实现mypwd
学习pwd命令
- 查看pwd命令的帮助信息man pwd
- 显示当前目录所在路径
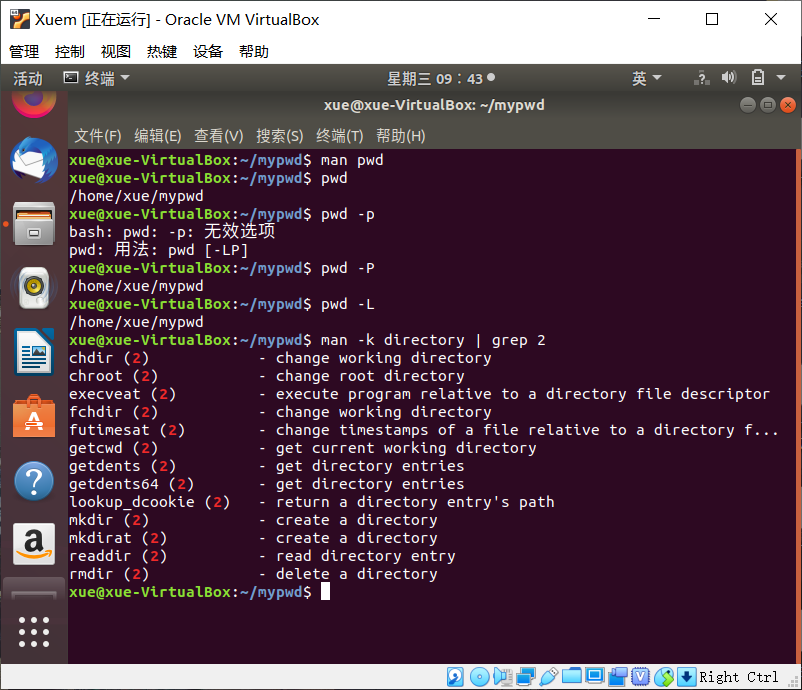
pwd - 显示当前目录的物理路径
pwd –P - 显示当前目录的连接路径
pwd -L pwd=Print Working Directory:打印当前目录(当前用户所位于的目录)。它会打印出以根目录(/)为起点的完整目录名(绝对目录)。这条命令是一条shell内建命令,并且在大多数shell中都可以使用,如bashBourneshellkshzsh等。
- 注意:
pwd通常不带选项运行,且没有任何参数 - 重要:运行的都是
/bin/pwd而不是pwd。 - 区别:
pwd意味着使用shell内置的pwd,shell可能有不同版本的pwd,具体请参考手册。当使用的是/bin/pwd时,则调用二进制版本的命令。虽然二进制的版本有更多的选项,但是它们两者都能打印当前的目录。
研究pwd实现需要的系统调用(man -k; grep),写出伪代码
man -k directory | grep 2寻找实现打印当前目录的系统调用函数
linux stat函数
- 表头文件:
#include <sys/stat.h>#include <unistd.h> - 定义函数:
int stat(const char *file_name, struct stat *buf); - 函数说明: 通过文件名filename获取文件信息,并保存在buf所指的结构体stat中
- 返回值: 执行成功则返回0,失败返回-1,错误代码存于errno
- 相应伪代码:
根据文件名获取文件的inode-number stat()通过文件名filename获取文件信息,并保存在buf所指的结构体stat中 根据inode-number, 在当前目录中查找对呀的文件名 opendir()打开一个目录,在失败的时候返回一个空的指针,成返回DIR结构体 readdir()用来读取目录。返回是dirent结构体指针 strdup()将串拷贝到新建的位置处,返回一个指针,指向为复制字符串分配的空间;如果分配空间失败,则返回NULL值 主函数中获取路径并打印
实现mypwd
mypwd.c
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <dirent.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#define MAX_DIR_DEPTH (256) //限制最大的目录深度
#define TRUE 1
#define FALSE 0
//根据文件名获取文件的inode-number
ino_t get_ino_byname(char *filename)
{
struct stat file_stat;
if(0 != stat(filename, &file_stat)) //stat()通过文件名filename获取文件信息,并保存在buf所指的结构体stat中
{
perror("stat");
exit(-1);
}
return file_stat.st_ino;
}
//根据inode-number, 在当前目录中查找对呀的文件名
char *find_name_byino(ino_t ino)
{
DIR *dp = NULL;
struct dirent *dptr = NULL;
char *filename = NULL;
if(NULL == (dp = opendir("."))) //opendir()打开一个目录,在失败的时候返回一个空的指针,成返回DIR结构体
{
fprintf(stderr, "Can not open Current Directory\n");
exit(-1);
}
else
{
while(NULL != (dptr = readdir(dp))) //readdir()用来读取目录。返回是dirent结构体指针
{
if(dptr->d_ino == ino)
{
filename = strdup(dptr->d_name); //strdup()将串拷贝到新建的位置处,返回一个指针,指向为复制字符串分配的空间;如果分配空间失败,则返回NULL值.
