目录
HttpClient
HttpClient 是Apache Jakarta Common 下的子项目,可以用来提供高效的、最新的、功能丰富的支持 HTTP 协议的客户端编程工具包,方便在日常项目开发中,调用第三方接口数据。
HttpClient的主要功能
实现了所有 HTTP 的方法(GET、POST、PUT、HEAD、DELETE、HEAD、OPTIONS 等)
支持 HTTPS 协议
支持代理服务器(Nginx等)等
支持自动(跳转)转向
环境说明:JDK1.8、SpringBoot(2.2.2)
在pom.xml中引入HttpClient的依赖和SpringBoot的基本依赖配置(web,jpa,fastjson,mysql)。
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.httpcomponents</groupId>
<artifactId>httpclient</artifactId>
<version>4.5.3</version>
</dependency>
httpclient使用示例主要步骤
【步骤】:
1)创建一个httpclient对象,注意以下版本问题说明
HttpClient4.0版本前:
HttpClient httpClient = new DefaultHttpClient();
4.0版本后:
CloseableHttpClient httpClient = HttpClientBuilder.create().build();
2)创建一个httpGet对象
HttpGet request = new HttpGet(uri);
3)执行请求调用httpclient的execute(),传入httpGet对象,返回CloseableHttpResponse response = httpClient.execute(request, HttpClientContext.create());
4)取得响应结果并处理
5)关闭HttpClient
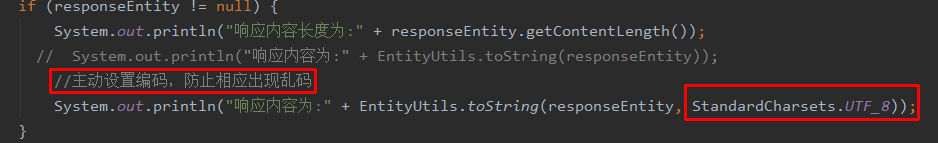
注意:主动设置编码,防止响应出现乱码

Spring Boot 工程结构

HttpClient实现主要代码:
GET
/**GET有参:
*/
@Autowired
private UserServiceImple userServiceImple;
@Test
public void getByUsername(){
List<User> users = userServiceImple.findByUserName("王三");
System.out.println(JSON.toJSONString(users));
}
@Test
public void doGetTestWayOne() {
// 获得Http客户端(可以理解为:你得先有一个浏览器;注意:实际上HttpClient与浏览器是不一样的)
CloseableHttpClient httpClient = HttpClientBuilder.create().build();
// 创建Get请求
HttpGet httpGet = new HttpGet("http://localhost:8080/user/2");
// 响应模型
CloseableHttpResponse response = null;
try {
// 配置信息
RequestConfig requestConfig = RequestConfig.custom()
// 设置连接超时时间(单位毫秒)
.setConnectTimeout(5000)
// 设置请求超时时间(单位毫秒)
.setConnectionRequestTimeout(5000)
// socket读写超时时间(单位毫秒)
.setSocketTimeout(5000)
// 设置是否允许重定向(默认为true)
.setRedirectsEnabled(true).build();
// 将上面的配置信息 运用到这个Get请求里
httpGet.setConfig(requestConfig);
// 由客户端执行(发送)Get请求
response = httpClient.execute(httpGet);
// 从响应模型中获取响应实体
HttpEntity responseEntity = response.getEntity();
System.out.println("响应状态为:" + response.getStatusLine());
if (responseEntity != null) {
System.out.println("响应内容长度为:" + responseEntity.getContentLength());
//主动设置编码,防止相应出现乱码
System.out.println("响应内容为:" + EntityUtils.toString(responseEntity, StandardCharsets.UTF_8));
}
} catch (ClientProtocolException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (ParseException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
try {
// 释放资源
if (httpClient != null) {
httpClient.close();
}
if (response != null) {
response.close();
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
POST
/**
* POST---有参测试(对象参数)
*
* @date
*/
@Test
public void dopostHaveObjectParam() {
// 获得Http客户端(可以理解为:你得先有一个浏览器;注意:实际上HttpClient与浏览器是不一样的)
CloseableHttpClient httpClient = HttpClientBuilder.create().build();
// 创建Post请求
HttpPost httpPost = new HttpPost("http://localhost:8080/user");
User user = new User();
user.setUserName("张山");
user.setPassword("Ss@1234");
// 我这里利用阿里的fastjson,将Object转换为json字符串;
// (需要导入com.alibaba.fastjson.JSON包)
String jsonString = JSON.toJSONString(user);
// 主动设置编码,防止出现乱码
StringEntity entity = new StringEntity(jsonString, "UTF-8");
// post请求是将参数放在请求体里面传过去的;这里将entity放入post请求体中
httpPost.setEntity(entity);
httpPost.setHeader("Content-Type", "application/json;charset=utf8");
// 响应模型
CloseableHttpResponse response = null;
try {
// 由客户端执行(发送)Post请求
response = httpClient.execute(httpPost);
// 从响应模型中获取响应实体
HttpEntity responseEntity = response.getEntity();
System.out.println("响应状态为:" + response.getStatusLine());
