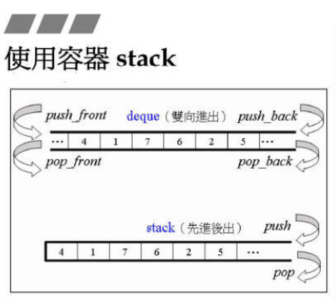
stack是栈,其实现也是使用了双端队列(只要不用双端队列的一端,仅用单端数据进出即完成单端队列的功能),由于queue和stack的实现均是使用deque,没有自己的数据结构和算法,所以这俩也被称为容器适配器(container adapter)。
例程
#include<stdexcept>
#include<string>
#include<cstdlib>
#include<cstdio>
#include<algorithm>
#include<iostream>
#include<ctime>
#include<stack>
using namespace std;
long get_a_target_long()
{
long target = 0;
cout<<"target(0~"<<RAND_MAX<<"):";
cin>>target;
return target;
}
string get_a_target_string()
{
long target = 0;
char buf[10];
cout<<"target(0~"<<RAND_MAX<<"):";
cin>>target;
snprintf(buf, 10, "%ld", target);
return string(buf);
}
int compareLongs(const void* a, const void* b)
{
return (*(long*)a - *(long*)b);
}
int compareStrings(const void *a, const void *b)
{
if(*(string*)a > *(string*)b)
return 1;
else if(*(string*)a < *(string*)b)
return -1;
else
return 0;
}
void test_stack(long& value)
{
cout << "\ntest_stack().......... \n";
stack<string> c;
char buf[10];
clock_t timeStart = clock();
for(long i=0; i< value; ++i)
{
try {
snprintf(buf, 10, "%d", rand());
c.push(string(buf));
}
catch(exception& p) {
cout << "i=" << i << " " << p.what() << endl;
abort();
}
}
cout << "milli-seconds : " << (clock()-timeStart) << endl;
cout << "stack.size()= " << c.size() << endl; //栈元素个数
cout << "stack.top()= " << c.top() << endl; //获得栈顶元素
c.pop(); //删除栈顶
cout << "stack.size()= " << c.size() << endl;
cout << "stack.top()= " << c.top() << endl;
}
int main()
{
long int value;
cout<<"how many elements: ";
cin>>value;
test_stack(value);
return 0;
}
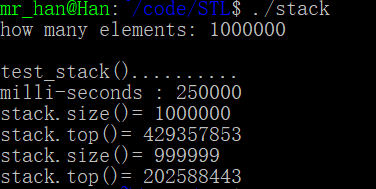
运行结果
deque、queue、stack因为其功能的原因,所以它们在实现上没有迭代器(iterator),也没有查找方法(find),这些方法会威胁到其功能性。(例如你可以获得栈底的迭代器(指针),将其删除,那么栈类没有移动操作,则其无法维护栈的合法性)
来源:https://www.cnblogs.com/area-h-p/p/12012763.html