需求:Map<key, value>中可以根据key, value 进行排序,由于 key 都是唯一的,可以很方便的进行比较操作,但是每个key 对应的value不是唯一的,有可能出现多个 相同的value对应key 是不一样的,所以需要采用不一样的方式。
详解:Map<key, value> 的目的是用来快速访问的存储结构。
通用的方法:
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.LinkedHashMap;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.Map.Entry;
import java.util.*;
public class MapUtil {
public void MapUtil() {
}
public static <K, V extends Comparable<? super V>> Map<K, V> sortByValue(Map<K, V> map) {
List<Entry<K, V>> list = new ArrayList<>(map.entrySet());
list.sort(Entry.comparingByValue());
Map<K, V> result = new LinkedHashMap<>();
for (Entry<K, V> entry : list) {
result.put(entry.getKey(), entry.getValue());
}
return result;
}
}
package com.compare;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Collections;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.Random;
public class test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Map<Integer, Integer> node_finalWeight = new HashMap();
node_finalWeight.put(5, 5);
node_finalWeight.put(35, 6);
node_finalWeight.put(45, 4);
node_finalWeight.put(25, 3);
node_finalWeight.put(20, 3);
System.out.println("按值排序之前:" +node_finalWeight);
MapUtil mu = new MapUtil();
// 类实例化后直接调用方法
System.out.println("按值排序之后:" + mu.sortByValue(node_finalWeight) );
}
}
输出结果:
按值排序之前:{35=6, 20=3, 5=5, 25=3, 45=4}
按值排序之后:{20=3, 25=3, 45=4, 5=5, 35=6}
值得注意的是:
Map是java中的接口,Map.Entry是Map的一个内部接口。 Map提供了一些常用方法,如keySet()、entrySet()等方法。 keySet()方法返回值是Map中key值的集合;entrySet()的返回值也是返回一个Set集合,此集合的类型为Map.Entry。 Map.Entry是Map声明的一个内部接口,此接口为泛型,定义为Entry<K,V>。它表示Map中的一个实体(一个key-value对)。 Map.entrySet 方法返回映射的 collection 视图,其中的元素属于此类。获得映射项引用的唯一 方法是通过此 collection 视图的迭代器来实现。这些 Map.Entry 对象仅 在迭代期间有效;更确切地讲,如果在迭代器返回项之后修改了底层映射,则某些映射项的行为是不确定的,除了通过 setValue 在映射项上执行操作之外。
或者重写Java里面的比较器:
https://www.baeldung.com/java-comparator-comparable
https://docs.oracle.com/javase/7/docs/api/java/util/Comparator.html
https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/comparator-interface-java/
https://www.cnblogs.com/shizhijie/p/7657049.html
接下来的介绍另外一种方法,可以当做复习知识点,稍微烧脑一下:
1、通过调用Map.entrySet()方法获取条目集 2、通过调用stream()方法获取条目流 3、用比较器调用排序方法 4、使用Map.Entry.comparingByValue()比较器按值对条目进行排序 5、使用Collect()方法收集结果 6、使用Collectors.to Map()方法在另一个映射中获取结果。 7、提供LinkedHashMap::new到最后一个参数,强制它返回LinkedHashMap,以保留排序顺序。为了按降序排序,只需使用Java 8的Collections.reverse order()或Comparator.reverse()方法反转Comparator的顺序。
PS: 下面是具体的collect框架图,
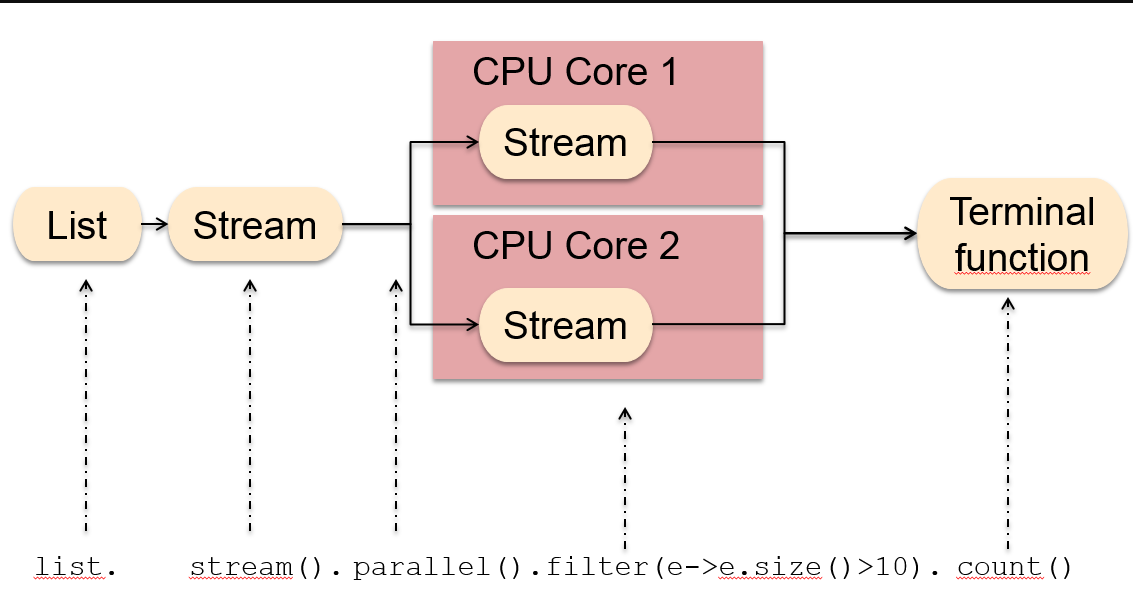
实例:
import java.util.Collections;
import java.util.Comparator;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.LinkedHashMap;
import java.util.Map;
import static java.util.stream.Collectors.*;
import static java.util.Map.Entry.*;
/*
* Java Program to sort a Map by values in Java 8
*
*/
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
// a Map with string keys and integer values
Map<String, Integer> budget = new HashMap<>();
budget.put("clothes", 120);
