防火墙
- 1. firewalld和netfilter
- SELINUX介绍
- 10.13 netfilter5表5链介绍
- 10.14 iptables语法
- iptables介绍:
- iptables参数示例:
- 1. 使用 iptables -nvL 命令查看 iptables 服务自带的一些规则:
- 2. iptables 的默认规则在 /etc/sysconfig/iptables 文件里保存着:
- 3. 清除规则使用 iptables -F 命令,这样虽然清空了规则,但是默认规则还会保存在 /etc/sysconfig/iptables 文件里:
- 4. 重启 iptables 规则:
- 5. 想要把当前规则保存到 /etc/sysconfig/iptables 文件里就要使用 service iptables save 命令:
- 6. 查看 nat 表的规则:
- 7. 使用 iptables -nvL 命令显示的规则里,可以看到第一行是有数字的,加上 iptables -Z 选项可以将计数器清零:
- 8. 添加一条规则示例:
- 9. 只写目标端口也可以,意思就是过滤掉给这个端口发送的数据包:
- 10. 使用 iptables -D 选项删除 INPUT 链里的规则:
- 更方便的删除规则,根据规则的行号来删除:
- 链里面没有匹配的规则,就会走默认的策略,-P 选项就是用来更改默认策略的:
- 10.15 iptables filter表案例
- 10.16/10.17/10.18 iptables nat表应用
- 实验一:
- 实验二:
- 实验三:
- 1.打开路由转发:
- 2.添加规则,因为之前添加了一条规则,现在先把那条规则删掉以免影响操作:
- 3.第一条是发送过来的包:
- 4.第二条是反馈回去的包,这条规则是把 192.168.100.100 返回的数据包,转发到 192.168.85.130 上去,然后回到 Windows 上。
- 5.添加完规则检查一下是否存在 nat 表里:
- 6.第三步,以上操作没问题后,给 B 机器设置默认网关:
- 7.完成以上操作之后,在 XShell 里新建一个会话,连接 192.168.85.130 的 1122 端口:
- 8.输入用户名,这里输入的是内网机器的用户名,不是 A 机器的用户名,因为这一步数据包实际上是通过了 A 机器上映射的 1122 端口转发到了 B 机器的 22 端口上了:
- 9.现在不单只外面的机器能够通过 A 机器来远程连接 B 机器,B 机器也可以连接外网:
- 10.19 iptables规则备份和恢复
- 10.20 firewalld的9个zone
- 10.21 firewalld关于zone的操作
- 10.22 firewalld关于service的操作
1. firewalld和netfilter
SELINUX介绍
安全增强型 Linux (SecurityEnhanced Linux) 简称 SELinux , 它是—个 Linux 内核模块, 也是Linux 的—个安全子系统。SELinux 主要由美国国家安全局开发。2.6及以上版本的 Linux 内核都已经集成了 SELinux 模块。 SELinux 的结构及配置非常复杂, 而且大量概念性的东西, 要学精难度较大。很多 Linux 系统管理员嫌麻烦都把 SELinux关闭 了。
1. 临时关闭:selinux:
[root@sc ~]# setenforce 0
2. 查看关闭状态:getenforce
[root@sc ~]# getenforce 0
Permissive #开启状态,但不生效。
[root@sc ~]#
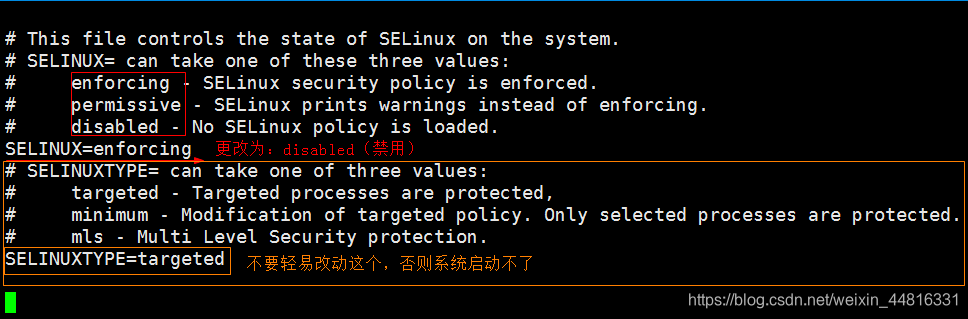
3. 永久关闭 selinux:编辑 /etc/selinux/config 文件,把 SELINUX 行改为 disabled ,然后重启操作系统:
三个状态:
enforcing:开启
permissive:开启状态, 但是不生效, 只记录日志。临时关闭, 会调整到这个状态。
disabled:关闭
更改完配置后, 需要重启系统, 方可生效。
SELINUX 一般情况下都是关闭的,因为开启的话会有很多服务受限于它,从而增大运维的成本,而且关闭了 SELINUX 也不会对安全有什么影响。
[root@sc ~]# vi /etc/selinux/config
4. 在 CentOS7 上也可以使用 netfilter 机制的防火墙:
netfilter 防火墙在 CentOS6 之前的版本是这个名字,在 CentOS7 则变成了 firewalld ,而且机制也变得不太一样,但是内部的工具: iptables 的用法是一样的。 iptables 可以去添加一些规则,比如关闭或开放端口。
5. 首先关闭 CentOS7 上的 firewalld 服务:
[root@sc ~]# systemctl disable firewalld #禁止 firewalld 开机自启动
Removed symlink /etc/systemd/system/multi-user.target.wants/firewalld.service.
Removed symlink /etc/systemd/system/dbus-org.fedoraproject.FirewallD1.service.
[root@sc ~]# systemctl stop firewalld #关闭 firewalld 服务
[root@sc ~]#
6. 如果想启动 netfilter 服务,我们需要安装 iptables-services 包,安装这个包等于开启了 netfilter 服务:
[root@sc ~]# yum install -y iptables-services #安装 iptables 服务
[root@sc ~]# systemctl enable iptables #启用服务
Created symlink from /etc/systemd/system/basic.target.wants/iptables.service to /usr/lib/systemd/system/iptables.service.
[root@sc ~]# systemctl start iptables #开始服务
[root@sc ~]#
10.13 netfilter5表5链介绍
netfilter 5表5链详解:http://www.cnblogs.com/metoy/p/4320813.html

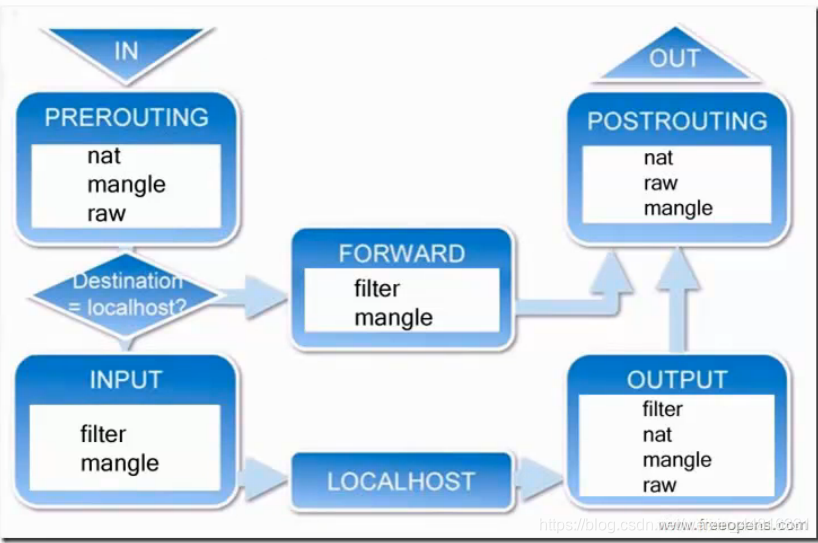
netfilter 5表:
filte表
三个链: INPUT、 FORWARD、 OUTPUT作用:过滤数据包
内核模块:iptables _filter.
Nat表
三个链: PRE ROUTING、POSTROUTING、OUTPUT
作用:用于网络地址转换(IP、 端口)内核模块:iptable_nat
Mangle表
五个链:PRE ROUTING、POSTROUTING、INPUT、OUTPUT、FORWARD
作用:修改数据包的服务类型、TTL、并且可以配置路由实现QOS
内核模块:iptable _ mangle(别看这个表这么麻烦,咱们设置策略时几乎都不会用到它)
Raw表
两个链:OUTPUT、PREROUTING
作用:决定数据包是否被状态跟踪机制处理
内核模块:iptable_raw
Security表
三个链:INPUT、OUTPUT和FORWARD
作用:Security表在centos6中并没有,用千强制访问控制(MAC)的网络规则
内核模块:iptable_security
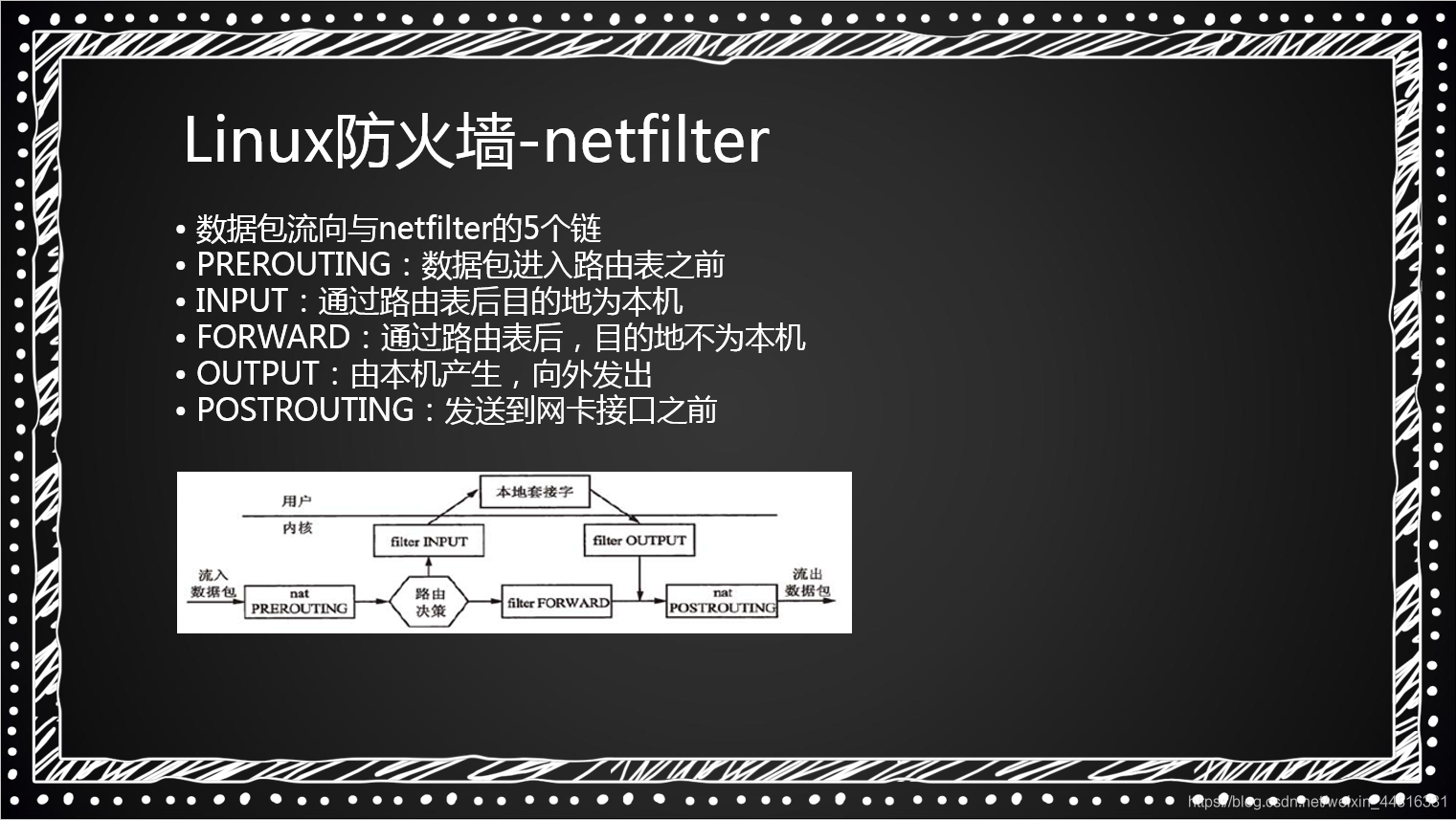
netfilter 5链:
PREROUTING: 数据包进入路由表之前
INPUT: 通过路由表后目的地为本机
FORWARD: 通过路由表后,目的地不为本机
OUTPUT: 由本机产生,向外发出
POSTROUTING: 发送到网卡接口之前
1. Nat表映射示意图:
2. netfilter 5链示意图:
10.14 iptables语法
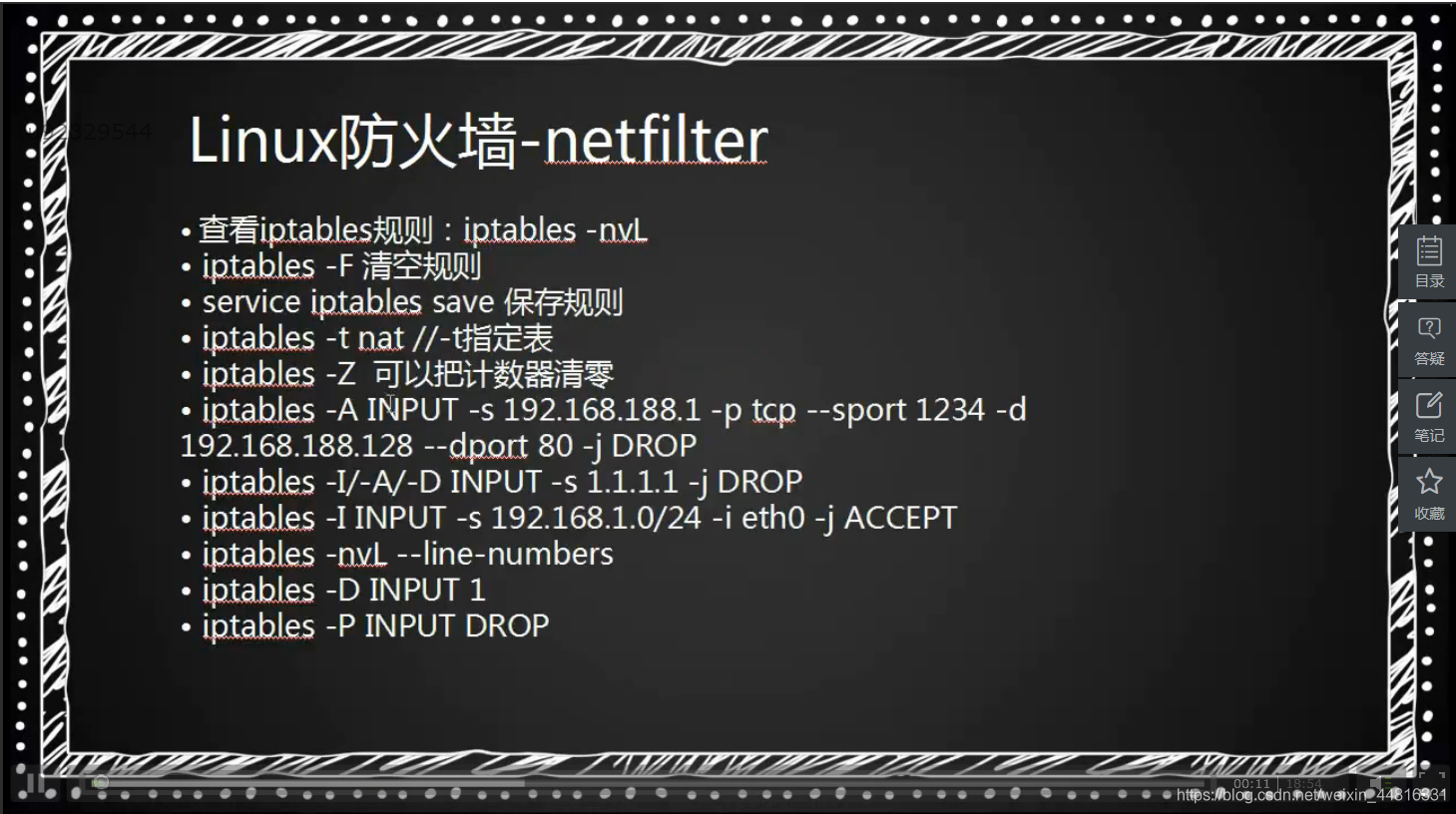
iptables介绍:
iptables -t 表名 <-A/I/D/R> 规则链名 [规则号] <-i/o 网卡名> -p 协议名 <-s 源IP/源子网> --sport 源端口 <-d 目标IP/目标子网> --dport 目标端口 -j 动作
| 参数 | 参数含义 |
|---|---|
| -t<表> | 指定要操纵的表 |
| -A | 向规则链中添加条目 |
| -D | 从规则链中删除条目 |
| -i | 向规则链中插入条目 |
| -R | 替换规则链中的条目 |
| -L | 显示规则链中已有的条目 |
| -F | 清除规则链中已有的条目 |
| -Z | 清空规则链中的数据包计算器和字节计数器 |
| -N | 创建新的用户自定义规则链 |
| -P | 定义规则链中的默认目标 |
| -h | 显示帮助信息 |
| -p | 指定要匹配的数据包协议类型 |
