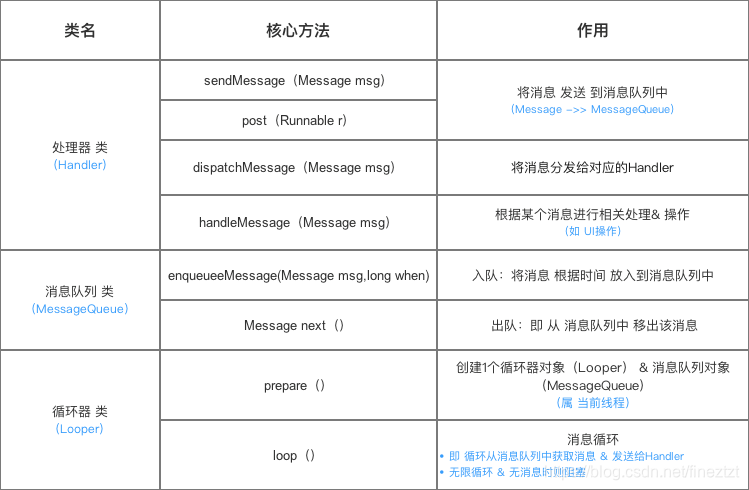
sendMessage方式:根据以上表格中三个关键类,下面分别从源码角度解释其作用
步骤:
1.Handler(创建handler对象时,主要做了两件事,1.指定looper对象;2.指定messageQueue对象)
//流程:创建handler对象——>Handler构造方法——>指定当前线程的looper对象
=绑定当前线程——>指定looper对象中保存的消息队列对象MessageQueue
/**
* a.使用
*/
private Handler mhandler = new Handler(){
// 通过复写handlerMessage()从而确定更新UI的操作
@Override
public void handleMessage(Message msg) {
...// 需执行的UI操作
}
};
/**
*b.源码
*/
public Handler(Callback callback, boolean async) {
// 1. 指定Looper对象
mLooper = Looper.myLooper();
if (mLooper == null) {
throw new RuntimeException(
"Can't create handler inside thread that has not called Looper.prepare()");
}
// 2. 绑定MessageQueue
mQueue = mLooper.mQueue;
}
2.Looper类(主要看两个核心方法,1.looper.prepare(),在activityThread中的静态Main方法中为主线程创建looper对象和messageQueue对象;2.Looper.loop:不断地循环地从消息队列中取出message,无消息时则阻塞)
public static void loop() {
...// 仅贴出关键代码
final Looper me = myLooper();
if (me == null) {
throw new RuntimeException("No Looper; Looper.prepare() wasn't called on this thread.");
}
// myLooper()作用:返回sThreadLocal存储的Looper实例;若me为null 则抛出异常
final MessageQueue queue = me.mQueue;
// 2. 消息循环(通过for循环)
for (;;) {
Message msg = queue.next();
if (msg == null) {
return;
}
// 若取出的消息为空,则线程阻塞
msg.target.dispatchMessage(msg);
// 把消息Message派发给消息对象msg的target属性
// target属性实际是1个handler对象
// 3. 释放消息占据的资源
msg.recycle();
}
}
3.MessageQueue(本质上是个链表,主要有两个方法,存和取。1.存:enqueueMessage;2.取:next)
/** a.enqueueMessadsge(放入消息)
* 单链表:提高插入、删除消息的效率
boolean enqueueMessage(Message msg, long when) {
synchronized (this) {
msg.markInUse();
msg.when = when;
Message p = mMessages;
boolean needWake;
if (p == null || when == 0 || when < p.when) {
msg.next = p;
mMessages = msg;
needWake = mBlocked;
} else {
needWake = mBlocked && p.target == null && msg.isAsynchronous();
Message prev;
for (;;) {
prev = p;
p = p.next;
if (p == null || when < p.when) {
break;
}
if (needWake && p.isAsynchronous()) {
needWake = false;
}
}
msg.next = p;
prev.next = msg;
}
if (needWake) {
nativeWake(mPtr);
}
}
return true;
}
b.next(取出消息)
Message next() {
// 该参数用于确定消息队列中是否还有消息
// 从而决定消息队列应处于出队消息状态 or 等待状态
int nextPollTimeoutMillis = 0;
for (;;) {
if (nextPollTimeoutMillis != 0) {
Binder.flushPendingCommands();
}
// nativePollOnce方法在native层,若是nextPollTimeoutMillis为-1,此时消息队列处于等待状态
nativePollOnce(ptr, nextPollTimeoutMillis);
synchronized (this) {
final long now = SystemClock.uptimeMillis();
Message prevMsg = null;
Message msg = mMessages;
// 出队消息,即 从消息队列中取出消息:按创建Message对象的时间顺序
if (msg != null) {
if (now < msg.when) {
nextPollTimeoutMillis = (int) Math.min(msg.when - now, Integer.MAX_VALUE);
} else {
// 取出了消息
mBlocked = false;
if (prevMsg != null) {
prevMsg.next = msg.next;
} else {
mMessages = msg.next;
}
msg.next = null;
if (DEBUG) Log.v(TAG, "Returning message: " + msg);
msg.markInUse();
return msg;
}
} else {
// 若 消息队列中已无消息,则将nextPollTimeoutMillis参数设为-1
// 下次循环时,消息队列则处于等待状态
nextPollTimeoutMillis = -1;
}
......
}
.....
}
}
总结:handler发送消息到消息队列中,调用messageQueue的enqueueMessage方法将消息入队,再通过next方法,looper不断循环从消息队列中取出消息,然后handler发送消息,最终由handleMessage处理消息。
来源:CSDN
作者:周涛_
链接:https://blog.csdn.net/fineztzt/article/details/103728752