实验报告(简单记事本的实现)
实验任务详情:
完成简单记事本的练习。
(1)实验代码:
package 测试;
import java.awt.EventQueue;
import java.awt.FileDialog;
import javax.swing.JFrame;
import javax.swing.JMenu;
import java.awt.BorderLayout;
import java.awt.event.ActionEvent;
import java.awt.event.ActionListener;
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.BufferedWriter;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileReader;
import java.io.FileWriter;
import java.io.IOException;
import javax.swing.JMenuBar;
import javax.swing.JOptionPane;
import javax.swing.JTextArea;
import javax.swing.JScrollPane;
import javax.swing.JMenuItem;
public class NotePad {
private JFrame frame;
private JTextArea text;
private File file;
public static void main(String[] args) {
EventQueue.invokeLater(new Runnable() {
public void run() {
try {
NotePad window = new NotePad();
window.frame.setVisible(true);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
});
}
public NotePad() {
initialize();
}
private void initialize() {
frame = new JFrame("记事本");
frame.setBounds(100, 100, 960, 720);
frame.setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE);
JMenuBar menuBar = new JMenuBar();
frame.setJMenuBar(menuBar);
JMenu mne = new JMenu("\u6587\u4EF6(F)");
menuBar.add(mne);
JMenuItem new_new = new JMenuItem("\u65B0\u5EFA");
mne.add(new_new);
//监听和处理新建
new_new.addActionListener(new ActionListener() {
public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e) {
int ret = JOptionPane.showOptionDialog(null, "已经打开的文件尚未保存,需要保存吗?", "提示",