| -s | 指定要匹配的数据包源ip地址 |
| -j<目标> | 指定要跳转的目标 |
| -i<网络接口> | 指定数据包进入本机的网络接口 |
| -o<网络接口> | 指定数据包要离开本机所使用的网络接口 |
表名包括:
filter:包过滤,用于防火墙规则。
net:地址转换,用于网关路由器。
规则链名包括:
INPUT链:处理输入数据包。
OUTPUT链:处理输出数据包。
PORWARD链:处理转发数据包。
PREROUTING链:用于目标地址转换(DNAT)。
POSTOUTING链:用于源地址转换(SNAT)。
动作包括:
ACCEPT:接收数据包。
DROP:丢弃数据包。
REDIRECT:重定向、映射、透明代理。
SNAT:源地址转换。
DNAT:目标地址转换。
MASQUERADE:IP伪装(NAT),用于ADSL。
LOG:日志记录。
iptables参数示例:
1. 使用 iptables -nvL 命令查看 iptables 服务自带的一些规则:
[root@sc ~]# iptables -nvL
Chain INPUT (policy ACCEPT 0 packets, 0 bytes)
pkts bytes target prot opt in out source destination
34 2448 ACCEPT all -- * * 0.0.0.0/0 0.0.0.0/0 state RELATED,ESTABLISHED
0 0 ACCEPT icmp -- * * 0.0.0.0/0 0.0.0.0/0
0 0 ACCEPT all -- lo * 0.0.0.0/0 0.0.0.0/0
0 0 ACCEPT tcp -- * * 0.0.0.0/0 0.0.0.0/0 state NEW tcp dpt:22
0 0 REJECT all -- * * 0.0.0.0/0 0.0.0.0/0 reject-with icmp-host-prohibited
Chain FORWARD (policy ACCEPT 0 packets, 0 bytes)
pkts bytes target prot opt in out source destination
0 0 REJECT all -- * * 0.0.0.0/0 0.0.0.0/0 reject-with icmp-host-prohibited
Chain OUTPUT (policy ACCEPT 23 packets, 3076 bytes)
pkts bytes target prot opt in out source destination
[root@sc ~]#
[root@sc ~]# service iptables restart #重启 iptables 这个服务的命令
2. iptables 的默认规则在 /etc/sysconfig/iptables 文件里保存着:
[root@sc ~]# cat /etc/sysconfig/iptables
# sample configuration for iptables service
# you can edit this manually or use system-config-firewall
# please do not ask us to add additional ports/services to this default configuration
*filter
:INPUT ACCEPT [0:0]
:FORWARD ACCEPT [0:0]
:OUTPUT ACCEPT [0:0]
-A INPUT -m state --state RELATED,ESTABLISHED -j ACCEPT
-A INPUT -p icmp -j ACCEPT
-A INPUT -i lo -j ACCEPT
-A INPUT -p tcp -m state --state NEW -m tcp --dport 22 -j ACCEPT
-A INPUT -j REJECT --reject-with icmp-host-prohibited
-A FORWARD -j REJECT --reject-with icmp-host-prohibited
COMMIT
[root@sc ~]#
3. 清除规则使用 iptables -F 命令,这样虽然清空了规则,但是默认规则还会保存在 /etc/sysconfig/iptables 文件里:
[root@sc ~]# iptables -F #清除规则命令
[root@sc ~]# iptables -nvL #查看指令
Chain INPUT (policy ACCEPT 16 packets, 1168 bytes)
pkts bytes target prot opt in out source destination
Chain FORWARD (policy ACCEPT 0 packets, 0 bytes)
pkts bytes target prot opt in out source destination
Chain OUTPUT (policy ACCEPT 9 packets, 1212 bytes)
pkts bytes target prot opt in out source destination
[root@sc ~]# cat /etc/sysconfig/iptables #虽然清除了规则,但是默认规则依然存在
# sample configuration for iptables service
# you can edit this manually or use system-config-firewall
# please do not ask us to add additional ports/services to this default configuration
*filter
:INPUT ACCEPT [0:0]
:FORWARD ACCEPT [0:0]
:OUTPUT ACCEPT [0:0]
-A INPUT -m state --state RELATED,ESTABLISHED -j ACCEPT
-A INPUT -p icmp -j ACCEPT
-A INPUT -i lo -j ACCEPT
-A INPUT -p tcp -m state --state NEW -m tcp --dport 22 -j ACCEPT
-A INPUT -j REJECT --reject-with icmp-host-prohibited
-A FORWARD -j REJECT --reject-with icmp-host-prohibited
COMMIT
[root@sc ~]#
4. 重启 iptables 规则:
[root@sc ~]# service iptables restart
5. 想要把当前规则保存到 /etc/sysconfig/iptables 文件里就要使用 service iptables save 命令:
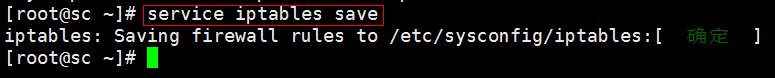
如果没有保存到 /etc/sysconfig/iptables 文件里的话,重启服务后就会重新加载 /etc/sysconfig/iptables 文件里的规则:
[root@sc ~]# service iptables restart #重启 iptables 服务
Redirecting to /bin/systemctl restart iptables.service
[root@sc ~]# iptables -nvL #查看指令
Chain INPUT (policy ACCEPT 0 packets, 0 bytes)
pkts bytes target prot opt in out source destination
6 428 ACCEPT all -- * * 0.0.0.0/0 0.0.0.0/0 state RELATED,ESTABLISHED
0 0 ACCEPT icmp -- * * 0.0.0.0/0 0.0.0.0/0
0 0 ACCEPT all -- lo * 0.0.0.0/0 0.0.0.0/0
0 0 ACCEPT tcp -- * * 0.0.0.0/0 0.0.0.0/0 state NEW tcp dpt:22
0 0 REJECT all -- * * 0.0.0.0/0 0.0.0.0/0 reject-with icmp-host-prohibited
Chain FORWARD (policy ACCEPT 0 packets, 0 bytes)
pkts bytes target prot opt in out source destination
0 0 REJECT all -- * * 0.0.0.0/0 0.0.0.0/0 reject-with icmp-host-prohibited
Chain OUTPUT (policy ACCEPT 4 packets, 496 bytes)
pkts bytes target prot opt in out source destination
