1.在文章开头给出博客作业要求地址。
博客园地址:https://www.cnblogs.com/happyzm/p/9559372.html
2.给出结对小伙伴的学号、博客地址,结对项目的码云地址。
结对小伙伴的学号:201621123012
博客地址:https://www.cnblogs.com/saodeyipi/p/9756450.html
结对的码云地址:https://gitee.com/wistarias/PersonalProject-Java
3.给出结对的PSP表格。
| PSP2.1 | 结对开发流程 | 预估耗费时间(分钟) | 实际耗费时间(分钟) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Planning | 计划 | 10 | 5 |
| · Estimate | 明确需求和其他相关因素,估计每个阶段的时间成本 | 5 | 0 |
| Development | 开发 | 150 | 200 |
| · Analysis | 需求分析 (包括学习新技术) | 10 | 15 |
| · Design Spec | 生成设计文档 | 10 | 0 |
| · Design Review | 设计复审 | 10 | 5 |
| · Coding Standard | 代码规范 | 0 | 0 |
| · Design | 具体设计 | 10 | 20 |
| · Coding | 具体编码 | 100 | 120 |
| · Code Review | 代码复审 | 10 | 5 |
| · Test | 测试(自我测试,修改代码,提交修改) | 10 | 25 |
| Reporting | 报告 | 10 | 6 |
| · | 测试报告 | 5 | 2 |
| · | 计算工作量 | 5 | 2 |
| · | 并提出过程改进计划 | 0 | 0 |
4.设计实现过程。设计包括代码如何组织,比如会有几个类,几个函数,他们之间关系如何,关键函数是否需要画出流程图?单元测试是怎么设计的?
1.这个程序我负责的是对文件的行,单词数,字符数,单词频率的计算,我的搭档负责的是图形化的界面。
public class words //文件读取并完成对行,单词数,字符数,单词频率的计算
2.在类中一共有6个函数
public static int line(String filename) //文件读取并完成对行的计算 public static int bytenumber(String filename) //文件读取并完成对字符数的计算 public static int wordnumber(String filename)//文件读取并完成对单词数的计算 public static List<Map.Entry<String, Integer>> out(String filename)//文件读取并完成对单词频率的计算 public static List<Map.Entry<String, Integer>> out(String filename, int h)//文件读取并完成对指定数量单词频率的计算 public static List<Map.Entry<String, Integer>> outg(String filename, int k)//文件读取并完成对指定数量单词组的计算
5.代码说明。展示出项目关键代码,并解释思路与注释说明。
1.关键代码
(1)line(String filename)
while ((line = bufReader.readLine()) != null) {
for (int i = 0; i <= line.length() - 1; i++) {
if (Character.isUpperCase(line.charAt(i))) //对大写字母的判断
{
Character.toLowerCase(line.charAt(i));
}
}
linecount++;//行数统计
text.add(line);
}
文件读取并完成对行的计算
(2)bytenumber(String filename)
while ((line = bufReader.readLine()) != null) {
for (int i = 0; i <= line.length() - 1; i++) {
