1.hashmap结构(jdk1.8)
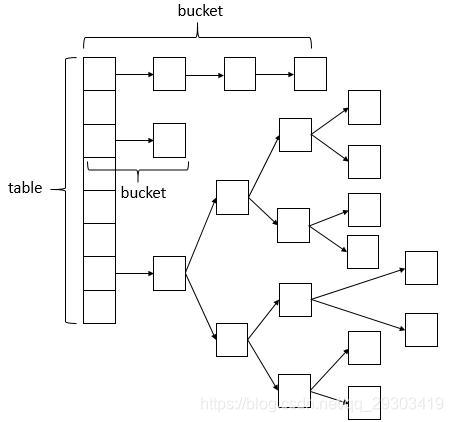
结构:hashmap采用数组+链表+红黑树的结构,
数组用查询快的特点,但是插入数据慢,链表有插入快的特点,但是查询慢,所以hashmap结合两者,而红黑树是为了链表过长影响查询速度,将链表转化为红黑树.
源码:
//hashmap默认初始化容量
static final int DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY = 1 << 4; // aka 16
//最大容量
static final int MAXIMUM_CAPACITY = 1 << 30;
//默认填充因子
static final float DEFAULT_LOAD_FACTOR = 0.75f;
//当大于时将链表转化为红黑树
static final int TREEIFY_THRESHOLD = 8;
//当小于时,将树转化为链表
static final int UNTREEIFY_THRESHOLD = 6;
//当table个数大于等于时才能转化为红黑树
static final int MIN_TREEIFY_CAPACITY = 64;
//包含key-value个数
transient int size;
//hashmap被修改次数
transient int modCount;
//要调整大小的下一个大小值(容量*负载因子)
int threshold;
//哈希表的填充因子
final float loadFactor;
1.hashmap如何计算数组下标:
在源码630行有一句:
if ((p = tab[i = (n - 1) & hash]) == null)//下标=(n-1)&hash
static final int hash(Object key) {
int h;
return (key == null) ? 0 : (h = key.hashCode()) ^ (h >>> 16);
}
2.hashmap如何添加数据
![[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-mOqey3uf-1575865521913)(C:\Users\Administrator\AppData\Roaming\Typora\typora-user-images\1574846625874.png)]](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/20191209122757501.png?x-oss-process=image/watermark,type_ZmFuZ3poZW5naGVpdGk,shadow_10,text_aHR0cHM6Ly9ibG9nLmNzZG4ubmV0L3FxXzI5MzAzNDE5,size_16,color_FFFFFF,t_70)
final V putVal(int hash, K key, V value, boolean onlyIfAbsent,
boolean evict) {
Node<K,V>[] tab; Node<K,V> p; int n, i;
//判断数组是否为空,为空初始化hashmap
if ((tab = table) == null || (n = tab.length) == 0)
n = (tab = resize()).length;
//判断节点是否为空(为空添加一个节点)
if ((p = tab[i = (n - 1) & hash]) == null)
tab[i] = newNode(hash, key, value, null);
else {
Node<K,V> e; K k;
//判断是否存在相同的key
if (p.hash == hash &&
((k = p.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k))))
e = p;
//判断是否为红黑树node
else if (p instanceof TreeNode)
e = ((TreeNode<K,V>)p).putTreeVal(this, tab, hash, key, value);
else {
//遍历链表
for (int binCount = 0; ; ++binCount) {
if ((e = p.next) == null) {
p.next = newNode(hash, key, value, null);
//如果大于转化为红黑树
if (binCount >= TREEIFY_THRESHOLD - 1) // -1 for 1st
treeifyBin(tab, hash);
break;
}
//判断是否存在相同值
if (e.hash == hash &&
((k = e.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k))))
break;
p = e;
}
}
if (e != null) { // existing mapping for key
V oldValue = e.value;
if (!onlyIfAbsent || oldValue == null)
e.value = value;
afterNodeAccess(e);
return oldValue;
}
}
++modCount;
//判断是否需要转化为红黑树
if (++size > threshold)
resize();
afterNodeInsertion(evict);
return null;
}
3.转化为红黑树的条件
final void treeifyBin(Node<K,V>[] tab, int hash) {
int n, index; Node<K,V> e;
//可以看出如果tab的长度小于MIN_TREEIFY_CAPACITY只会进行扩容,不会转化
if (tab == null || (n = tab.length) < MIN_TREEIFY_CAPACITY)
resize();
else if ((e = tab[index = (n - 1) & hash]) != null) {
TreeNode<K,V> hd = null, tl = null;
do {
TreeNode<K,V> p = replacementTreeNode(e, null);
if (tl == null)
hd = p;
else {
p.prev = tl;
tl.next = p;
}
tl = p;
} while ((e = e.next) != null);
if ((tab[index] = hd) != null)
hd.treeify(tab);
}
}
总结:当链表长度大于8且table长度大于64才会进行红黑树转化,不满足只会扩容.
4.扩容的条件
if (++size > threshold)
resize();
当当前容量大于总容量*填充因子时发生扩容.
总结发生扩容的条件:
1.当hashmap第一次put数据时,会发生扩容.
2.当链表长度大于8但是不满足树型化条件时.发生扩容.
3.当容量到达阈值时发生扩容
5.为何扩容为2的倍数
hashmap的hash采用的位运算,增加一位就是2的倍数,同时 当数组长度为15的时候,hashcode的值会与14(1110)进行“与”,那么最后一位永远是0,而0001,0011,0101,1001,1011,0111,1101这几个位置永远都不能存放元素了,空间浪费相当大,更糟的是这种情况中,数组可以使用的位置比数组长度小了很多,这意味着进一步增加了碰撞的几率,减慢了查询的效率!
来源:CSDN
作者:qq_29303419
链接:https://blog.csdn.net/qq_29303419/article/details/103455889