budget.put("grocery", 150);
budget.put("transportation", 100);
budget.put("utility", 130);
budget.put("rent", 1150);
budget.put("miscellneous", 90);
System.out.println("map before sorting: " + budget);
// let's sort this map by values first
Map<String, Integer> sorted = budget
.entrySet()
.stream()
.sorted(comparingByValue())
.collect(
toMap(e -> e.getKey(), e -> e.getValue(), (e1, e2) -> e2,
LinkedHashMap::new));
System.out.println("map after sorting by values: " + sorted);
// above code can be cleaned a bit by using method reference
sorted = budget
.entrySet()
.stream()
.sorted(comparingByValue())
.collect(
toMap(Map.Entry::getKey, Map.Entry::getValue, (e1, e2) -> e2,
LinkedHashMap::new));
// now let's sort the map in decreasing order of value
sorted = budget
.entrySet()
.stream()
.sorted(Collections.reverseOrder(Map.Entry.comparingByValue()))
.collect(
toMap(Map.Entry::getKey, Map.Entry::getValue, (e1, e2) -> e2,
LinkedHashMap::new));
System.out.println("map after sorting by values in descending order: "
+ sorted);
}
}
输出结果:
map before sorting: {grocery=150, utility=130, miscellneous=90, rent=1150, clothes=120, transportation=100}
map after sorting by values: {miscellneous=90, transportation=100, clothes=120, utility=130, grocery=150, rent=1150}
map after sorting by values in descending order: {rent=1150, grocery=150, utility=130, clothes=120, transportation=100, miscellneous=90}
附录一下如果想直接通过key 排序的话,可以借用一下TreeMap 的结构:
import java.text.ParseException;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.Set;
import java.util.TreeMap;
public class HashMapSorting{
public static void main(String args[]) throws ParseException {
// let's create a map with Java releases and their code names
HashMap<String, String> codenames = new HashMap<String, String>();
codenames.put("JDK 1.1.4", "Sparkler");
codenames.put("J2SE 1.2", "Playground");
codenames.put("AJ2SE 1.3", "Kestrel");
codenames.put("DJ2SE 1.4", "Merlin");
codenames.put("CJ2SE 5.0", "Tiger");
codenames.put("FJava SE 6", "Mustang");
codenames.put("Java SE 7", "Dolphin");
Map<String, Float> map = new TreeMap(codenames); // codenames 需要替换成自己的Map结构
System.out.println(map);
}
}
输出结果:
{AJ2SE 1.3=Kestrel, CJ2SE 5.0=Tiger, DJ2SE 1.4=Merlin, FJava SE 6=Mustang, J2SE 1.2=Playground, JDK 1.1.4=Sparkler, Java SE 7=Dolphin}
参考资料:
https://www.cnblogs.com/heganlin/p/5914892.html
https://tool.oschina.net/uploads/apidocs/jdk-zh/java/util/Map.Entry.html
https://www.javacodegeeks.com/2017/09/java-8-sorting-hashmap-values-ascending-descending-order.html
https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/sorting-a-hashmap-according-to-values/
额外的资源:
https://www.java67.com/2015/01/how-to-sort-hashmap-in-java-based-on.html
https://stackoverflow.com/questions/109383/sort-a-mapkey-value-by-values
https://www.jb51.net/article/90660.htm#comments
来源:https://www.cnblogs.com/qianyuesheng/p/12102482.html