break;
}
}
closedir(dp);
}
return filename;
}
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
//记录目名的栈
char *dir_stack[MAX_DIR_DEPTH];
unsigned current_depth = 0;
while(TRUE)
{
ino_t current_ino = get_ino_byname("."); //通过特殊的文件名"."获取当期目录的inode-number
ino_t parent_ino = get_ino_byname(".."); //通过特殊的文件名".."获取当前目录的父目录的inode-number
if(current_ino == parent_ino)
break; //达到根目录,推出循环
/*两个inode-number不一样*/
chdir(".."); //更改当前工作目录,变为当前目录的父目录
dir_stack[current_depth++] = find_name_byino(current_ino); //"文件名"地址存放
if(current_depth >= MAX_DIR_DEPTH) //路径名太深
{
fprintf(stderr, "Directory tree is too deep.\n");
exit(-1);
}
}
int i = current_depth - 1;
for(i = current_depth - 1; i >= 0; i--) //打印路径
{
fprintf(stdout, "/%s", dir_stack[i]);
}
fprintf(stdout, "%s\n", current_depth == 0 ? "/" : "");
return 0;
}
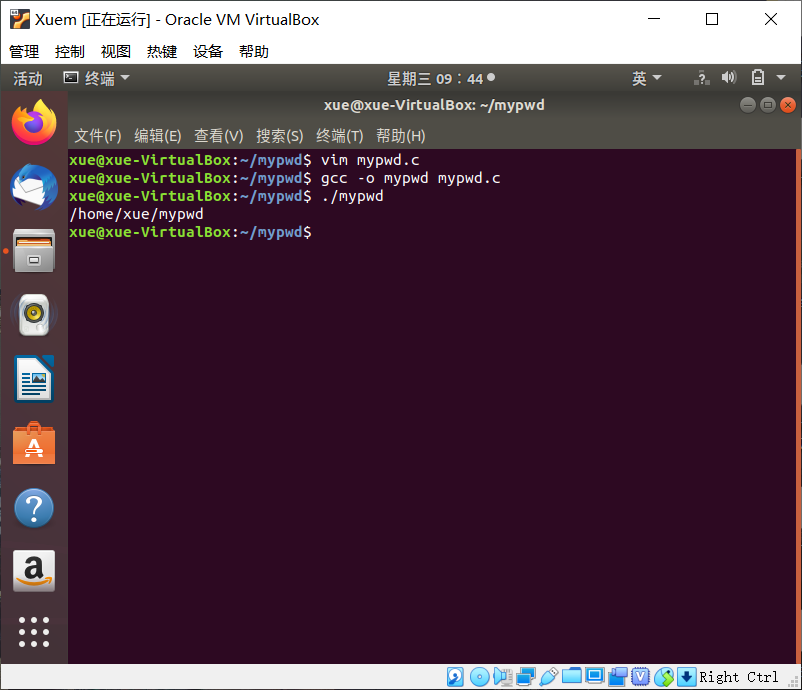
测试mypwd
来源:https://www.cnblogs.com/SANFENs/p/12020711.html