0. 字节流与二进制文件
我的代码
public class WriterStu {
public static void main(String[] args) {
DataOutputStream dos = null;
Student[] stus = new Student[100];
Student d1 = new Student(1, "x", 18, 99.5);
Student d2 = new Student(2, "x", 19, 100.0);
Student d3 = new Student(3, "x", 20, 59.5);
try (FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream(new File("e:/Student.data"))) {
dos = new DataOutputStream(fos);
for (Student student : stus) {
dos.writeInt(student.getId());
dos.writeUTF(student.getName());
dos.writeInt(student.getAge());
dos.writeDouble(student.getGrade());
}
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
try (DataInputStream dis = new DataInputStream(new FileInputStream("e:/Student.data"))) {
int id = dis.readInt();
String name = dis.readUTF();
int age = dis.readInt();
double grade = dis.readDouble();
Student stu=new Student(id,name,age,grade);
System.out.println(stu);
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
我的总结
文本文件中的数据都是以字符的形式进行组织,通常可以逐行或全部读取到一个字符串变量中。二进制文件可以存储int/double/char等基本数据类型。
1. 字符流与文本文件:使用 PrintWriter(写),BufferedReader(读)
我的代码
4.
String fileName1="e:/data.txt";
try(
FileOutputStream fos=new FileOutputStream(fileName1);
ObjectOutputStream oos=new ObjectOutputStream(fos))
{
Student s=new Student(5,"l",12,85);
oos.writeObject(s);
}
catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
try(
FileInputStream fis=new FileInputStream(fileName1);
ObjectInputStream ois=new ObjectInputStream(fis))
{
Student newStudent =(Student)ois.readObject();
System.out.println(newStudent);
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
我的总结
将对象流写在txt中会发生乱码,改为dat格式则不会发生乱码。
2. 缓冲流(结合使用JUint进行测试)
我的代码
public class PrintWriterTest {
public static void main(String[] args) throws FileNotFoundException {
File file = new File("e:/data.txt");
if(file.exists())
{
System.out.println("文件已存在!");
System.exit(0);
}
PrintWriter pw=new PrintWriter(file);
Random r=new Random(100);
for(int i=0;i<1000_0000;i++) {
int j=r.nextInt(11);
pw.println(j);
}
pw.close();
}
}
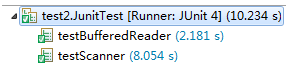
JunitTest
public class JunitTest {
@Test
public void testBufferedReader() {
BufferedReader br = null;
int n = 0, sum = 0;
double average = 0;
try {
br = new BufferedReader(new FileReader("e:/data.txt"));
String line = null;
try {
while ((line = br.readLine()) != null) {
int num = Integer.parseInt(line);
n++;
sum += num;
}
average = sum / n;
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
System.out.format("%d %d %.5f", n, sum, average);
System.out.println();
if (br != null) {
try {
br.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
@Test
public void testScanner() {
File file = new File("e:/data.txt");
Scanner sc = null;
int n = 0, sum = 0;
double average = 0;
try {
sc = new Scanner(file);
while (sc.hasNext()) {
int num = sc.nextInt();
sum+=num;
n++;
}
average = sum / n;
System.out.format("%d %d %.5f", n, sum, average);
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
我的总结
使用BufferedReader更快,BufferedReader使用缓冲可以减少IO次数,因为IO操作很耗时间,所以读取速度变快。
3. 字节流之对象流
我的代码
public static void writeStudent(List<Student> stuList) {
String fileName = "e:/data.txt";
try (FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream(fileName);
ObjectOutputStream ois = new ObjectOutputStream(fos)) {
ois.writeObject(stuList);
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e1) {
e1.printStackTrace();
}
}
public static List<Student> readStudents(String fileName) {
List<Student> stuList = new ArrayList<>();
try (FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream(fileName); ObjectInputStream ois = new ObjectInputStream(fis)) {
stuList = (List<Student>) ois.readObject();
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e1) {
e1.printStackTrace();
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return stuList;
}
我的总结
ObjectOutputStream 和 ObjectInputStream 分别与 FileOutputStream 和 FileInputStream 一起使用时,可以为应用程序提供对对象图形的持久存储。
5. 文件操作
我的代码
import java.io.File;
import java.nio.file.Path;
import java.nio.file.Paths;
public class Files {
Path dir=Paths.get("e:/data.txt");
public static void findFile(Path dir,String fileName) {
File file =dir.toFile();
File[] files =file.listFiles();
for(File file1:files) {
if(file1.isDirectory()) {
findFile(file1.toPath(),fileName);
}else {
if(file1.equals(new File(fileName))) {
System.out.println("Found:");
System.out.println(file1.getAbsolutePath());
}
}
}
}
}
我的总结
File类和Path类可以相互转换,Paths类可以直接获得Path对象,不需要new Path。
6. 正则表达式
判断一个给定的字符串是否是10进制数字格式
我的代码
import java.util.regex.Pattern;
public class testIsDigit {
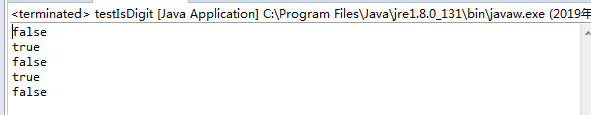
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println(isDigit("123a"));
System.out.println(isDigit("-123"));
System.out.println(isDigit("a123a"));
System.out.println(isDigit("123"));
System.out.println(isDigit("-"));
}
public static boolean isDigit(String s) {
return Pattern.matches("^-?\\d+$", s);
}
}
我的总结
熟悉正则表达式的语法可以帮助我们更加简便得编写代码。