JOptionPane.YES_NO_CANCEL_OPTION,
JOptionPane.WARNING_MESSAGE, null, null, null);
if(ret == JOptionPane.NO_OPTION){
text.setText(null);
}
if(ret == JOptionPane.YES_OPTION){
//new JFileChooser();
FileDialog fd = new FileDialog(frame, "保存", FileDialog.SAVE);
if(file==null)
{
fd.setVisible(true);
String dirPath = fd.getDirectory();
String fileName = fd.getFile();
if(dirPath==null || fileName==null)
return ;
file = new File(dirPath,fileName);
}
try
{
BufferedWriter bufw = new BufferedWriter(new FileWriter(file));
String text1 = text.getText();
bufw.write(text1);
bufw.close();
}
catch (IOException ex)
{
throw new RuntimeException();
}
text.setText(null);
}
}
});
JMenuItem open = new JMenuItem("\u6253\u5F00");
mne.add(open);
//监听和处理打开
open.addActionListener(new ActionListener() {
public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e) {
FileDialog fd = new FileDialog(frame, "打开", FileDialog.LOAD);
fd.setVisible(true);
String dir = fd.getDirectory();
String f = fd.getFile();
File f_open = new File(dir, f);
try {
BufferedReader buf = new BufferedReader(new FileReader(f_open));
String line = null;
while((line=buf.readLine())!=null) {
text.append(line+"\r\n");
}
buf.close();
} catch (IOException e1) {
e1.printStackTrace();
}
}
});
JMenuItem save = new JMenuItem("\u4FDD\u5B58");
mne.add(save);
//监听和处理保存
save.addActionListener(new ActionListener() {
public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent arg0) {
FileDialog fd = new FileDialog(frame, "保存", FileDialog.SAVE);
fd.setVisible(true);