[root@sc ~]#
目前我们做的这些操作都是针对的 filter 表:
[root@sc ~]# iptables -t filter -nvL
Chain INPUT (policy ACCEPT 0 packets, 0 bytes)
pkts bytes target prot opt in out source destination
159 12520 ACCEPT all -- * * 0.0.0.0/0 0.0.0.0/0 state RELATED,ESTABLISHED
0 0 ACCEPT icmp -- * * 0.0.0.0/0 0.0.0.0/0
0 0 ACCEPT all -- lo * 0.0.0.0/0 0.0.0.0/0
0 0 ACCEPT tcp -- * * 0.0.0.0/0 0.0.0.0/0 state NEW tcp dpt:22
7 702 REJECT all -- * * 0.0.0.0/0 0.0.0.0/0 reject-with icmp-host-prohibited
Chain FORWARD (policy ACCEPT 0 packets, 0 bytes)
pkts bytes target prot opt in out source destination
0 0 REJECT all -- * * 0.0.0.0/0 0.0.0.0/0 reject-with icmp-host-prohibited
Chain OUTPUT (policy ACCEPT 113 packets, 15952 bytes)
pkts bytes target prot opt in out source destination
[root@sc ~]#
6. 查看 nat 表的规则:
[root@sc ~]# iptables -t nat -nvL #查看 nat 的指令
Chain PREROUTING (policy ACCEPT 0 packets, 0 bytes)
pkts bytes target prot opt in out source destination
Chain INPUT (policy ACCEPT 0 packets, 0 bytes)
pkts bytes target prot opt in out source destination
Chain OUTPUT (policy ACCEPT 0 packets, 0 bytes)
pkts bytes target prot opt in out source destination
Chain POSTROUTING (policy ACCEPT 0 packets, 0 bytes)
pkts bytes target prot opt in out source destination
[root@sc ~]#
7. 使用 iptables -nvL 命令显示的规则里,可以看到第一行是有数字的,加上 iptables -Z 选项可以将计数器清零:
清零是为了在某些需求下,可以计算某个时间段某个 ip 传送过来的数据包数量。
[root@sc ~]# iptables -Z;iptables -nvL # iptables -Z 是清除计数器命令
Chain INPUT (policy ACCEPT 0 packets, 0 bytes)
pkts bytes target prot opt in out source destination
0 0 ACCEPT all -- * * 0.0.0.0/0 0.0.0.0/0 state RELATED,ESTABLISHED
0 0 ACCEPT icmp -- * * 0.0.0.0/0 0.0.0.0/0
0 0 ACCEPT all -- lo * 0.0.0.0/0 0.0.0.0/0
0 0 ACCEPT tcp -- * * 0.0.0.0/0 0.0.0.0/0 state NEW tcp dpt:22
0 0 REJECT all -- * * 0.0.0.0/0 0.0.0.0/0 reject-with icmp-host-prohibited
Chain FORWARD (policy ACCEPT 0 packets, 0 bytes)
pkts bytes target prot opt in out source destination
0 0 REJECT all -- * * 0.0.0.0/0 0.0.0.0/0 reject-with icmp-host-prohibited
Chain OUTPUT (policy ACCEPT 0 packets, 0 bytes)
pkts bytes target prot opt in out source destination
[root@sc ~]#
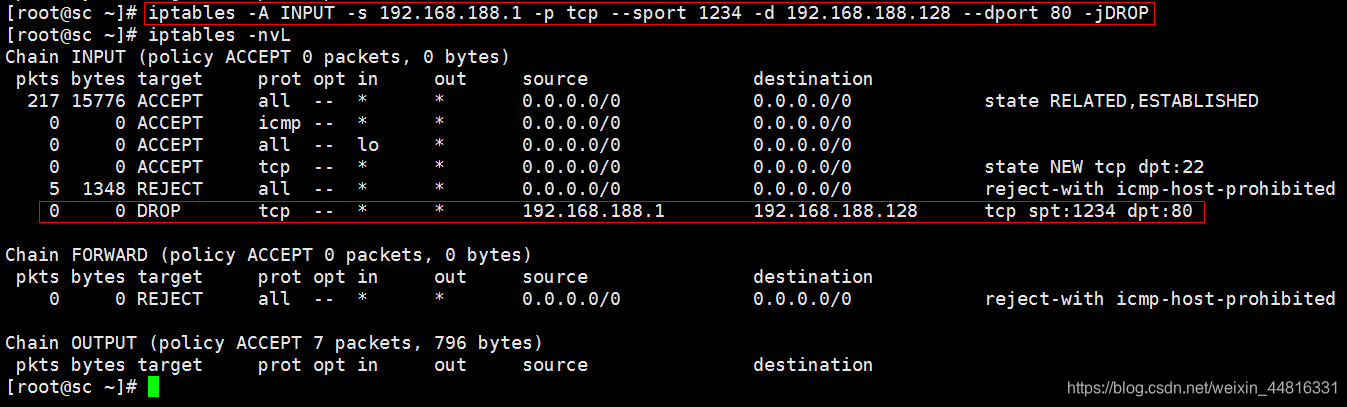
8. 添加一条规则示例:
[root@sc ~]# iptables -A INPUT -s 192.168.188.1 -p tcp --sport 1234 -d 192.168.188.128 --dport 80 -j DROP(不看,直接踢掉) / REJECT(看一下,友好的拒绝)

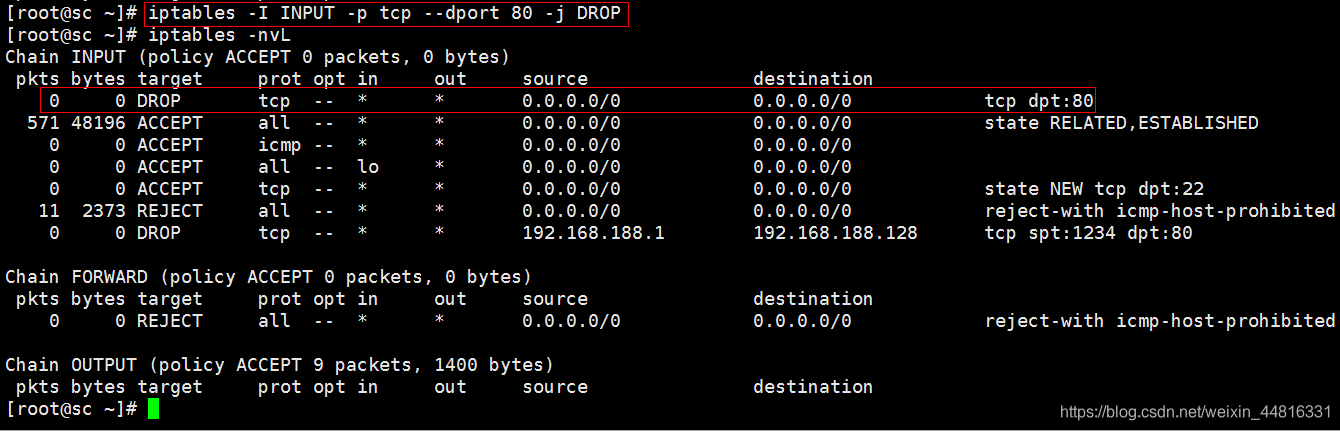
9. 只写目标端口也可以,意思就是过滤掉给这个端口发送的数据包:
规则在前面和后面区别就是先匹配前面的规则,然后再匹配后面的规则。
[root@sc ~]# iptables -I INPUT -p tcp --dport 80 -j DROP

10. 使用 iptables -D 选项删除 INPUT 链里的规则:
[root@sc ~]# iptables -D INPUT -p tcp --dport 80 -j DROP
[root@sc ~]# iptables -nvL
Chain INPUT (policy ACCEPT 0 packets, 0 bytes)
pkts bytes target prot opt in out source destination
665 56404 ACCEPT all -- * * 0.0.0.0/0 0.0.0.0/0 state RELATED,ESTABLISHED
0 0 ACCEPT icmp -- * * 0.0.0.0/0 0.0.0.0/0
0 0 ACCEPT all -- lo * 0.0.0.0/0 0.0.0.0/0
0 0 ACCEPT tcp -- * * 0.0.0.0/0 0.0.0.0/0 state NEW tcp dpt:22
21 3861 REJECT all -- * * 0.0.0.0/0 0.0.0.0/0 reject-with icmp-host-prohibited
0 0 DROP tcp -- * * 192.168.188.1 192.168.188.128 tcp spt:1234 dpt:80
Chain FORWARD (policy ACCEPT 0 packets, 0 bytes)
pkts bytes target prot opt in out source destination
0 0 REJECT all -- * * 0.0.0.0/0 0.0.0.0/0 reject-with icmp-host-prohibited
Chain OUTPUT (policy ACCEPT 10 packets, 1088 bytes)
pkts bytes target prot opt in out source destination
[root@sc ~]# iptables -D INPUT -s 192.168.188.1 -p tcp --sport 1234 -d 192.168.188.128 --dport 80 -jDROP
[root@sc ~]# iptables -nvL
Chain INPUT (policy ACCEPT 0 packets, 0 bytes)
pkts bytes target prot opt in out source destination
776 67124 ACCEPT all -- * * 0.0.0.0/0 0.0.0.0/0 state RELATED,ESTABLISHED
0 0 ACCEPT icmp -- * * 0.0.0.0/0 0.0.0.0/0
0 0 ACCEPT all -- lo * 0.0.0.0/0 0.0.0.0/0
0 0 ACCEPT tcp -- * * 0.0.0.0/0 0.0.0.0/0 state NEW tcp dpt:22
21 3861 REJECT all -- * * 0.0.0.0/0 0.0.0.0/0 reject-with icmp-host-prohibited
Chain FORWARD (policy ACCEPT 0 packets, 0 bytes)
pkts bytes target prot opt in out source destination
