当前台传参为Requset Payload时:
后台需要在参数列表中加[FromBody]
[Route("/create"))] public string Create([FromBody] Model model) { }
或者用流来进行接收
using (var bufferStream = new MemoryStream())
{
Request.Body.CopyToAsync(bufferStream);
byte[] buffer = bufferStream.ToArray();
string param = System.Text.Encoding.UTF8.GetString(buffer);
Model model = JsonConvert.DeserializeObject<Model>(param);
}
当前台传参为FormData时:
直接在参数列表中映射实体类
[Route("/create"))] public string Create(Model model) { }
两者的区别:
当POST请求的请求头里设置Content-Type: application/x-www-form-urlencoded(ajax默认), 参数在请求体以标准的Form Data的形式提交,以&符号拼接,参数格式为key=value&key=value&key=value...
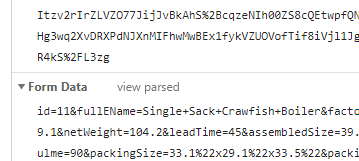
如果使用AJAX原生POST请求,请求头里设置Content-Type:application/json(axios默认是这种请求,且axios无法自动将对象转换成formdata格式),请求的参数会显示在Request Payload中,参数格式为JSON格式:{"key":"value","key":"value"...},这种方式可读性会更好。
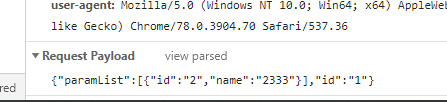
axios将对象转换为FormData
//axiox将简单对象转换为FormData,该方法不可用于深层次的转换,例如对象嵌套对象的复杂对象
axios({
url: '../../rest/manage/product/add',
method: 'post',
data: data,
transformRequest: [functioson (data) {
let ret = ''
for (let it in data) {
ret += encodeURIComponent(it) + '=' + encodeURIComponent(data[it]) + '&'
}
return ret
}],
headers: {
'Content-Type': 'application/x-www-form-urlencoded'
}
})
//使用QS将对象转换为FormData,可用于复杂对象
//ES6下可直接import引入,否则需要下载QS的包
axios({
headers: {
'Content-Type': 'application/x-www-form-urlencoded'
},
url: '../../rest/manage/product/add',
method: 'post',
data: Qs.stringify(data),
})
参考链接:https://blog.csdn.net/feizhong_web/article/details/80514436
https://www.cnblogs.com/yang-shuai/p/9929158.html
来源:CSDN
作者:qq_32314965
链接:https://blog.csdn.net/qq_32314965/article/details/103548435