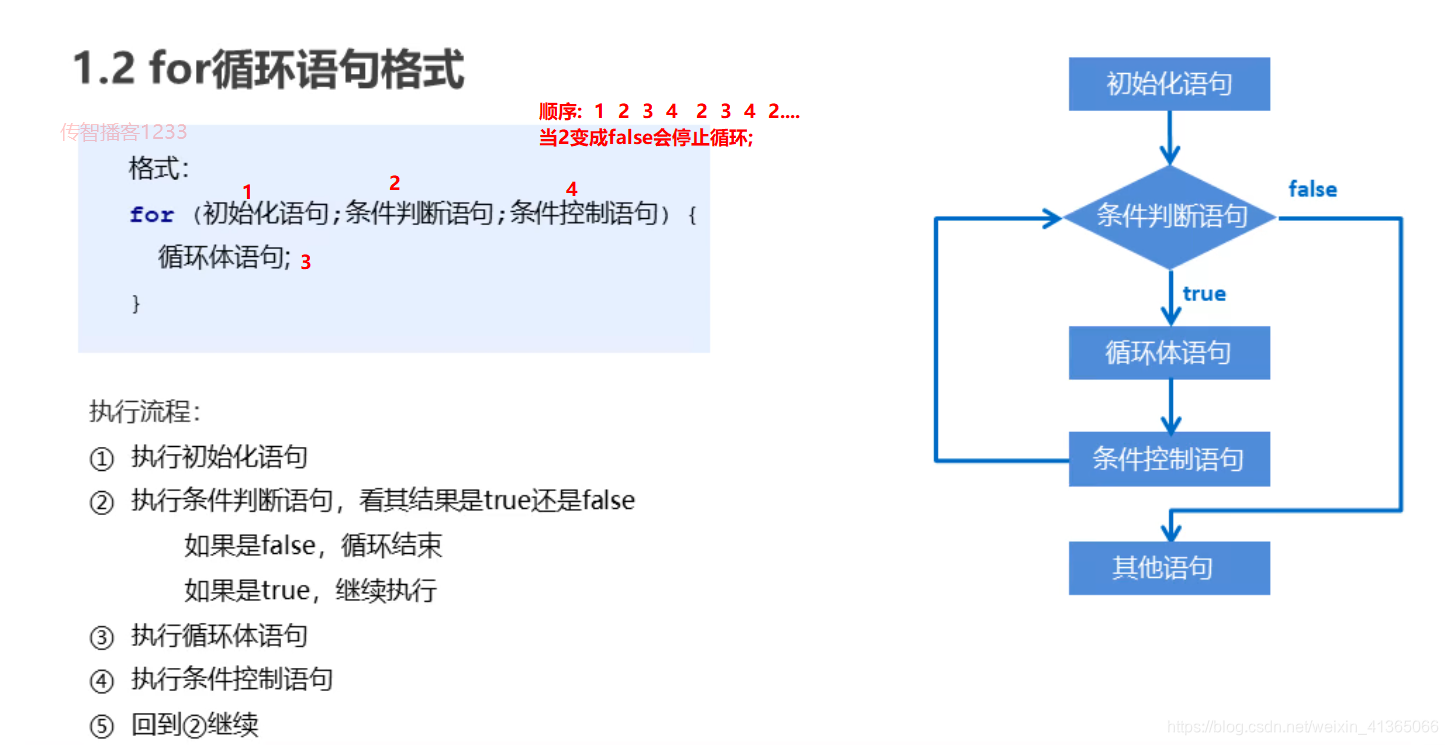

//code3 五次helloworld
//for循环中条件判断语句比其他部分多一次 没有明确循环次数用while
//for循环版
for(int x=1;x<11;x++){
System.out.println("第"+x+"次刘清波");
}
//while版
int i=1;
while(i<=5){
System.out.println("我爱JAVA");
i++;
}
//do...while循环版 (不常用)
int x=0;
do{
System.out.println("HelloWorld");
x++;
}while(x<5);
//code7 水仙花for循环版
int count=0;
for (int x = 100; x < 1000; x++) {
int ge = x % 10;
int shi = x / 10 % 10;
int bai = x / 100 % 10;
if ((ge * ge * ge + shi * shi * shi + bai * bai * bai) == x) {
count++;
System.out.print("水仙花数是:"+x+"\t");
}
}
System.out.println("水仙花数一共有:"+count+"个");
//水仙花while循环版
int count = 0;
int x=100;
while(x>99&&x<1000){
int ge = x % 10;
int shi = x / 10 % 10;
int bai = x / 100 % 10;
if ((ge * ge * ge + shi * shi * shi + bai * bai * bai) == x) {
count++;
System.out.print("水仙花数是:"+x+"\t");
}
x++;
}
System.out.println("水仙花的个数是:"+count);
//code7 end
//code8 珠穆朗玛峰while版
int mount = 8844430;
double paper = 0.1;
int count = 0;
while(paper<=mount){
paper*=2;
count++;
}
System.out.println("需要对折"+count+"次");
//珠穆朗玛峰for循环版
int mount = 8844430;
double paper = 0.1;
int count = 0;
for(;paper<=mount;paper*=2){
count++;
}
System.out.println("需要对折"+count+"次");
//code8 end
2.switch概述
switch表示这是switch语句
表达式的取值:byte,short,int,char
JDK5以后可以是枚举
JDK7以后可以是String
case后面跟的是要和表达式进行比较的值
语句体部分可以是一条或多条语句
break表示中断,结束的意思,可以结束switch语句
default语句表示所有情况都不匹配的时候,就执行该处的内容,和if语句的else相似。
执行流程
首先计算出表达式的值
其次,和case依次比较,一旦有对应的值,就会执行相应的语句,在执行的过程中,遇到break就会结束。
最后,如果所有的case都和表达式的值不匹配,就会执行default语句体部分,然后程序结束掉。
//code 1:
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("请输入一个(0~7)的数字:");