0 0 REJECT all -- * * 0.0.0.0/0 0.0.0.0/0 reject-with icmp-host-prohibited
Chain OUTPUT (policy ACCEPT 4 packets, 576 bytes)
pkts bytes target prot opt in out source destination
[root@sc ~]#
更方便的删除规则,根据规则的行号来删除:
iptables -nvL --line-number
iptables -D INPUT 7 (7 代表第几行)
[root@sc ~]# iptables -nvL --line-number #显示行号
Chain INPUT (policy ACCEPT 0 packets, 0 bytes)
num pkts bytes target prot opt in out source destination
1 0 0 DROP tcp -- * * 0.0.0.0/0 0.0.0.0/0 tcp dpt:80
2 906 77380 ACCEPT all -- * * 0.0.0.0/0 0.0.0.0/0 state RELATED,ESTABLISHED
3 0 0 ACCEPT icmp -- * * 0.0.0.0/0 0.0.0.0/0
4 0 0 ACCEPT all -- lo * 0.0.0.0/0 0.0.0.0/0
5 0 0 ACCEPT tcp -- * * 0.0.0.0/0 0.0.0.0/0 state NEW tcp dpt:22
6 23 4423 REJECT all -- * * 0.0.0.0/0 0.0.0.0/0 reject-with icmp-host-prohibited
7 0 0 DROP tcp -- * * 192.168.188.1 192.168.188.128 tcp spt:1234 dpt:80
[root@sc ~]# iptables -D INPUT 7 #根据行号删除服务
[root@sc ~]# iptables -nvL
Chain INPUT (policy ACCEPT 0 packets, 0 bytes)
pkts bytes target prot opt in out source destination
0 0 DROP tcp -- * * 0.0.0.0/0 0.0.0.0/0 tcp dpt:80
1013 85380 ACCEPT all -- * * 0.0.0.0/0 0.0.0.0/0 state RELATED,ESTABLISHED
0 0 ACCEPT icmp -- * * 0.0.0.0/0 0.0.0.0/0
0 0 ACCEPT all -- lo * 0.0.0.0/0 0.0.0.0/0
0 0 ACCEPT tcp -- * * 0.0.0.0/0 0.0.0.0/0 state NEW tcp dpt:22
24 4652 REJECT all -- * * 0.0.0.0/0 0.0.0.0/0 reject-with icmp-host-prohibited
Chain FORWARD (policy ACCEPT 0 packets, 0 bytes)
pkts bytes target prot opt in out source destination
0 0 REJECT all -- * * 0.0.0.0/0 0.0.0.0/0 reject-with icmp-host-prohibited
Chain OUTPUT (policy ACCEPT 28 packets, 3200 bytes)
pkts bytes target prot opt in out source destination
[root@sc ~]#
链里面没有匹配的规则,就会走默认的策略,-P 选项就是用来更改默认策略的:
ACCEPT是接收,DROP是终止,如果使用DROP的话,远程终端就会断开,因为服务器拒绝通信了,所以默认策略一般不用更改。
[root@sc ~]# iptables -P OUTPUT DROP #默认允许所有OUTPUT链的数据包终止
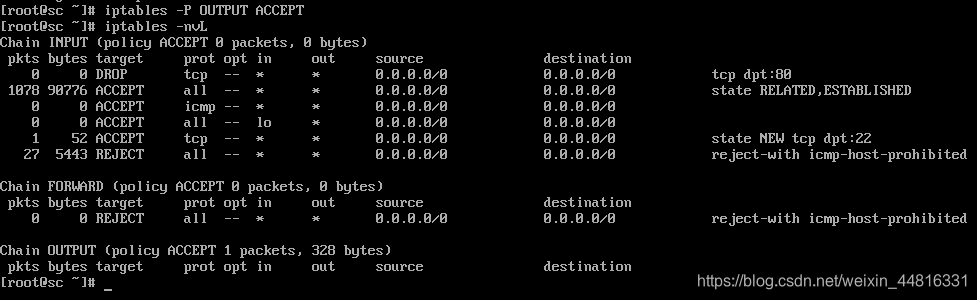
10.15 iptables filter表案例

第一案例:
这个案例的需求是把80、22、21端口方放行,然后给22端口指定一个IP段,只有这个指定的IP访问才能访问到22端口,其他IP则一概拒绝访问22端口,这个需求用一个shell脚本来实现。
1.使用此命令新建一个文件: vim /usr/local/sbin/iptables.sh
2.输入以下内容:
#!/bin/bash
ipt="/usr/sbin/iptables"
$ipt -F
$ipt -P INPUT DROP
$ipt -P OUTPUT ACCEPT
$ipt -P FORWARD ACCEPT
$ipt -A INPUT -m state --state RELATED,ESTABLISHED -j ACCEPT
$ipt -A INPUT -s 192.168.77.1/24 -p tcp --dport 22 -j ACCEPT
$ipt -A INPUT -p tcp --dport 80 -j ACCEPT
$ipt -A INPUT -p tcp --dport 21 -j ACCEPT
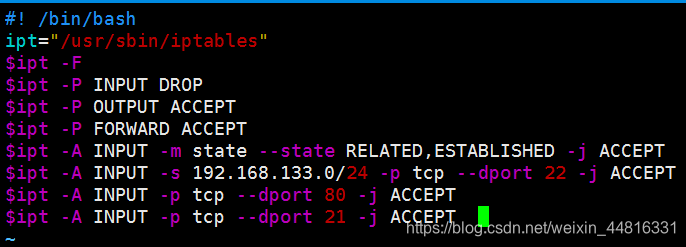
3.完成后保存退出:
ipt="/usr/sbin/iptables"(这句是定义一个变量,定义变量时使用的路径尽量使用绝对路径,以免出现环境变量的问题,导致命令无法执行。)
$ipt -F(清空之前的所有规则,因为没有加-t所以默认修改的是filter表。)
$ipt -P INPUT DROP(把默认的INPUT策略定义为DROP。)
$ipt -P OUTPUT ACCEPT(把默认的OUTPUT策略定义为ACCEPT。)
$ipt -P FORWARD ACCEPT(把默认的FORWARD 策略定义为ACCEPT。)
$ipt -A INPUT -m state --state RELATED,ESTABLISHED -j ACCEPT(添加一个规则,使用-m指定一些状态,然后-j指定对 RELATED,ESTABLISHED状态的数据包放行,它的目的是为了相关的数据包能够更方便的连接。)
$ipt -A INPUT -s 192.168.77.1/24 -p tcp --dport 22 -j ACCEPT(添加一个规则,使用-s指定一个源IP和端口,-p指定连接协议,接着指定放行此IP对22端口访问。)
$ipt -A INPUT -p tcp --dport 80 -j ACCEPT(添加一个规则,把80端口放行。)
$ipt -A INPUT -p tcp --dport 21 -j ACCEPT(添加一个规则,把21端口放行。)
使用 shell 脚本是为了能够执行批量的命令,因为脚本中第三句命令就是 DROP 掉I NPUT ,如果不使用 shell 脚本的话会直接断开远程终端的连接,后续的命令就无法在进行输入了。
4.使用sh命令执行写好的shell脚本:sh /usr/local/sbin/iptables.sh
[root@sc ~]# sh /usr/local/sbin/iptables.sh
5.执行完脚本后使用iptables -nvL命令就可以查看到添加上去的规则:
[root@sc ~]# iptables -nvL
Chain INPUT (policy DROP 0 packets, 0 bytes)
pkts bytes target prot opt in out source destination
64 5352 ACCEPT all -- * * 0.0.0.0/0 0.0.0.0/0 state RELATED,ESTABLISHED
0 0 ACCEPT tcp -- * * 192.168.133.0/24 0.0.0.0/0 tcp dpt:22
0 0 ACCEPT tcp -- * * 0.0.0.0/0 0.0.0.0/0 tcp dpt:80
0 0 ACCEPT tcp -- * * 0.0.0.0/0 0.0.0.0/0 tcp dpt:21
Chain FORWARD (policy ACCEPT 0 packets, 0 bytes)
pkts bytes target prot opt in out source destination
Chain OUTPUT (policy ACCEPT 47 packets, 4836 bytes)
pkts bytes target prot opt in out source destination
[root@sc ~]#
第二案列:
添加这条 iptables -I INPUT -p icmp --icmp-type 8 -j DROP 规则后, 可以本机可以 ping 通其他 ip , 但是其他机器 ping 不通本机了:
丢弃 icmp 包类型为 8 的数据包。 icmp 类型为 8 的数据包是 icmp 请求,类型为 0 的是应答包
