ID: 452
TITLE: 用最少数量的箭引爆气球
TAG: Java,Python,C++,贪心算法
方法:贪心算法
贪心算法一般用来解决需要 “找到要做某事的最小数量” 或 “找到在某些情况下适合的最大物品数量” 的问题,且提供的是无序的输入。
贪心算法的思想是每一步都选择最佳解决方案,最终获得全局最佳的解决方案。
标准解决方案具有 的时间复杂度且由以下两部分组成:
- 思考如何排序输入数据( 的时间复杂度)。
- 思考如何解析排序后的数据( 的时间复杂度)
如果输入数据本身有序,则我们不需要进行排序,那么该贪心算法具有 的时间复杂度。
如何证明你的贪心思想具有全局最优的效果:可以使用反证法来证明。
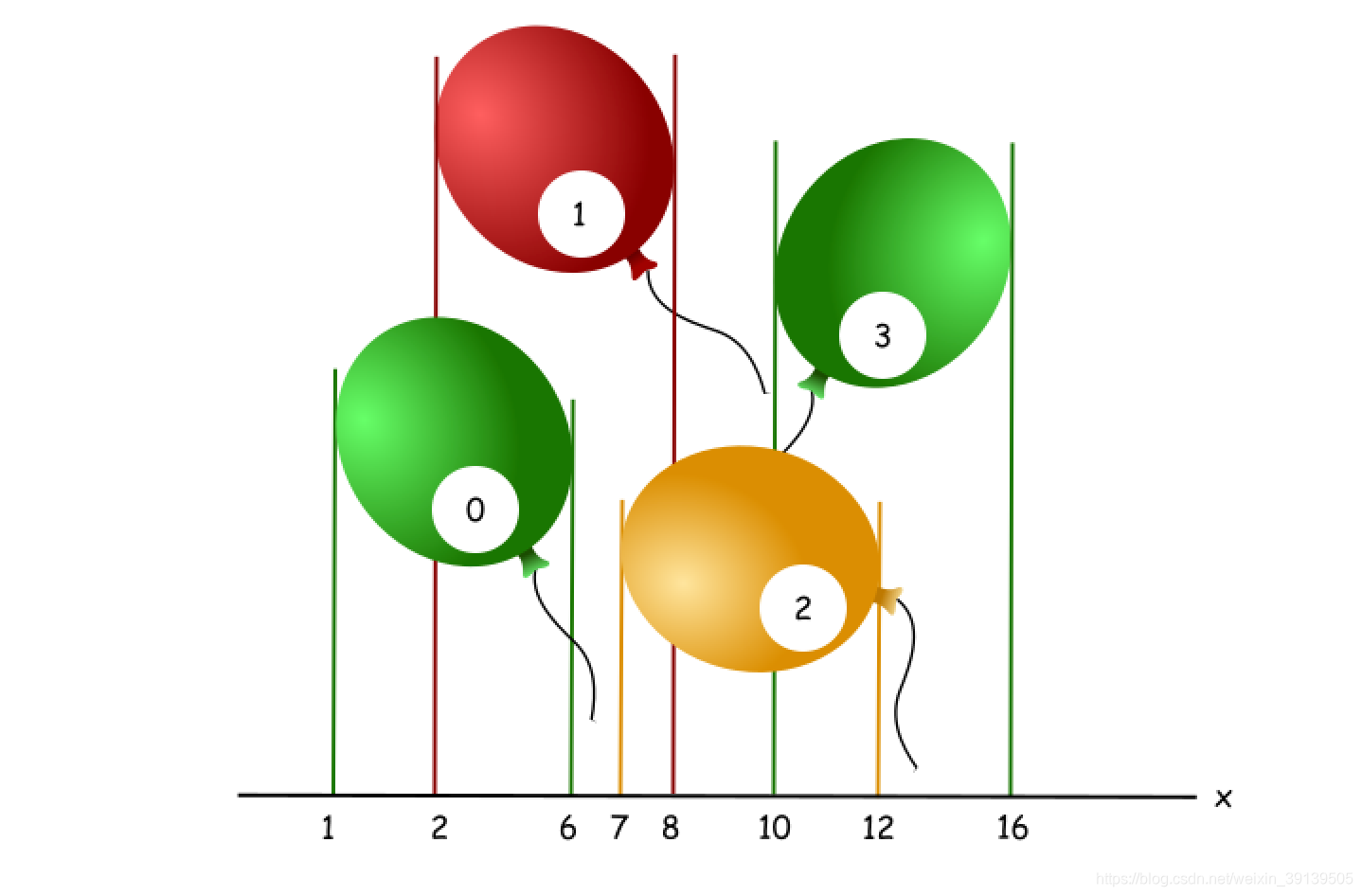
让我们来看下面的气球箭的组合情况。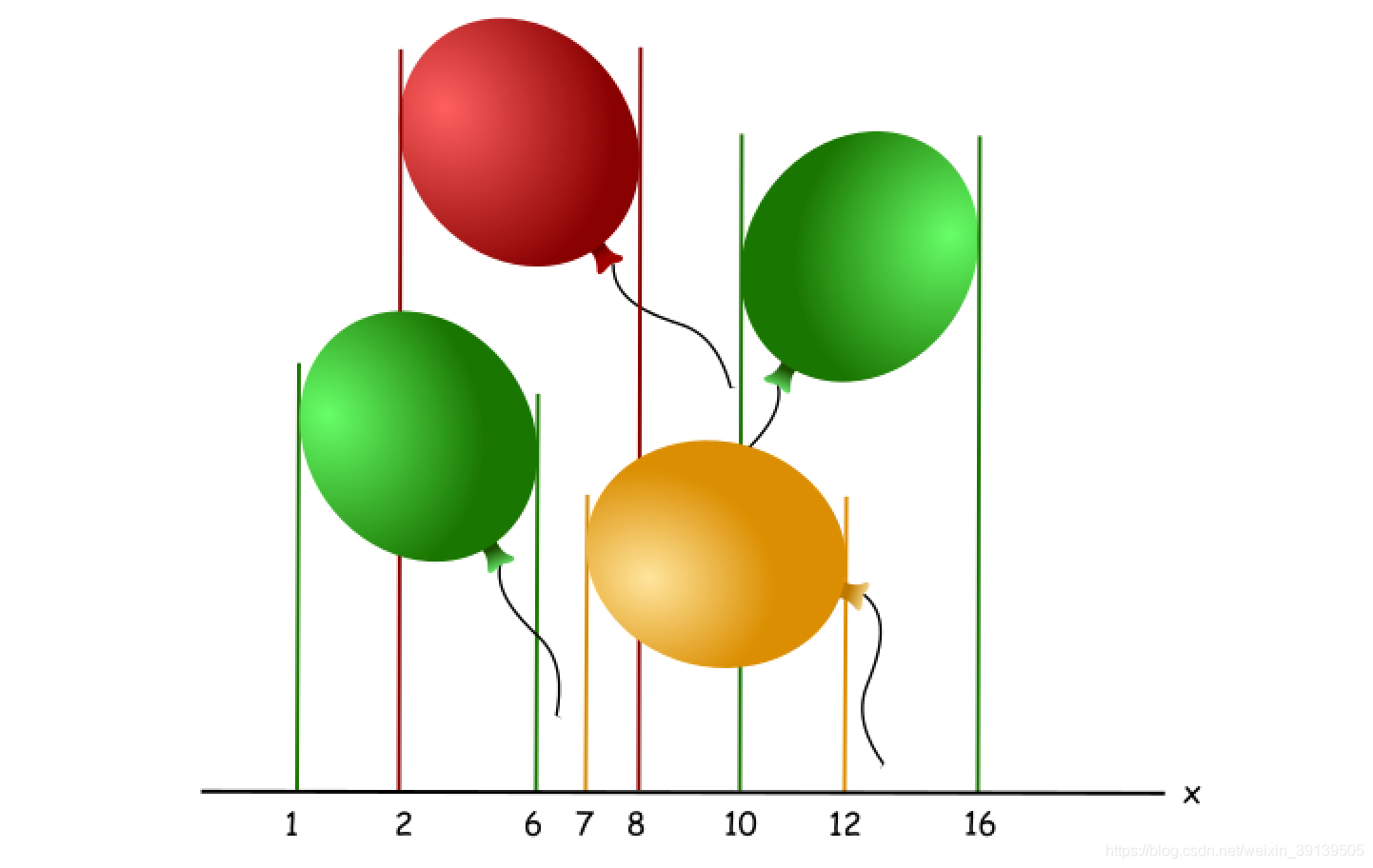
很明显我们使用两支箭就能使全部气球引爆,我们借助此例子来思考如何用贪心算法的思想来计算结果。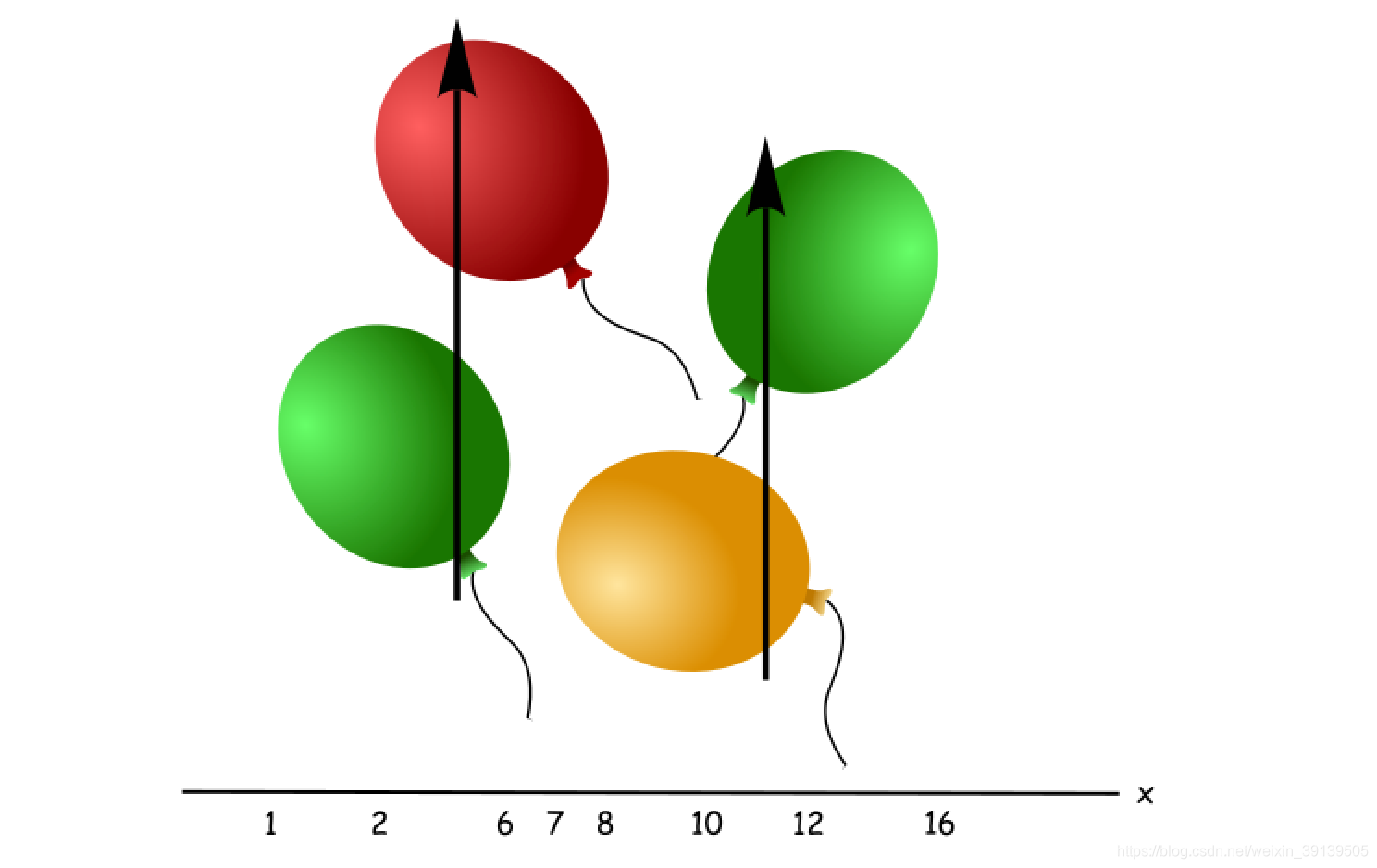
让我们根据气球的结束坐标进行排序,然后一个个进行检查。第一个气球是标有 0 的绿色气球,它的结束坐标是 6。
其他的气球有两种情况:
- 开始坐标小于
6,例如红色气球,它可以与0气球一起被一支箭引爆。 - 开始坐标大于
6,例如黄色气球,它不可以与0气球被一支箭引爆,因此需要增加箭的数量。