int week = sc.nextInt();
switch(week){
case 1:
System.out.print("星期一");
break;
case 2:
System.out.print("星期二");
break;
case 3:
System.out.print("星期三");
break;
case 4:
System.out.print("星期四");
break;
case 5:
System.out.print("星期五");
break;
case 6:
System.out.print("星期六");
break;
case 7:
System.out.print("星期日");
break;
default:
System.out.println("您输入的是个屁");
break;
}
//code1 end;
//code2
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("请输入一个月份:");
int month = sc.nextInt();
switch (month){
//不写break;会发生case穿透直到下一个break;或者到switch语句结束。
case 3:
case 4:
case 5:
System.out.println("您输入的月份是春天!");
break;
case 6:
case 7:
case 8:
System.out.println("您输入的月份是夏天!");
break;
case 9:
case 10:
case 11:
System.out.println("您输入的月份是秋天!");
break;
case 12:
case 1:
case 2:
System.out.println("您输入的月份是春冬天!");
break;
default:
System.out.println("您输入的是个屁!!");
break;
}
//code2 end;
3.Random随机数概述
使用步骤(和Scanner类似)
导包
import java.util.Random;
创建对象
Random r = new Random();
获取随机数
int number = r.nextInt(10);
产生的数据在0到10之间,包括0,不包括10。
括号里面的10是可以变化的,如果是100,就是0-100之间的数据
//code13猜数字
Random r = new Random();
int randomNumber = r.nextInt(81)+120;
while(true){
Scanner sc =new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("请输入您猜的数字");
int guessNumber = sc.nextInt();
if(guessNumber>randomNumber){
System.out.println("您输入的数"+guessNumber+"大了");
}else if(guessNumber<randomNumber){
System.out.println("您输入的是数"+guessNumber+"小了");
}else{
System.out.println("您猜中了");
break;
}
}
//code13 end
来源:CSDN
作者:血~小~板
链接:https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_41365066/article/details/103753494