[root@sc ~]# iptables -I INPUT -p icmp --icmp-type 8 -j DROP
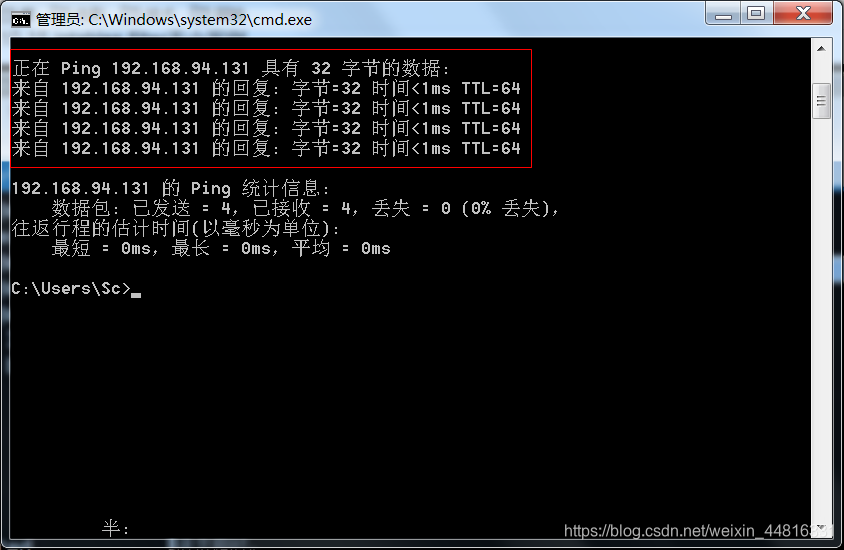
ping 一个网址,可以 ping 通:
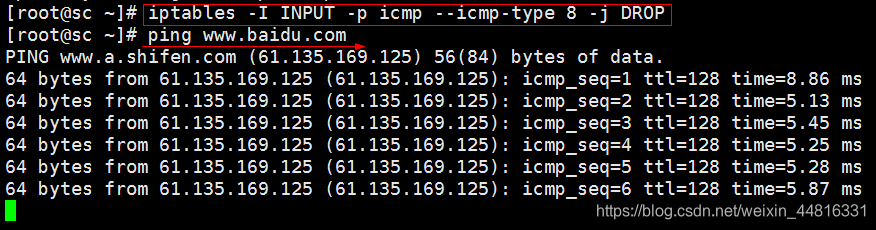
但是外面的机器要 ping 过来就 ping 不通:
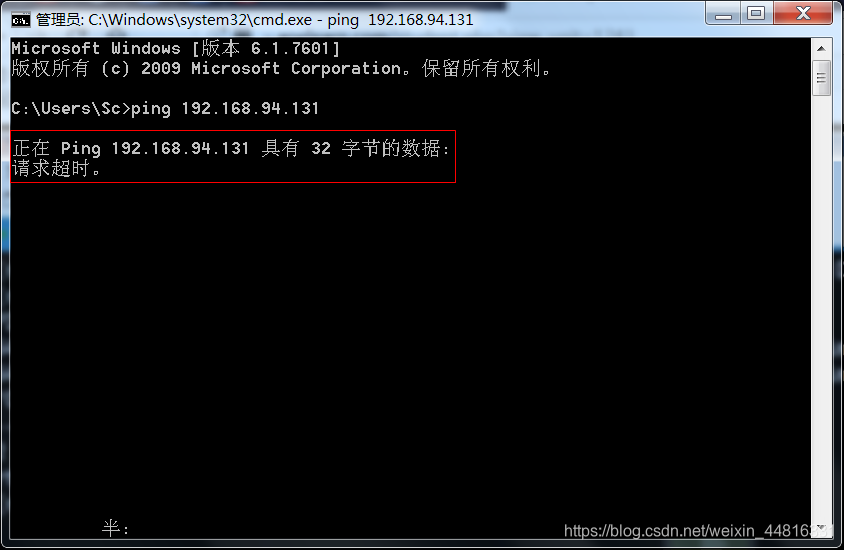
把规则删除后其他机器才能 ping 过来:
[root@sc ~]# iptables -D INPUT -p icmp --icmp-type 8 -j DROP
[root@sc ~]# service iptables restart
[root@sc ~]# iptables -nvL
Chain INPUT (policy ACCEPT 0 packets, 0 bytes)
pkts bytes target prot opt in out source destination
35 2856 ACCEPT all -- * * 0.0.0.0/0 0.0.0.0/0 state RELATED,ESTABLISHED
1 60 ACCEPT icmp -- * * 0.0.0.0/0 0.0.0.0/0
0 0 ACCEPT all -- lo * 0.0.0.0/0 0.0.0.0/0
0 0 ACCEPT tcp -- * * 0.0.0.0/0 0.0.0.0/0 state NEW tcp dpt:22
4 562 REJECT all -- * * 0.0.0.0/0 0.0.0.0/0 reject-with icmp-host-prohibited
Chain FORWARD (policy ACCEPT 0 packets, 0 bytes)
pkts bytes target prot opt in out source destination
0 0 REJECT all -- * * 0.0.0.0/0 0.0.0.0/0 reject-with icmp-host-prohibited
Chain OUTPUT (policy ACCEPT 28 packets, 5168 bytes)
pkts bytes target prot opt in out source destination
[root@sc ~]#
10.16/10.17/10.18 iptables nat表应用

实验一:
需求:现在我有两台机器, A 机器共有两块网卡,一块是可以连接外网的,一块是可以连接内网的。 B 机器则只有一个内网网卡,不能连接外网,只能连接内网。现在的需求就是想要 B 机器能够连接外网,说白了就是想做一个路由器的功能。
1.首先做这个实验需要两个虚拟机,记得先拍摄一个快照,以免在实验过程中出现问题无法恢复:
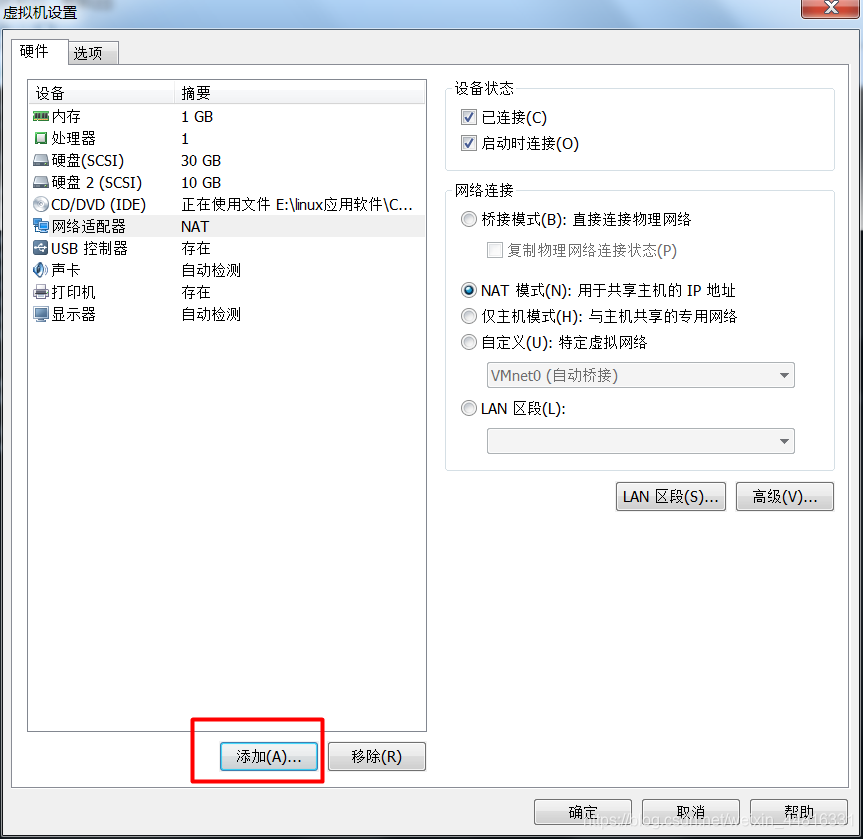
2.给 A 虚拟机添加一个网卡:
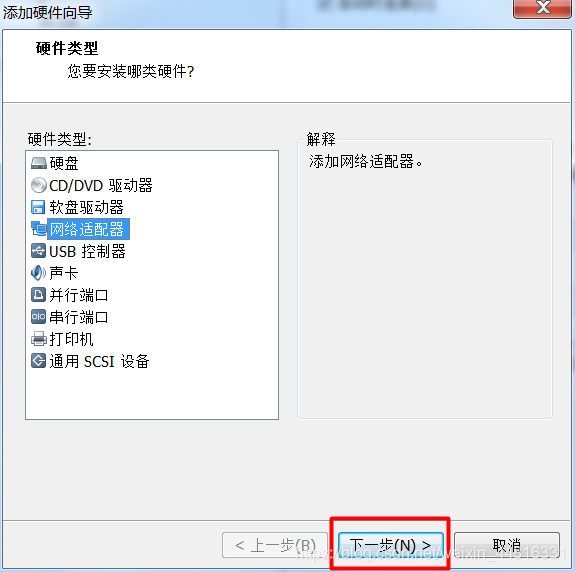
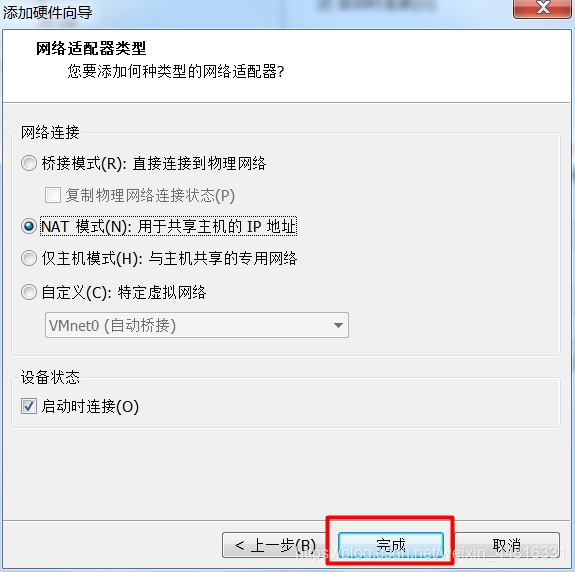
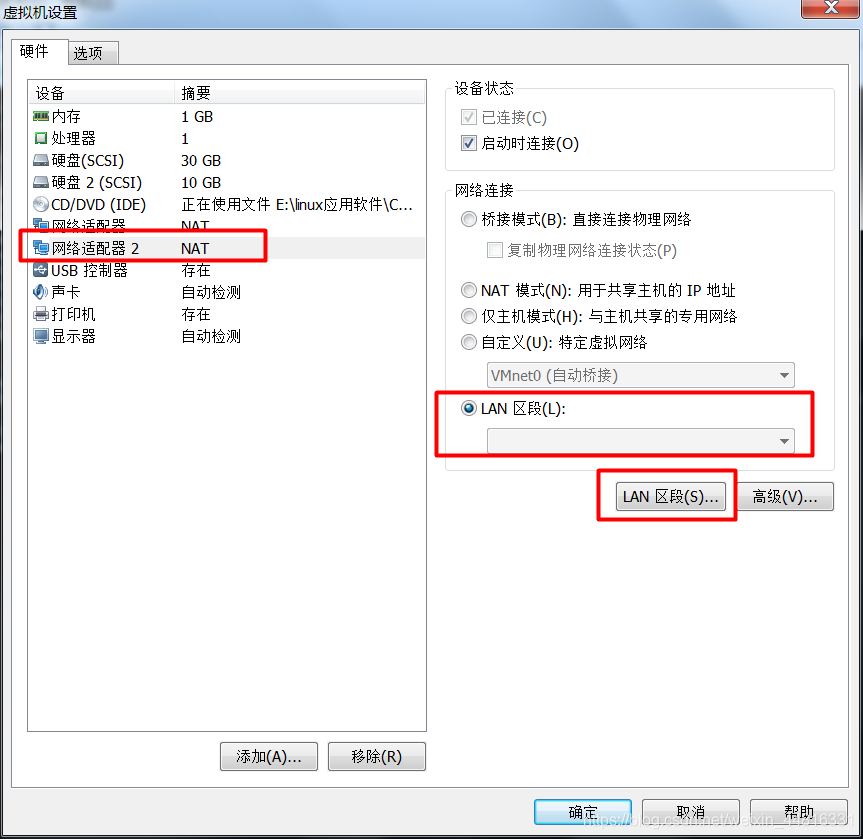
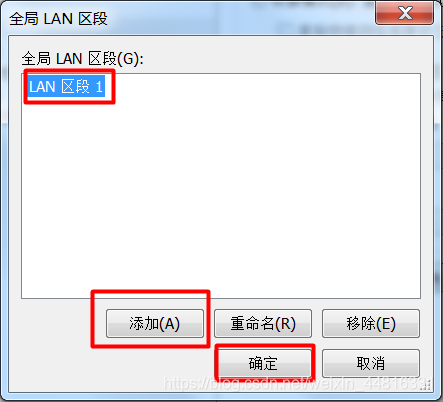
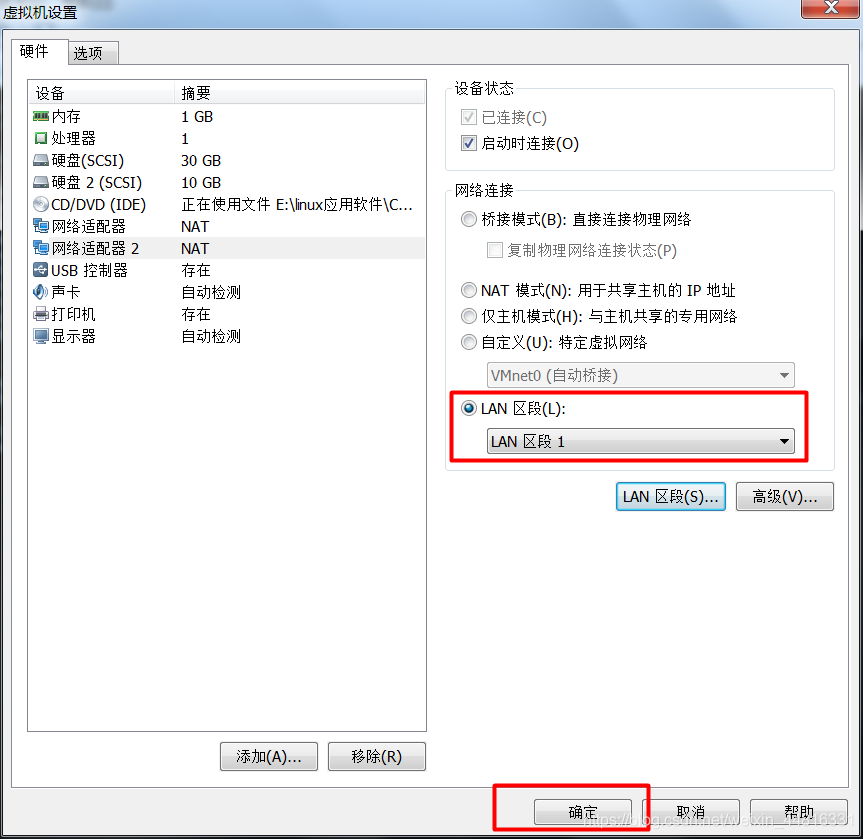
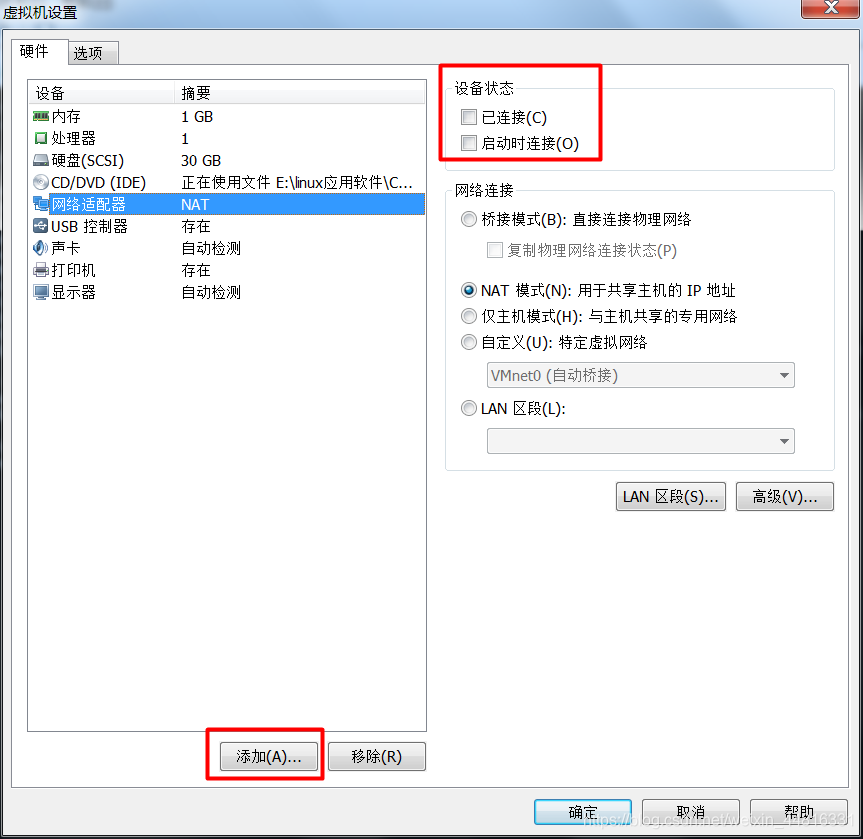
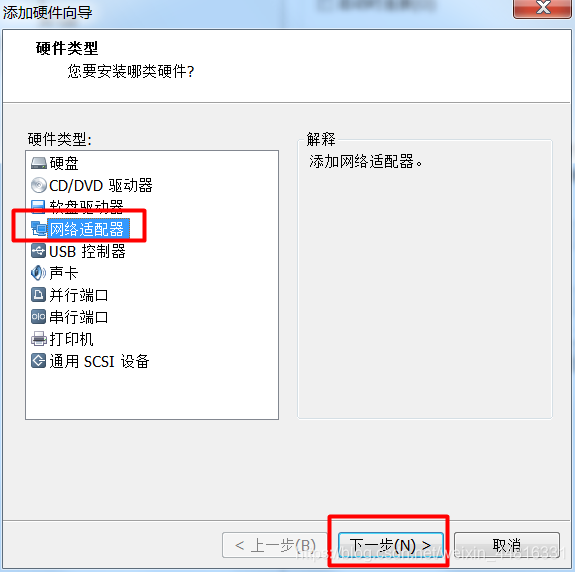
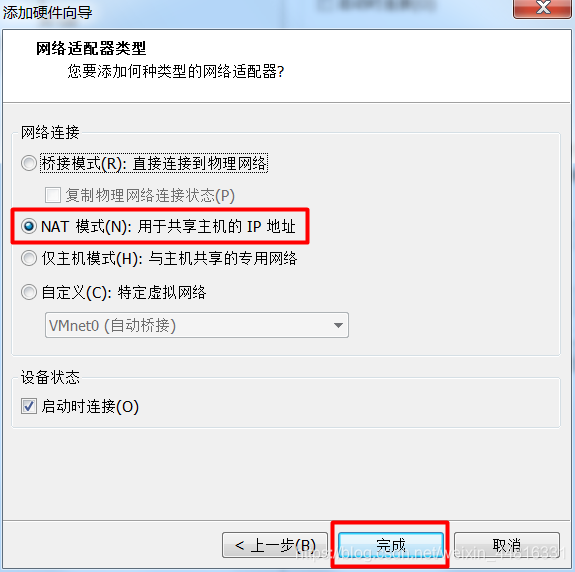
3.把 B 虚拟机的网卡禁止掉,然后添加一个新网卡,同样指定刚刚添加的那个 LAN 区段:
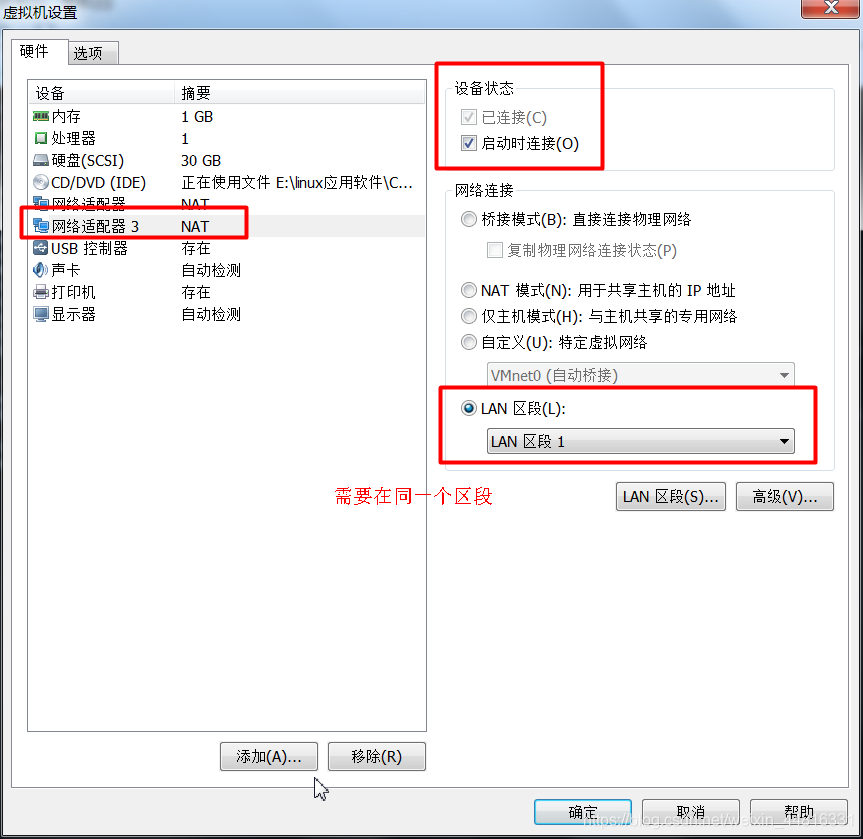
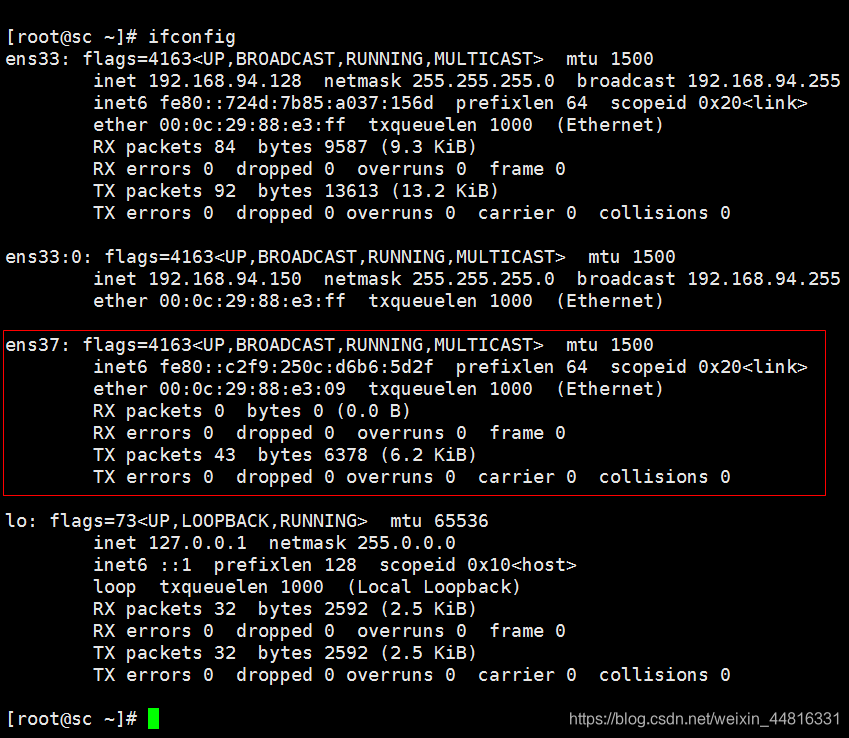
4.将两台虚拟机启动起来,然后给新网卡配置 IP,先配置 A,使用 ifconfig 命令可以看到新网卡的信息:
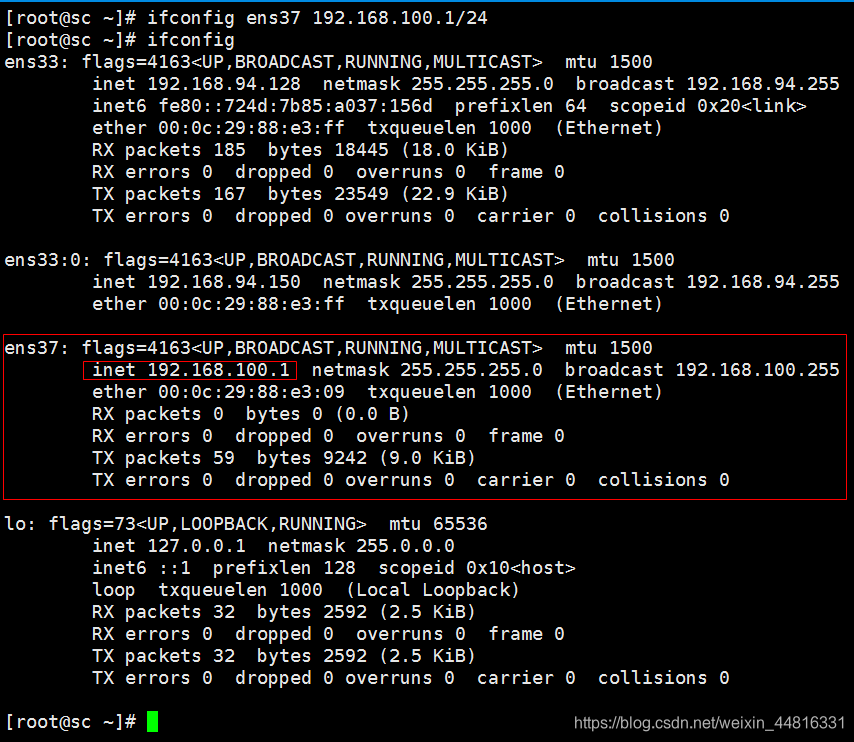
[root@sc ~]# ifconfig ens37 192.168.100.1/24
#一条命令直接配置ens37 的网址,但是重启会没有
或者
[root@sc network-scripts]# cp ifcfg-ens33 ifcfg-ens37
#复制一个ens33,起名ens37,把IP,子网掩码,添加好
IPADDR=192.168.100.1
NETMASK=255.255.255.0
5.配置 B 虚拟机的网卡 IP:
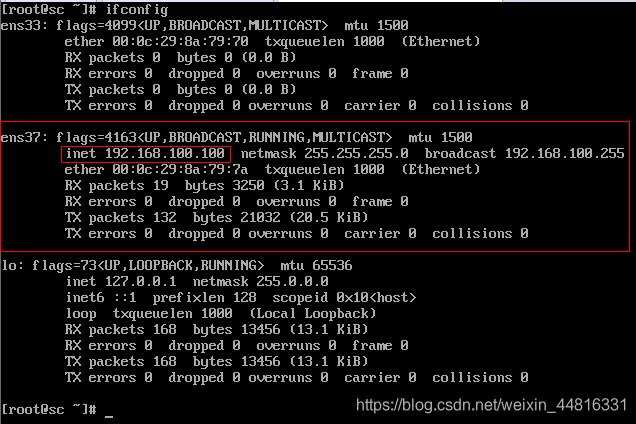
[root@sc ~]# ifconfig ens37 192.168.100.100/24 #一条命令直接配置ens37 的网址,但是重启会没有
或者
[root@sc network-scripts]# cp ifcfg-ens33 ifcfg-ens37 #复制一个ens33,起名ens37,把IP,子网掩码,添加好
IPADDR=192.168.100.100
NETMASK=255.255.255.0
GATEWAY=192.168.100.1
DNS=119.29.29.29
查看一下 A 机器和 B 机器 是否可以互相 ping 通:
mii-tool 是一个用来查看,管理介质的网络接口的状态的工具。
service network restart 重启网络服务。
实验二:
注意:确保 A 机器是可以 ping 通外网和内网的(这一步很关键),然后把 filete 表的服务全部删除,再打开 A 机器 的 nat 路由转发,这一步需要修改一下内核参数,需要修改 echo “1”>/proc/sys/net/ipv4/ip_forward 文件,这个文件默认的值为0,0代表没有开启转发,所以我们要将这个值改为 1 ,最后在 nat 表里增加一条规则:iptables -t nat -A POSTROUTING -s 192.168.100.0/24 -o ens33 -j MASQUERADE
1.先把 filete 表的服务全部删除:
[root@sc ~]# iptables -F
2.在 A 机器上设置,打开路由转发:
[root@sc ~]# echo "1">/proc/sys/net/ipv4/ip_forward
[root@sc ~]# cat /proc/sys/net/ipv4/ip_forward
1
3.增加一条规则:iptables -t nat -A POSTROUTING -s 192.168.100.0/24 -o ens33 -j MASQUERADE
[root@sc ~]# iptables -t nat -A POSTROUTING -s 192.168.100.0/24 -o ens37 -j MASQUERADE
[root@sc ~]# iptables -t nat -nvL #查看nat表
Chain PREROUTING (policy ACCEPT 0 packets, 0 bytes)
pkts bytes target prot opt in out source destination
Chain INPUT (policy ACCEPT 0 packets, 0 bytes)
pkts bytes target prot opt in out source destination
Chain OUTPUT (policy ACCEPT 0 packets, 0 bytes)
pkts bytes target prot opt in out source destination
Chain POSTROUTING (policy ACCEPT 0 packets, 0 bytes)
pkts bytes target prot opt in out source destination
0 0 MASQUERADE all -- * ens37 192.168.100.0/24 0.0.0.0/0
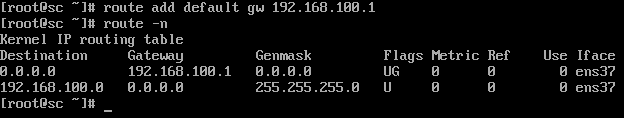
注意:ifconfig 查看一下 B 机器的网址,如果里面的 ens33 有IP地址,需要 ifdown ens33 一下,然后给 ens37 设置默认网关,设置了默认网关后可以使用 route -n 查看一下,是否设置成功
1.给 B 机器设置网关:
[root@sc ~]# route add default yw 192.168.100.1 #设置网关
[root@sc ~]# [root@sc ~]# route -n #查看网关
2.在机器 B 上添加 DNS :
[root@sc ~]#vim /etc/resolv.conf #编辑DNS配置文件
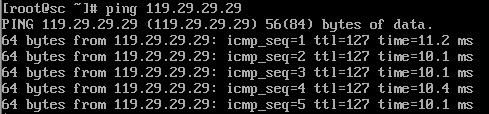