if (Character.isUpperCase(line.charAt(i))) //对大写字母的判断
{
Character.toLowerCase(line.charAt(i));
}
}
wordcount += line.length();//字符数统计
text.add(wordcount );
}
文件读取并完成对字符数的计算
(3)wordnumber(String filename)
for (String words : text) {
String[] word = words.split("[^a-zA-Z0-9]");
for (String pp : word) {
String regex = "^[a-z]{4}[a-z0-9\\s]*$";
if (pp.matches(regex) == true) {
text2.add(pp);
}
}
}
return text2.size();
文件读取并完成对单词数的计算
(4)out(String filename)
Map<String, Integer> map = new TreeMap<String, Integer>();
for (String word : text2) {
if (map.get(word) != null) {
map.put(word, map.get(word) + 1);
} else {
map.put(word, 1);
}
}
List<Map.Entry<String, Integer>> infoIds = new ArrayList<Map.Entry<String, Integer>>(map.entrySet());
List<Map.Entry<String, Integer>> infoIds1 = new ArrayList<Map.Entry<String, Integer>>();
Collections.sort(infoIds, new Comparator<Map.Entry<String, Integer>>() {
public int compare(Map.Entry<String, Integer> o1,
Map.Entry<String, Integer> o2) {
return (o2.getValue() - o1.getValue());
}
});
System.out.println("--------------排序后--------------");
for (int i = 0; i < infoIds.size(); i++) {
Entry<String, Integer> ent = infoIds.get(i);
if (i <= 9) {
infoIds1.add(ent);
}
}
return infoIds1;
文件读取并完成对单词频率的计算
2.代码测试
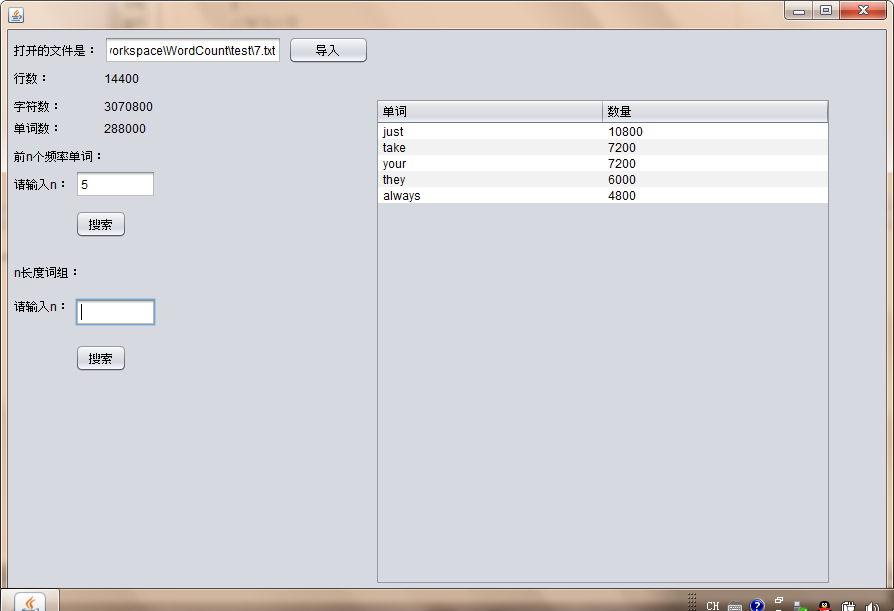
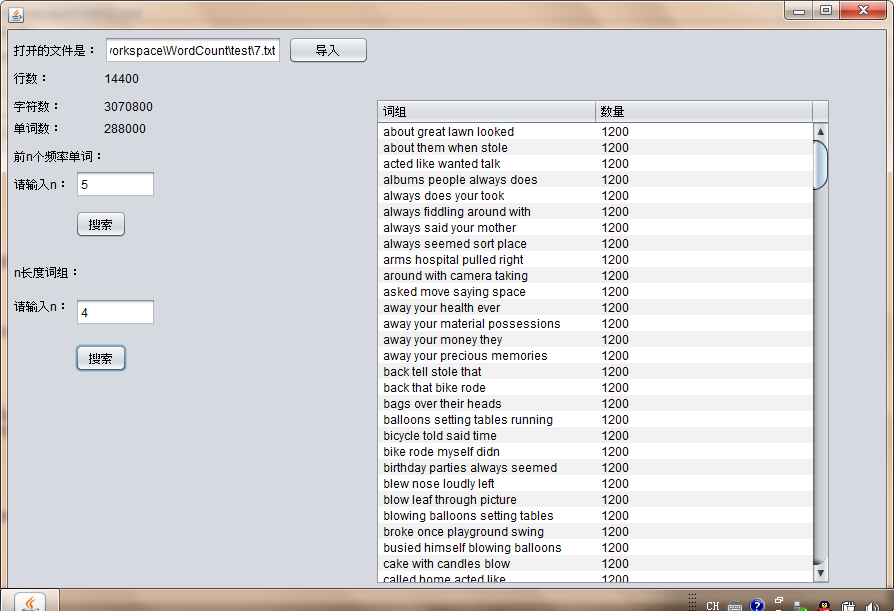
3.代码的提交

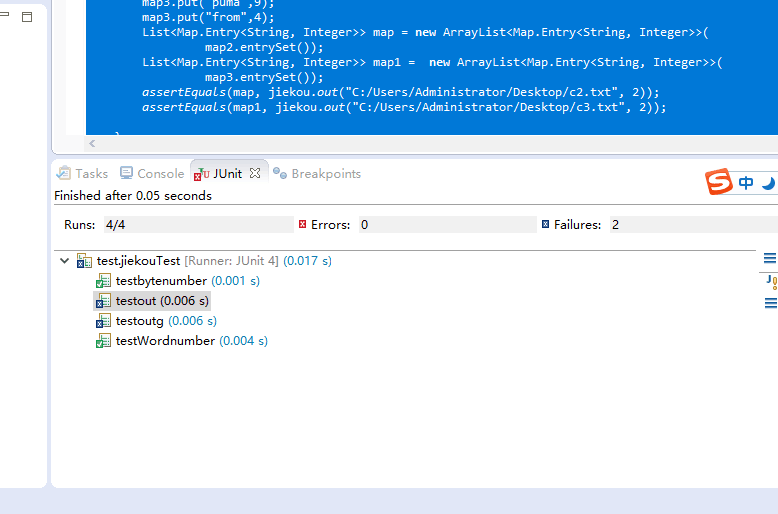
6.单元测试
测试数据
c1.txt:空文件
c2.txt:包含英文,特殊字符,中文等
c3.txt:一篇完整的英语的短文
import static org.junit.Assert.*;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.TreeMap;
import org.junit.Before;
import org.junit.Test;
import one.jiekou;
public class jiekouTest {
@Before
public void setUp() throws Exception {
}
@Test
public void testWordnumber() {
assertEquals(0, jiekou.wordnumber("C:/Users/Administrator/Desktop/c1.txt"));//空文件
assertEquals(14, jiekou.wordnumber("C:/Users/Administrator/Desktop/c2.txt"));//14个单词的纯英文