if (responseEntity != null) {
System.out.println("响应内容长度为:" + responseEntity.getContentLength());
//主动设置编码,防止相应出现乱码
System.out.println("响应内容为:" + EntityUtils.toString(responseEntity, StandardCharsets.UTF_8));
}
} catch (ClientProtocolException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (ParseException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
try {
// 释放资源
if (httpClient != null) {
httpClient.close();
}
if (response != null) {
response.close();
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
PUT
/**
* Put---有参测试(对象参数)
*
* @date
*/
@Test
public void doPutObjectParam() {
// 获得Http客户端(可以理解为:你得先有一个浏览器;注意:实际上HttpClient与浏览器是不一样的)
CloseableHttpClient httpClient = HttpClientBuilder.create().build();
// 创建Put请求
HttpPost httpPut = new HttpPost("http://localhost:8080/user");
User user = new User();
user.setId((long) 2);
user.setUserName("张山");
user.setPassword("Ss@1234");
// 我这里利用阿里的fastjson,将Object转换为json字符串;
// (需要导入com.alibaba.fastjson.JSON包)
String jsonString = JSON.toJSONString(user);
// 主动设置编码,防止出现乱码
StringEntity entity = new StringEntity(jsonString, "UTF-8");
// post请求是将参数放在请求体里面传过去的;这里将entity放入Put请求体中
httpPut.setEntity(entity);
httpPut.setHeader("Content-Type", "application/json;charset=utf8");
// 响应模型
CloseableHttpResponse response = null;
try {
// 由客户端执行(发送)Put请求
response = httpClient.execute(httpPut);
// 从响应模型中获取响应实体
HttpEntity responseEntity = response.getEntity();
System.out.println("响应状态为:" + response.getStatusLine());
if (responseEntity != null) {
System.out.println("响应内容长度为:" + responseEntity.getContentLength());
//主动设置编码,防止相应出现乱码
System.out.println("响应内容为:" + EntityUtils.toString(responseEntity, StandardCharsets.UTF_8));
}
} catch (ClientProtocolException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (ParseException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
try {
// 释放资源
if (httpClient != null) {
httpClient.close();
}
if (response != null) {
response.close();
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
Delete
/**
* DeleteTest
*/
@Test
public void doDeleteTest() {
// 获得Http客户端(可以理解为:你得先有一个浏览器;注意:实际上HttpClient与浏览器是不一样的)
CloseableHttpClient httpClient = HttpClientBuilder.create().build();
// 创建Delete请求
HttpDelete httpDelete = new HttpDelete("http://localhost:8080/user/41");
// 响应模型
CloseableHttpResponse response = null;
try {
// 配置信息
RequestConfig requestConfig = RequestConfig.custom()
// 设置连接超时时间(单位毫秒)
.setConnectTimeout(5000)
// 设置请求超时时间(单位毫秒)
.setConnectionRequestTimeout(5000)
// socket读写超时时间(单位毫秒)
.setSocketTimeout(5000)
// 设置是否允许重定向(默认为true)
.setRedirectsEnabled(true).build();
// 将上面的配置信息 运用到这个Delete请求里
httpDelete.setConfig(requestConfig);
// 由客户端执行(发送)Delete请求
response = httpClient.execute(httpDelete);
// 从响应模型中获取响应实体
HttpEntity responseEntity = response.getEntity();
System.out.println("响应状态为:" + response.getStatusLine());
if (responseEntity != null) {
System.out.println("响应内容长度为:" + responseEntity.getContentLength());
//主动设置编码,防止相应出现乱码
System.out.println("响应内容为:" + EntityUtils.toString(responseEntity, StandardCharsets.UTF_8));
}
} catch (ClientProtocolException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (ParseException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
try {
// 释放资源
if (httpClient != null) {
httpClient.close();
}
if (response != null) {
response.close();
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
来源:CSDN
作者:紫蝶侠
链接:https://blog.csdn.net/yangshengwei230612/article/details/103964905