nameserver 119.29.29.29 (119.29.29.29是公网DNS)
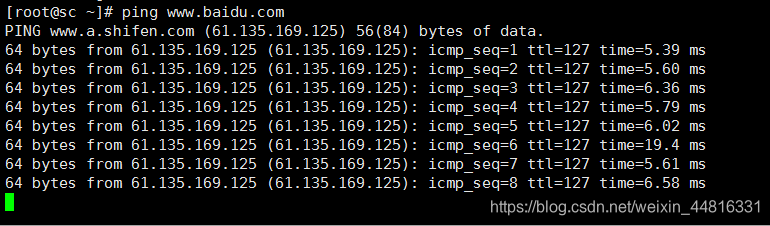
3.然后 ping 一下 DNS 的地址看看是否能 ping 通,ping 一下百度:
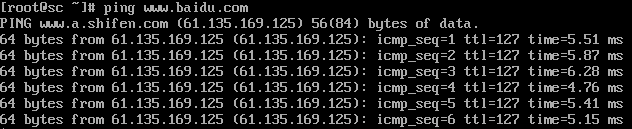
实验三:
注意:现在使用 Windows 是不能连接 B 机器的,所以现在的需求就是能够远程连接 B 机器。要实现这个需求需要通过 A 机器进行一个跳转,也就是所谓的端口映射,把 B 机器的 22 端口映射到 A 机器上。
1.打开路由转发:
[root@sc ~]# echo "1">/proc/sys/net/ipv4/ip_forward
2.添加规则,因为之前添加了一条规则,现在先把那条规则删掉以免影响操作:
[root@sc ~]# iptables -t nat -D POSTROUTING -s 192.168.100.0/24 -o ens33 -j MASQUERADE
3.第一条是发送过来的包:
[root@sc ~]# iptables -t nat -A PREROUTING -d 192.168.85.130 -p tcp --dport 1122 -j DNAT --to 192.168.100.100:22
4.第二条是反馈回去的包,这条规则是把 192.168.100.100 返回的数据包,转发到 192.168.85.130 上去,然后回到 Windows 上。
[root@sc ~]# iptables -t nat -A POSTROUTING -s 192.168.100.100 -j SNAT --to 192.168.85.130
5.添加完规则检查一下是否存在 nat 表里:
[root@sc ~]# iptables -t nat -nvL
Chain PREROUTING (policy ACCEPT 0 packets, 0 bytes)
pkts bytes target prot opt in out source destination
0 0 DNAT tcp -- * * 0.0.0.0/0 192.168.85.130 tcp dpt:1122 to:192.168.100.100:22
Chain INPUT (policy ACCEPT 0 packets, 0 bytes)
pkts bytes target prot opt in out source destination
Chain OUTPUT (policy ACCEPT 0 packets, 0 bytes)
pkts bytes target prot opt in out source destination
Chain POSTROUTING (policy ACCEPT 0 packets, 0 bytes)
pkts bytes target prot opt in out source destination
0 0 SNAT all -- * * 192.168.100.100 0.0.0.0/0 to:192.168.85.130
6.第三步,以上操作没问题后,给 B 机器设置默认网关:
[root@sc ~]#route add default gw 192.168.100.1
7.完成以上操作之后,在 XShell 里新建一个会话,连接 192.168.85.130 的 1122 端口:
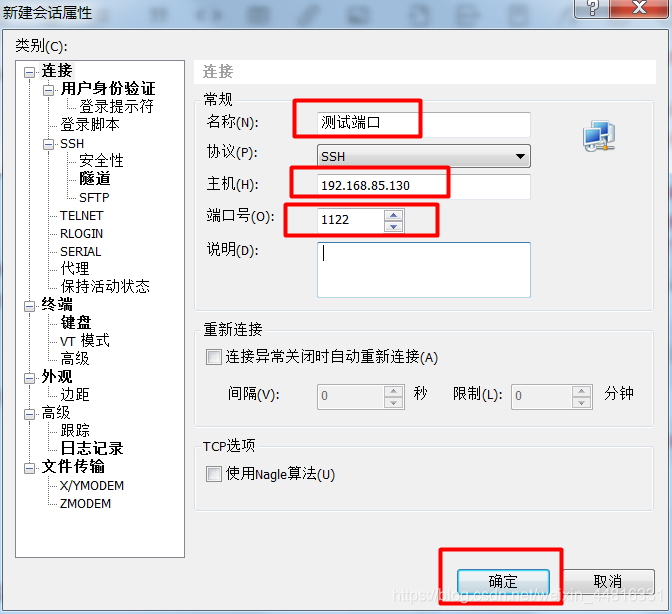
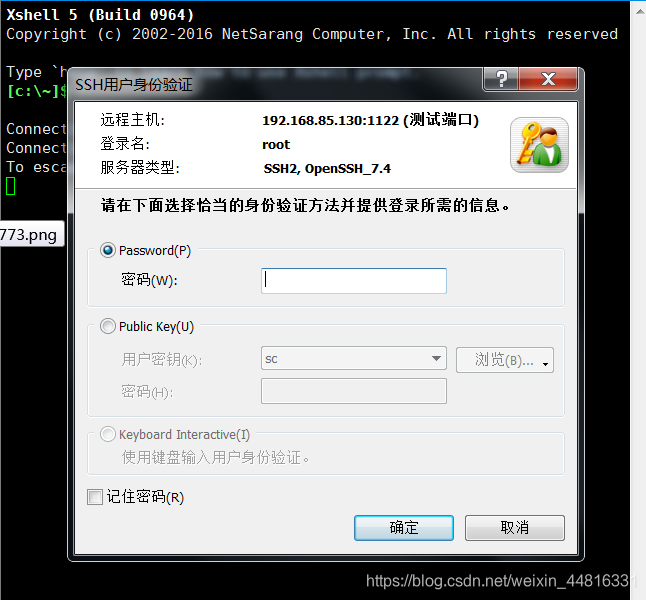
8.输入用户名,这里输入的是内网机器的用户名,不是 A 机器的用户名,因为这一步数据包实际上是通过了 A 机器上映射的 1122 端口转发到了 B 机器的 22 端口上了:
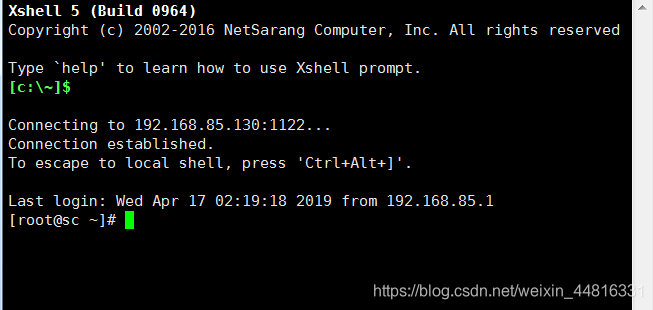
9.现在不单只外面的机器能够通过 A 机器来远程连接 B 机器,B 机器也可以连接外网:
10.19 iptables规则备份和恢复

保存和备份 iptables 规则:
service iptables save 会把规则保存到 /etc/sysconfig/iptables 里
iptables-save 可以将规则重定向保存到指定的文件中:
[root@sc ~]# iptables-save >/tmp/ipt.txt
[root@sc ~]# iptables-save >/tmp/ipt.txt #把规则保存到文件夹
[root@sc ~]# cat /tmp/ipt.txt
# Generated by iptables-save v1.4.21 on Thu Apr 18 12:26:25 2019
*filter
:INPUT ACCEPT [0:0]
:FORWARD ACCEPT [0:0]
:OUTPUT ACCEPT [641:53121]
-A INPUT -m state --state RELATED,ESTABLISHED -j ACCEPT
-A INPUT -p icmp -j ACCEPT
-A INPUT -i lo -j ACCEPT
-A INPUT -p tcp -m state --state NEW -m tcp --dport 22 -j ACCEPT
-A INPUT -j REJECT --reject-with icmp-host-prohibited
-A FORWARD -j REJECT --reject-with icmp-host-prohibited
COMMIT
# Completed on Thu Apr 18 12:26:25 2019
[root@sc ~]#
iptables-restore 则是相反,把文件里的规则恢复到 iptables 中:
[root@sc ~]# iptables-restore </tmp/ipt.txt
[root@sc ~]# iptables -F #先把 filte 表清空
[root@sc ~]# iptables -nvL #查看一下规则
Chain INPUT (policy ACCEPT 41 packets, 3096 bytes)
pkts bytes target prot opt in out source destination
Chain FORWARD (policy ACCEPT 0 packets, 0 bytes)
pkts bytes target prot opt in out source destination
Chain OUTPUT (policy ACCEPT 30 packets, 2764 bytes)
pkts bytes target prot opt in out source destination
[root@sc ~]# iptables-restore </tmp/ipt.txt #再恢复规则
[root@sc ~]# iptables -nvL
Chain INPUT (policy ACCEPT 0 packets, 0 bytes)
pkts bytes target prot opt in out source destination
5 388 ACCEPT all -- * * 0.0.0.0/0 0.0.0.0/0 state RELATED,ESTABLISHED
0 0 ACCEPT icmp -- * * 0.0.0.0/0 0.0.0.0/0
0 0 ACCEPT all -- lo * 0.0.0.0/0 0.0.0.0/0
0 0 ACCEPT tcp -- * * 0.0.0.0/0 0.0.0.0/0 state NEW tcp dpt:22
0 0 REJECT all -- * * 0.0.0.0/0 0.0.0.0/0 reject-with icmp-host-prohibited
Chain FORWARD (policy ACCEPT 0 packets, 0 bytes)
pkts bytes target prot opt in out source destination
0 0 REJECT all -- * * 0.0.0.0/0 0.0.0.0/0 reject-with icmp-host-prohibited
Chain OUTPUT (policy ACCEPT 4 packets, 464 bytes)
pkts bytes target prot opt in out source destination
[root@sc ~]#
10.20 firewalld的9个zone

firewalld 是 CentOS7 的防火墙机制,之前我们学习 iptables 时,把 firewalld 防火墙禁掉了,所以现在我们要反着操作一下,开启 firewalld 关闭 iptables:
关闭 iptables :
[root@sc ~]# systemctl disable iptables
Removed symlink /etc/systemd/system/basic.target.wants/iptables.service.