这代表了我们可以跟踪气球的结束坐标,若下个气球开始坐标在当前气球的结束坐标前,则我们可以用一支箭一起引爆;若下个气球的开始坐标在当前气球的结束坐标后,则我们必须增加箭的数量。并跟踪下个气球的结束坐标。
算法:
- 根据
x_end将气球进行排序。 - 初始化
first_end为第一个气球结束的坐标points[0][1]。 - 初始化箭的数量
arrows = 1。 - 遍历所有的气球:
- 如果气球的开始坐标大于
first_end:- 则增加箭的数量。
- 将
first_end设置为当前气球的x_end。
- 如果气球的开始坐标大于
- 返回
arrows。
class Solution:
def findMinArrowShots(self, points: List[List[int]]) -> int:
if not points:
return 0
# sort by x_end
points.sort(key = lambda x : x[1])
arrows = 1
first_end = points[0][1]
for x_start, x_end in points:
# if the current balloon starts after the end of another one,
# one needs one more arrow
if first_end < x_start:
arrows += 1
first_end = x_end
return arrows
class Solution {
public int findMinArrowShots(int[][] points) {
if (points.length == 0) return 0;
// sort by x_end
Arrays.sort(points, new Comparator<int[]>() {
@Override
public int compare(int[] o1, int[] o2) {
return o1[1] - o2[1];
}
});
int arrows = 1;
int xStart, xEnd, firstEnd = points[0][1];
for (int[] p : points) {
xStart = p[0];
xEnd = p[1];
// if the current balloon starts after the end of another one,
// one needs one more arrow
if (firstEnd < xStart) {
arrows++;
firstEnd = xEnd;
}
}
return arrows;
}
}
class Solution {
public:
int findMinArrowShots(vector<vector<int>>& points) {
if (points.size() == 0) return 0;
// sort by x_end
sort(begin(points), end(points),
[](const vector<int> &o1, const vector<int> &o2) {
return (o1[1] < o2[1]);
});
int arrows = 1;
int xStart, xEnd, firstEnd = points[0][1];
for (auto p : points) {
xStart = p[0];
xEnd = p[1];
// if the current balloon starts after the end of another one,
// one needs one more arrow
if (firstEnd < xStart) {
arrows++;
firstEnd = xEnd;
}
}
return arrows;
}
};
复杂度分析
- 时间复杂度:。因为对输入数据进行了排序。
- 空间复杂度:,仅仅使用了常数空间。
来源:CSDN
作者:陈乐乐happy
链接:https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_39139505/article/details/103495306