assertEquals(160, jiekou.wordnumber("C:/Users/Administrator/Desktop/c3.txt"));//160个单词的英文数字混合
}
@Test
public void testbytenumber() {
assertEquals(0, jiekou.bytenumber("C:/Users/Administrator/Desktop/c1.txt"));
assertEquals(136, jiekou.bytenumber("C:/Users/Administrator/Desktop/c2.txt"));
assertEquals(1505, jiekou.bytenumber("C:/Users/Administrator/Desktop/c3.txt"));
}
@Test
public void testout() {
Map<String, Integer> map2 = new TreeMap<String, Integer>();
Map<String, Integer> map3 = new TreeMap<String, Integer>();
map2.put("xmkczui84", 4);
map2.put("agisckxvn", 4);
map3.put("puma", 9);
map3.put("from", 4);
List<Map.Entry<String, Integer>> map = new ArrayList<Map.Entry<String, Integer>>(
map2.entrySet());
List<Map.Entry<String, Integer>> map1 = new ArrayList<Map.Entry<String, Integer>>(
map3.entrySet());
assertEquals(map, jiekou.out("C:/Users/Administrator/Desktop/c2.txt", 2));
assertEquals(map1, jiekou.out("C:/Users/Administrator/Desktop/c3.txt", 2));
}
@Test
public void testoutg() {
Map<String, Integer> map3 = new TreeMap<String, Integer>();
Map<String, Integer> map2 = new TreeMap<String, Integer>();
map3.put("accumulate experts from felt obliged", 1);
map2.put("america when reports came into", 1);
List<Map.Entry<String, Integer>> map1 = new ArrayList<Map.Entry<String, Integer>>(
map3.entrySet());
assertEquals(map3, "{" + jiekou.outg("C:/Users/Administrator/Desktop/c3.txt", 5).get(0) + "}");
assertEquals(map2, "{" + jiekou.outg("C:/Users/Administrator/Desktop/c3.txt", 5).get(1) + "}");
}
}
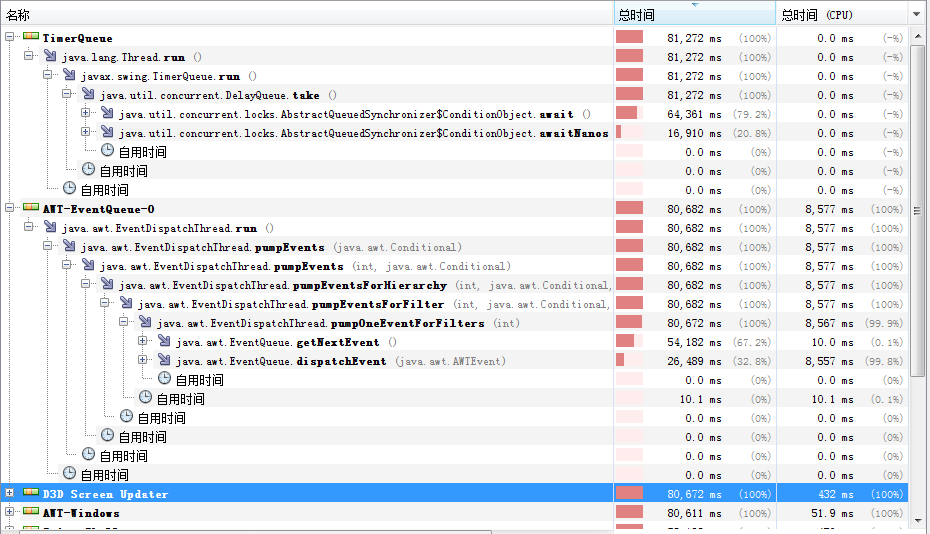
7.效能分析
8.结合在构建之法中学习到的相关内容与结对项目的实践经历,描述结对的感受,是否1+1>2?。
进行结对编程遇到的问题比我想象的多,在开始决定要做网页还是gui时就产生了不同的想法,之后在代码分工时碰到分工的不明确,导致有些功能重叠,还有就是有个人写得较快时,另一个人没有写好,这导致另一个人的进度不得不放缓。最后的一个问题是大家的代码风格不太相同,所以在对接时容易遇到一些问题。当然这结对编程也是有好处的,当其中一方比较放松时,另一方的需求就会时时激励你不断的前进。而且要写的代码量减少了很多,总的来说还是1+1>2的。
来源:https://www.cnblogs.com/wistaria/p/9748952.html