[root@sc ~]# systemctl stop iptables
[root@sc ~]#
开启 firewalld :
[root@sc ~]# systemctl enable firewalld
Created symlink from /etc/systemd/system/dbus-org.fedoraproject.FirewallD1.service to /usr/lib/systemd/system/firewalld.service.
Created symlink from /etc/systemd/system/multi-user.target.wants/firewalld.service to /usr/lib/systemd/system/firewalld.service.
[root@sc ~]# systemctl start firewalld
[root@sc ~]#
现在使用 iptables -nvL 查看 iptables 的规则会发现多了很多规则:
[root@sc ~]# iptables -nvL #查看一下 firewalld 的规则
Chain INPUT (policy ACCEPT 0 packets, 0 bytes)
pkts bytes target prot opt in out source destination
35 2564 ACCEPT all -- * * 0.0.0.0/0 0.0.0.0/0 ctstate RELATED,ESTABLISHED
0 0 ACCEPT all -- lo * 0.0.0.0/0 0.0.0.0/0
2 184 INPUT_direct all -- * * 0.0.0.0/0 0.0.0.0/0
2 184 INPUT_ZONES_SOURCE all -- * * 0.0.0.0/0 0.0.0.0/0
2 184 INPUT_ZONES all -- * * 0.0.0.0/0 0.0.0.0/0
0 0 DROP all -- * * 0.0.0.0/0 0.0.0.0/0 ctstate INVALID
0 0 REJECT all -- * * 0.0.0.0/0 0.0.0.0/0 reject-with icmp-host-prohibited
Chain FORWARD (policy ACCEPT 0 packets, 0 bytes)
pkts bytes target prot opt in out source destination
0 0 ACCEPT all -- * * 0.0.0.0/0 0.0.0.0/0 ctstate RELATED,ESTABLISHED
0 0 ACCEPT all -- lo * 0.0.0.0/0 0.0.0.0/0
0 0 FORWARD_direct all -- * * 0.0.0.0/0 0.0.0.0/0
0 0 FORWARD_IN_ZONES_SOURCE all -- * * 0.0.0.0/0 0.0.0.0/0
0 0 FORWARD_IN_ZONES all -- * * 0.0.0.0/0 0.0.0.0/0
0 0 FORWARD_OUT_ZONES_SOURCE all -- * * 0.0.0.0/0 0.0.0.0/0
0 0 FORWARD_OUT_ZONES all -- * * 0.0.0.0/0 0.0.0.0/0
0 0 DROP all -- * * 0.0.0.0/0 0.0.0.0/0 ctstate INVALID
0 0 REJECT all -- * * 0.0.0.0/0 0.0.0.0/0 reject-with icmp-host-prohibited
Chain OUTPUT (policy ACCEPT 26 packets, 2180 bytes)
pkts bytes target prot opt in out source destination
26 2180 OUTPUT_direct all -- * * 0.0.0.0/0 0.0.0.0/0
Chain FORWARD_IN_ZONES (1 references)
pkts bytes target prot opt in out source destination
0 0 FWDI_public all -- ens37 * 0.0.0.0/0 0.0.0.0/0 [goto]
0 0 FWDI_public all -- ens33 * 0.0.0.0/0 0.0.0.0/0 [goto]
0 0 FWDI_public all -- + * 0.0.0.0/0 0.0.0.0/0 [goto]
Chain FORWARD_IN_ZONES_SOURCE (1 references)
pkts bytes target prot opt in out source destination
Chain FORWARD_OUT_ZONES (1 references)
pkts bytes target prot opt in out source destination
0 0 FWDO_public all -- * ens37 0.0.0.0/0 0.0.0.0/0 [goto]
0 0 FWDO_public all -- * ens33 0.0.0.0/0 0.0.0.0/0 [goto]
0 0 FWDO_public all -- * + 0.0.0.0/0 0.0.0.0/0 [goto]
Chain FORWARD_OUT_ZONES_SOURCE (1 references)
pkts bytes target prot opt in out source destination
Chain FORWARD_direct (1 references)
pkts bytes target prot opt in out source destination
Chain FWDI_public (3 references)
pkts bytes target prot opt in out source destination
0 0 FWDI_public_log all -- * * 0.0.0.0/0 0.0.0.0/0
0 0 FWDI_public_deny all -- * * 0.0.0.0/0 0.0.0.0/0
0 0 FWDI_public_allow all -- * * 0.0.0.0/0 0.0.0.0/0
0 0 ACCEPT icmp -- * * 0.0.0.0/0 0.0.0.0/0
Chain FWDI_public_allow (1 references)
pkts bytes target prot opt in out source destination
Chain FWDI_public_deny (1 references)
pkts bytes target prot opt in out source destination
Chain FWDI_public_log (1 references)
pkts bytes target prot opt in out source destination
Chain FWDO_public (3 references)
pkts bytes target prot opt in out source destination
0 0 FWDO_public_log all -- * * 0.0.0.0/0 0.0.0.0/0
0 0 FWDO_public_deny all -- * * 0.0.0.0/0 0.0.0.0/0
0 0 FWDO_public_allow all -- * * 0.0.0.0/0 0.0.0.0/0
Chain FWDO_public_allow (1 references)
pkts bytes target prot opt in out source destination
Chain FWDO_public_deny (1 references)
pkts bytes target prot opt in out source destination
Chain FWDO_public_log (1 references)
pkts bytes target prot opt in out source destination
Chain INPUT_ZONES (1 references)
pkts bytes target prot opt in out source destination
0 0 IN_public all -- ens37 * 0.0.0.0/0 0.0.0.0/0 [goto]
2 184 IN_public all -- ens33 * 0.0.0.0/0 0.0.0.0/0 [goto]
0 0 IN_public all -- + * 0.0.0.0/0 0.0.0.0/0 [goto]
Chain INPUT_ZONES_SOURCE (1 references)
pkts bytes target prot opt in out source destination
Chain INPUT_direct (1 references)
pkts bytes target prot opt in out source destination
Chain IN_public (3 references)
pkts bytes target prot opt in out source destination
2 184 IN_public_log all -- * * 0.0.0.0/0 0.0.0.0/0
2 184 IN_public_deny all -- * * 0.0.0.0/0 0.0.0.0/0
2 184 IN_public_allow all -- * * 0.0.0.0/0 0.0.0.0/0
0 0 ACCEPT icmp -- * * 0.0.0.0/0 0.0.0.0/0
Chain IN_public_allow (1 references)
pkts bytes target prot opt in out source destination
2 184 ACCEPT tcp -- * * 0.0.0.0/0 0.0.0.0/0 tcp dpt:22 ctstate NEW
Chain IN_public_deny (1 references)
pkts bytes target prot opt in out source destination
Chain IN_public_log (1 references)
pkts bytes target prot opt in out source destination
Chain OUTPUT_direct (1 references)
pkts bytes target prot opt in out source destination
[root@sc ~]#
firewalld 默认有 9 个 zone,zone 是 firewalld 的一个单位,默认的是 public zone ,每个 zone 都是一个规则集,规则集就是 zone 里面自带的一些规则的一个集合体,使用 firewall-cmd --get-zones 命令可以查看所有的 zone :
[root@sc ~]# firewall-cmd --get-zones #查看 firewalld 里都有那些 zone
block dmz drop external home internal public trusted work
[root@sc ~]#
firewall-cmd --get-default-zone 命令可以查看默认的 zone :
[root@sc ~]# firewall-cmd --get-default-zone #查看 firewalld 里默认的 zone 是谁
public
[root@sc ~]#

10.21 firewalld关于zone的操作

给 firewalld 设置默认的 zone:
[root@sc ~]# firewall-cmd --set-default-zone=work #设置默认的 zone 是 work
success #成功
[root@sc ~]# firewall-cmd --get-default-zone #查看默认的 zone
work
[root@sc ~]#
查看指定网卡的 zone :
[root@sc ~]# firewall-cmd --get-zone-of-interface=ens33 #ens33 默认的 zone 是 work
work
[root@sc ~]# firewall-cmd --get-zone-of-interface=ens37 #查看 ens37
work
[root@sc ~]# firewall-cmd --get-zone-of-interface=lo
no zone
[root@sc ~]#
- 如果你新添加的网卡 ens37 显示的是 no zone 的话。
- 你就需要进入到 /etc/sysconfig/network-scripts/ 目录下,把正常的网卡 ens33 配置文件复制一份为你新网卡名称命名的文件 ens37 。
- 然后修改一下 ens37 配置文件为你新网卡的信息。
- 然后重启一下网络服务:service network restart
- 再重启一下firewalld的服务:systemctl restart firewalld
给指定网卡 ens37 设定 zone 为 dmz :
[root@sc ~]# firewall-cmd --zone=dmz --add-interface=ens37
The interface is under control of NetworkManager, setting zone to 'dmz'.
success
[root@sc ~]# firewall-cmd --get-zone-of-interface=ens37
dmz
[root@sc ~]# firewall-cmd --zone=public --add-interface=lo
success
[root@sc ~]# firewall-cmd --get-zone-of-interface=lo
public
[root@sc ~]#
针对网卡更改 zone :
[root@sc ~]# firewall-cmd --zone=dmz --change-interface=lo
success
[root@sc ~]# firewall-cmd --get-zone-of-interface=lo
dmz
[root@sc ~]#
针对网卡删除 zone :
[root@sc ~]# firewall-cmd --zone=block --add-interface=ens37 #更改 ens37 的 zone 为 block
The interface is under control of NetworkManager, setting zone to 'block'.
success
[root@sc ~]# firewall-cmd --zone=block --remove-interface=ens37 #删除 ens37 的 zone
The interface is under control of NetworkManager, setting zone to default.