String dir = fd.getDirectory();
String f = fd.getFile();
File file = new File(dir, f);
try {
BufferedWriter buf = new BufferedWriter(new FileWriter(file));
String s = text.getText();
buf.write(s);
buf.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
});
JMenuItem exit = new JMenuItem("\u9000\u51FA");
mne.add(exit);
//监听和处理退出
exit.addActionListener(new ActionListener() {
public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent arg0) {
String s = text.getText();
if(s==null) {
System.exit(0);
}
else {
int ret = JOptionPane.showOptionDialog(null, "是否将更改保存到 无标题?", "记事本",
JOptionPane.YES_NO_CANCEL_OPTION,
JOptionPane.WARNING_MESSAGE, null, null, null);
if(ret == JOptionPane.NO_OPTION){
System.exit(0);
}
if(ret == JOptionPane.YES_OPTION){
FileDialog fd = new FileDialog(frame, "保存", FileDialog.SAVE);
fd.setVisible(true);
String dir = fd.getDirectory();
String f = fd.getFile();
File file = new File(dir, f);
try {
BufferedWriter buf = new BufferedWriter(new FileWriter(file));
String s1 = text.getText();
buf.write(s1);
buf.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.exit(0);
}
}
}
});
JScrollPane scrollPane = new JScrollPane();
frame.getContentPane().add(scrollPane, BorderLayout.CENTER);
text = new JTextArea();
scrollPane.setViewportView(text);
}
}
(2)实验运行结果截图:

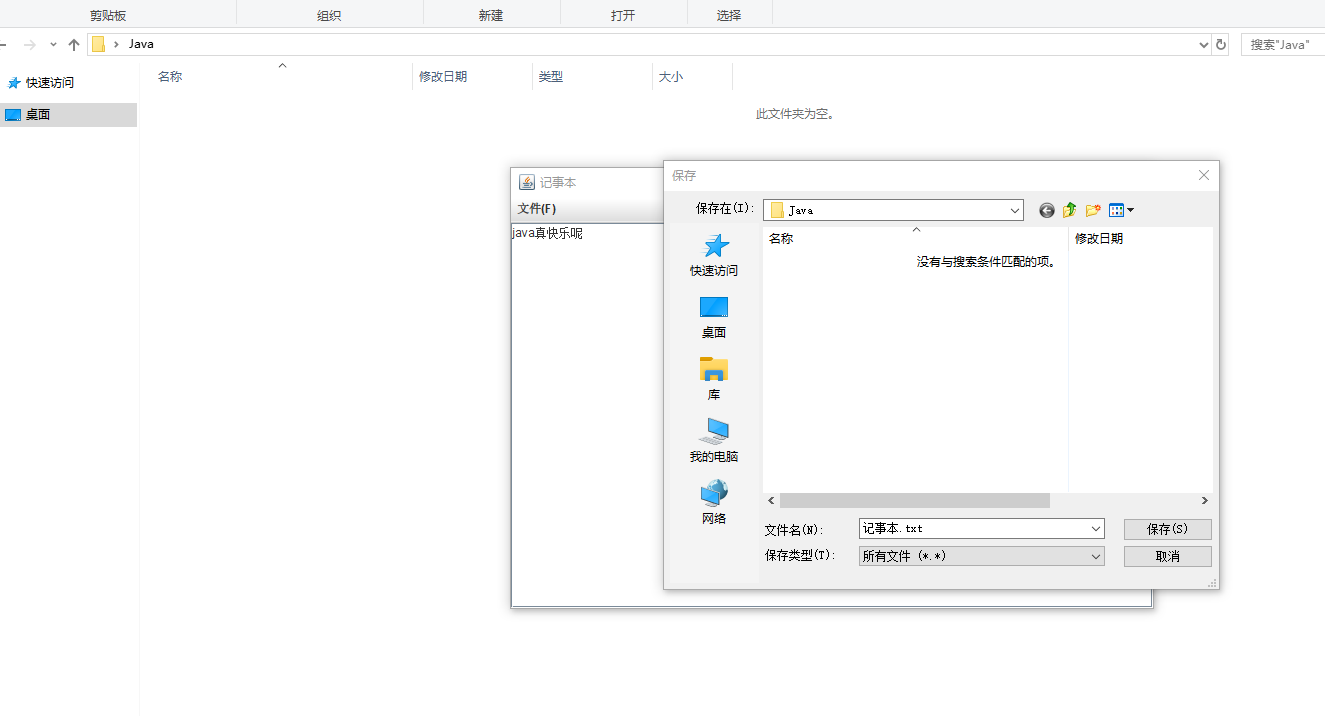
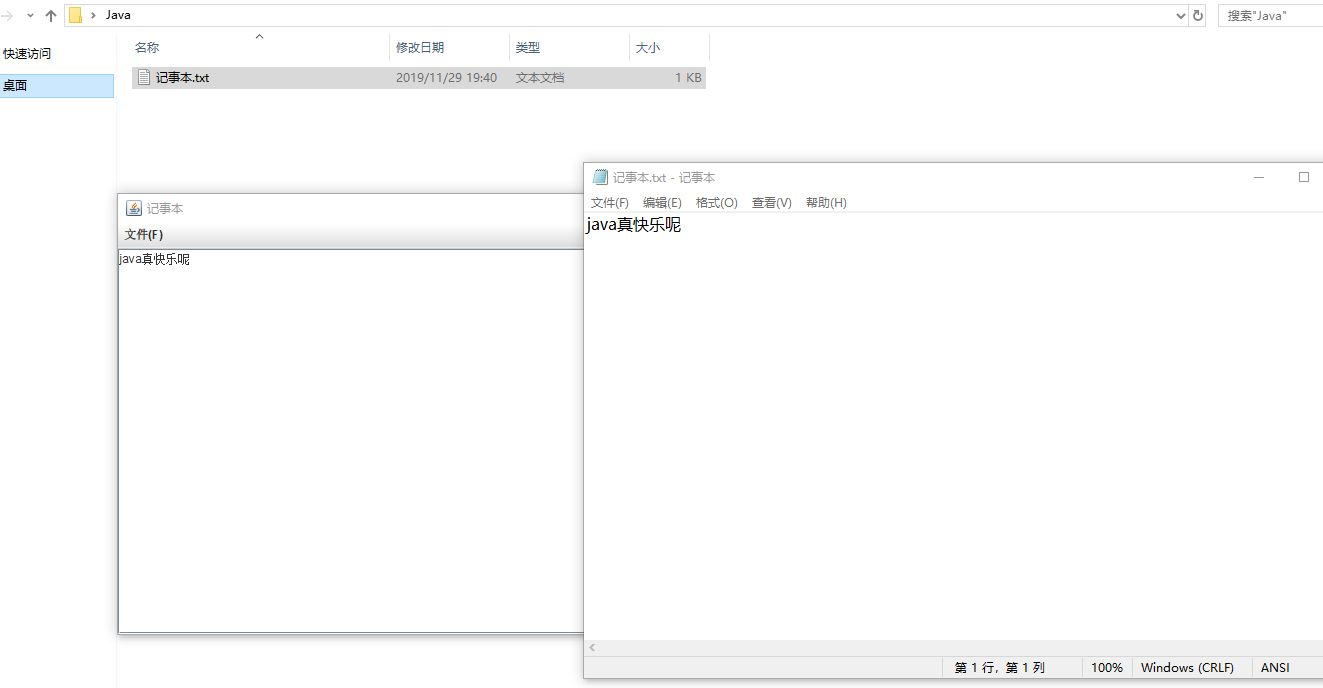

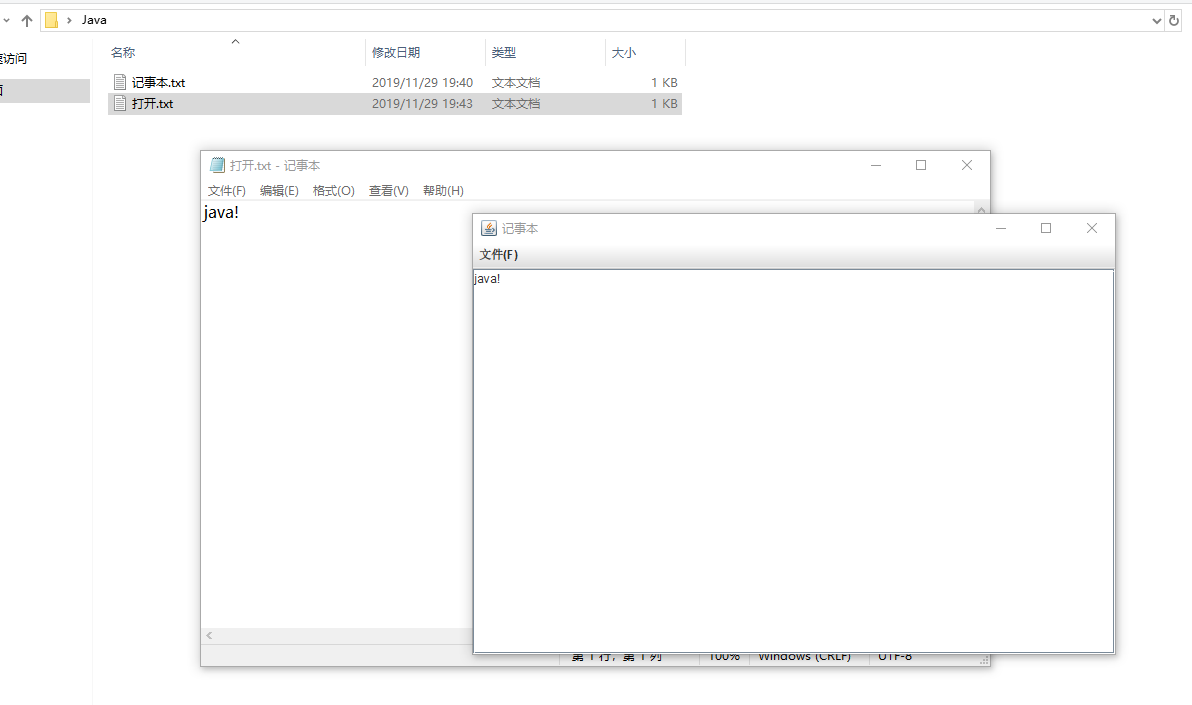
(3)实验中遇到的问题:
做这个记事本,我发现自己对于这些代码的运用还不太熟练,出现了大量的错误,勉强完成了这个代码,但是还是会有些bug,比如说读取的时候有时候会出现乱码,不太清楚应该如何解决.实力不行,还需再练.
第十四周课程总结
这周主要学习了JDBC
这周学习的内容:
1.JDBC
- JDBC(Java Database Connectivity,Java数据库连接),提供了一种与平台无关的用于执行SQL语句的标准Java API,可以方便的实现多种关系型数据库的统一操作,它由一组用Java语言编写的类和接口组成。
- 在实际开发中可以直接使用JDBC进行各个数据库的连接与操作,而且可以方便的向数据库中发送各种SQL命令。在JDBC中提供的是一套标准的接口,这样,各个支持JAVA的数据库生产商只要按照此接口提供相应的实现,则就都可以使用JDBC进行操作。极大的体现了JAVA的可移植性的设计思想。
2.JDBC驱动分类
JDBC本身提供的是一套数据库操作标准,而这些标准又需要各个数据库厂商实现,所以针对于每一个数据库厂商都会提供一个JDBC的驱动程序,目前比较常见的JDBC驱动程序可分为以下四类:
(1).JDBC-ODBC桥驱动
JDBC-ODBC是SUN提供的一个标准的JDBC操作,直接利用微软的ODBC进行数据库的连接操作,但是,这种操作性能较低,所以通常情况下是不推荐使用这种方式进行操作的。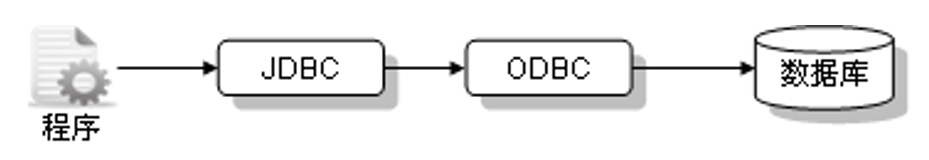
(2).JDBC本地驱动
直接使用各个数据库生产商提供的JDBC驱动程序,但是因为其只能应用在特定的数据库上,会丧失掉程序的可移植性,但是这样操作的性能较高。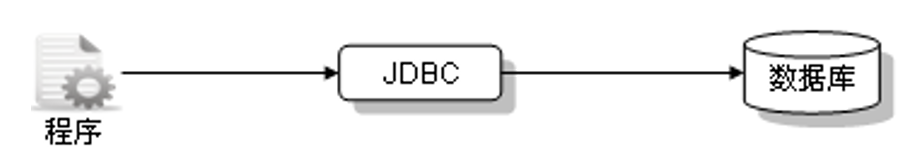
(3).JDBC网络驱动
这种驱动程序将JDBC转换为与DBMS无关的网络协议,之后这种协议又被某个服务器转换为一种DBMS协议。这种网络服务器中间件能够将它的纯Java客户机连接到多种不同的数据库上。所用的具体协议取决于提供者。通常,这是最为灵活的JDBC驱动程序。
(4).本地协议纯JDBC驱动
这种类型的驱动程序将JDBC调用直接转换为DBMS所使用的网络协议。这将允许从客户机机器上直接调用DBMS服务器,是Intranet访问的一个很实用的解决方法。
3.JDBC的主要操作类及接口