success
[root@sc ~]# firewall-cmd --get-zone-of-interface=ens37 #查看 ens37 的 zone 变成什么
work #变为默认的 zone 了
[root@sc ~]#
查看系统所有网卡所在的 zone :
[root@sc ~]# firewall-cmd --get-active-zones
dmz
interfaces: lo
work
interfaces: ens33 ens37
[root@sc ~]#
10.22 firewalld关于service的操作

所谓service就是zone下面的一个子单元,可以理解为一个指定的端口,因为防火墙无外乎就是对某个端口进行限制,例如http连接的是80端口、https连接的是43端口、ssh连接的22端等等。
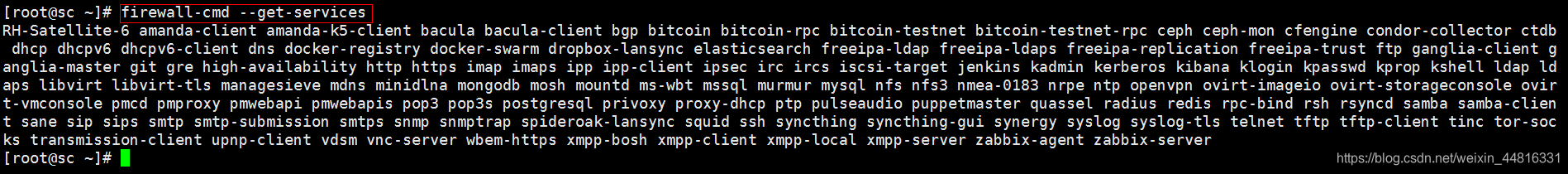
查看所有的 service :
查看当前的 zone 里都有哪些 service :
[root@sc ~]# firewall-cmd --get-default-zone
work
[root@sc ~]# firewall-cmd --list-service
ssh dhcpv6-client
[root@sc ~]#
查看指定的 zone下面有哪些 service :
[root@sc ~]# firewall-cmd --zone=public --list-service
ssh dhcpv6-client
[root@sc ~]# firewall-cmd --zone=block --list-service
[root@sc ~]# firewall-cmd --zone=work --list-service
ssh dhcpv6-client
[root@sc ~]#
把 http 增加到 public 的 zone 下面:
[root@sc ~]# firewall-cmd --zone=public --add-service=http
success
[root@sc ~]# firewall-cmd --zone=public --list-services
ssh dhcpv6-client http
[root@sc ~]#
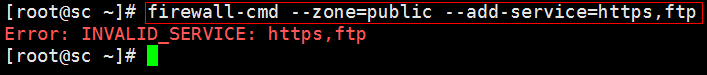
同时加两个端口就会报错:
现在仅仅是在内存里把 zone 增加了 service ,重启之后就会失效,想要永久有效,就要保存到 /etc/firewalld/zones/ 目录下,每次更改完都要备份一个配置文件:
[root@sc ~]# firewall-cmd --zone=public --add-service=ftp
success
[root@sc ~]# firewall-cmd --zone=public --add-service=ftp --permanent
success
[root@sc ~]# ls /etc/firewalld/zones/
public.xml public.xml.old
success
[root@sc ~]# cat /etc/firewalld/zones/public.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<zone>
<short>Public</short>
<description>For use in public areas. You do not trust the other computers on networks to not harm your computer. Only selected incoming connections are accepted.</description>
<service name="ssh"/>
<service name="dhcpv6-client"/>
<service name="ftp"/>
<service name="http"/>
</zone>
[root@sc ~]# firewall-cmd --zone=public --list-services
ssh dhcpv6-client http ftp
[root@sc ~]#
/usr/lib/firewalld/zones/ 目录下存放的是 zone 配置文件的模板:
[root@sc ~]# ls /usr/lib/firewalld/zones/
block.xml dmz.xml drop.xml external.xml home.xml internal.xml public.xml trusted.xml work.xml
[root@sc ~]#
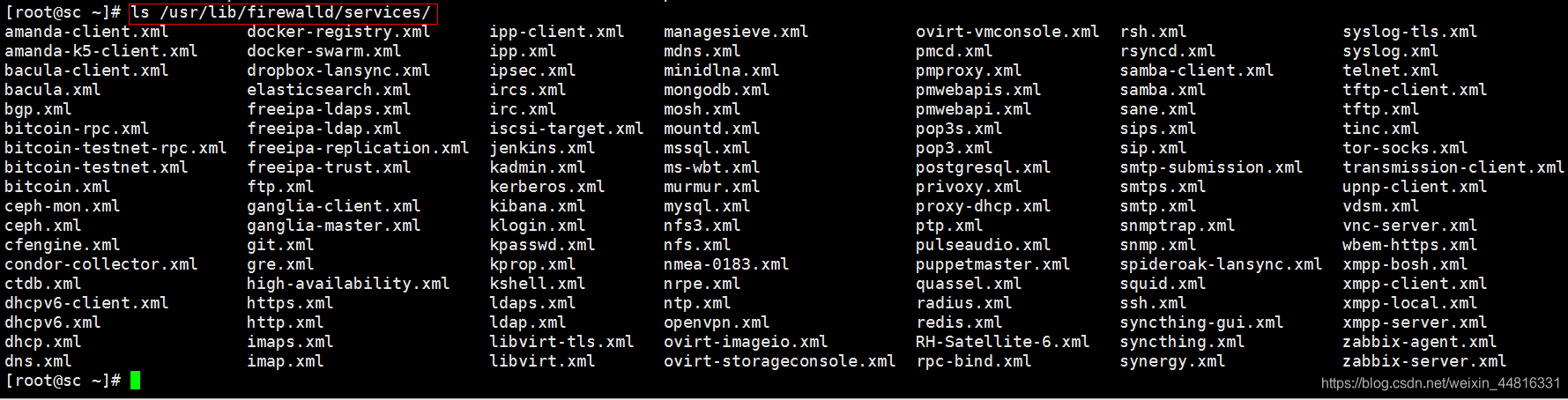
实验一 : 把ftp服务自定义端口1121,需要在 work zone 下面放行 ftp:
第一步,把 ftp 的配置文件拷贝到 /etc/firewalld/services/ 目录下:
[root@sc ~]# cp /usr/lib/firewalld/services/ftp.xml /etc/firewalld/services/
[root@sc ~]# vi /etc/firewalld/services/ftp.xml
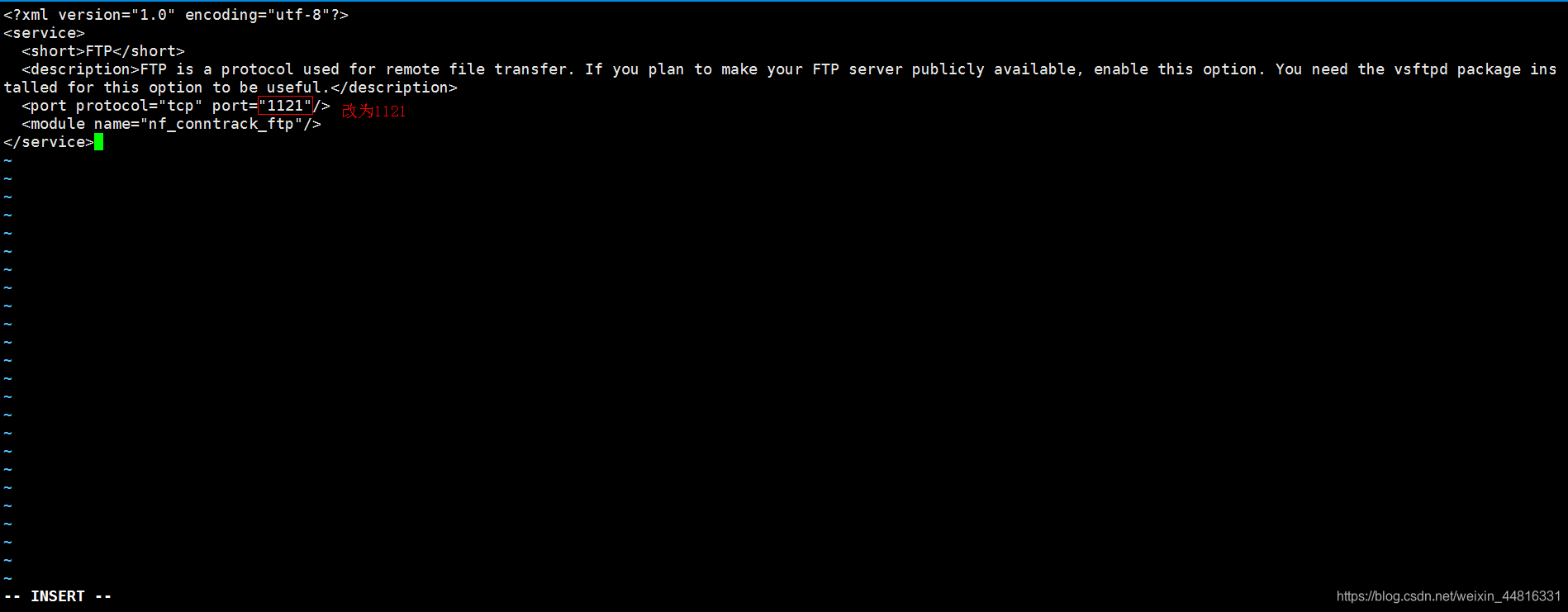
第二步,编辑 /etc/firewalld/services/ftp.xml 文件:
第三步,把 /usr/lib/firewalld/zones/work.xml 复制到 /etc/firewalld/zones/ 目录下:
[root@sc ~]# cp /usr/lib/firewalld/zones/work.xml /etc/firewalld/zones/
[root@sc ~]# vim /etc/firewalld/zones/work.xml
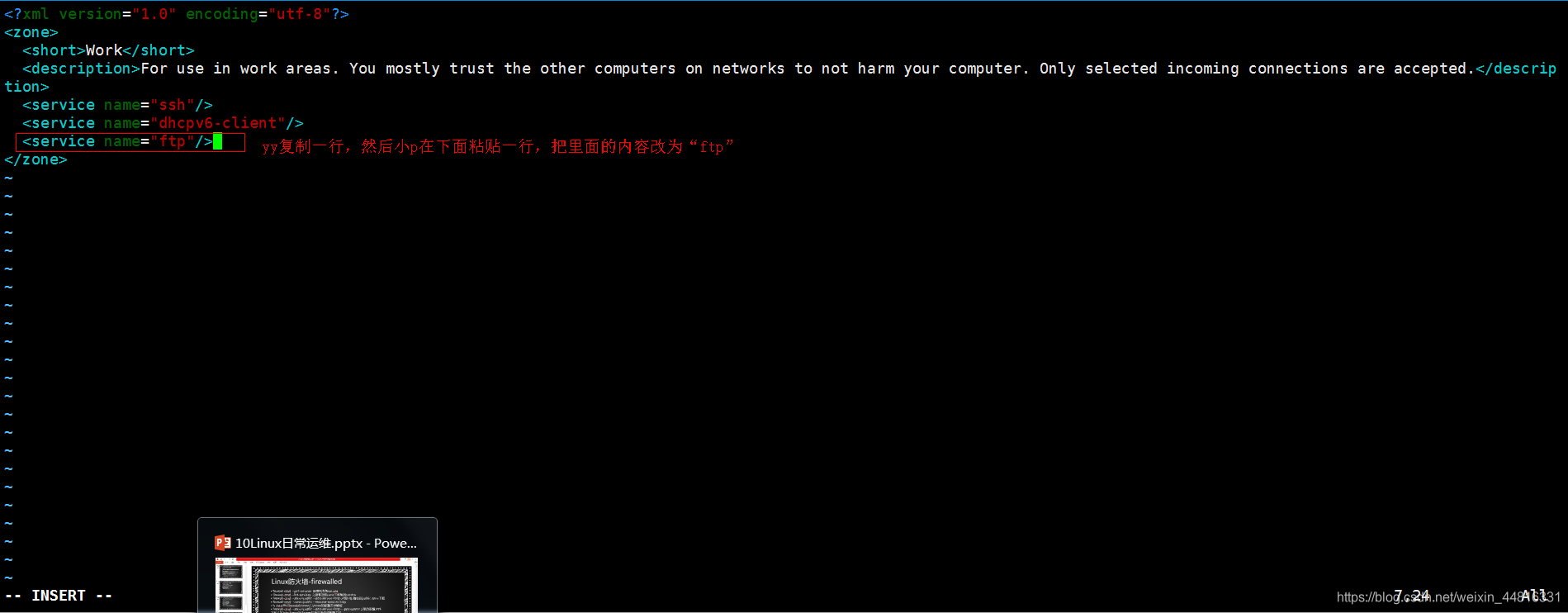
第四步,编辑 /etc/firewalld/zones/work.xml 文件:
配置文件修改完成后,重新加载一下:
[root@sc ~]# firewall-cmd --reload
success
[root@sc ~]# firewall-cmd --zone=work --list-services
ssh dhcpv6-client ftp
[root@sc ~]#
总结:
firewalled 服务有两个角色,一个是 zone 一个是 service,zone 是 firewalled 的一个规则集合,每个 zone 里都会有对应的 iptables 规则。每个 zone 下面都有一些service,这些 service 就像是这个 zone 的白名单,放行这些service。如果遇到需求,需要放行某个服务,就可以把这个服务增加到配置文件里去,再重新 reload 就可以了,操作方式和上面的那个例子一样。
- 开启防火墙并添加 nginx 80 端口
[root@test01 nginx]# firewall-cmd --add-port=80/tcp --permanent
success
[root@test01 nginx]# firewall-cmd --reload
success
来源:https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_44816331/article/details/98172457