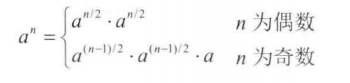3-1 数组中重复的数字

每遍历数组中的一个数字,就让其归位(放置在正确的数组下标)。当在归位的过程中,发现该数组下标所存放的数字和当前要归位的数字相同时,则发生了重复,返回该数字。
空间复杂度O(1),时间复杂度O(n)。
public class FindDuplicateNum_3 {
public static boolean findDuplicateNum(int[] arr, int length, int[] dup) {
if (arr == null || length <= 0) {
return false;
}
//时间复杂度O(n)
for (int i = 0; i < length; i++) {
//每个数字最多交换2次
while (arr[i] != i) {
if (arr[i] == arr[arr[i]]) {
dup[0] = arr[i];
return true;
}
swap(arr, i, arr[i]);
}
}
return false;
}
private static void swap(int[] arr, int i, int j) {
int tmp = arr[i];
arr[i] = arr[j];
arr[j] = tmp;
}
}
3-2 不修改数组找出重复数字

空间复杂度O(1),采用类似二分查找的算法,时间复杂度O(nlogn)。
思路:将1~ n上的数字划分成两块:1~ m和m+1~ n,然后统计数组中该区间上的数字个数,如果数字个数大于区间长度,则发生了重复,然后在该区间上继续二分,直至区间长度等于1。
//不修改数组找出重复数字
public static int findDuplicateNumNoEdit(int[] arr, int length) {
if (arr == null || length <= 0) {
return -1;
}
int start = 1;
int end = length - 1;
while (start <= end) {
int mid = start + ((end - start) >> 1);
int count = getCount(arr, length, start, mid);
//System.out.println(mid+" "+count);
if (start == end) {
if (count > 1) {
return start;
} else {
return -1;
}
}
if (count > (mid - start + 1)) {
end = mid;
} else {
start = mid + 1;
}
}
return -1;
}
private static int getCount(int[] arr, int length, int start, int end) {
int count = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < length; i++) {
if (arr[i] >= start && arr[i] <= end) {
count++;
}
}
return count;
}
4 二维数组查找

从左下或者右上角开始查找,每次判断可以剔除一行或者是一列,时间复杂度O(n+m)
public static boolean Find(int target, int[][] array) {
/*左下查找*/
int rows = array.length;
if (rows == 0) {
return false;
}
int columns = array[0].length;
if (columns == 0) {
return false;
}
int column = 0;
int row = rows - 1;
//注意数组边界
while (row >= 0 && column < columns) {
if (target == array[row][column]) {
return true;
} else if (target < array[row][column]) {
row--;
} else {
column++;
}
}
return false;
}
5 替换空格

先统计出字符串中的空格数量,然后计算出替换后的字符串长度,从后往前遍历字符串,依次填充。
public static String replaceBlankSpace_2(String str) {
if (str == null) {
return null;
}
char[] chars = str.toCharArray();
int count = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < chars.length; i++) {
if (chars[i] == ' ') {
count++;
}
}
int newLength = chars.length + (count << 1);
int p1 = chars.length - 1;
int p2 = newLength - 1;
char[] newChars = new char[newLength];
while (p1 >= 0) {
if (chars[p1] == ' ') {
newChars[p2--] = '0';
newChars[p2--] = '2';
newChars[p2--] = '%';
p1--;
} else {
newChars[p2--] = chars[p1--];
}
}
return String.valueOf(newChars);
}
6 从尾到头打印链表

使用栈,遍历一遍链表,将链表中的节点压栈,然后输出栈中的节点
import java.util.Stack;
public class FromHeadtoTailPrintLinkedList_6 {
static class ListNode {
int key;
ListNode next;
public ListNode(int key) {
this.key = key;
}
}
public static void fromHeadtoTailPrintLinkedListByStack(ListNode head) {
if (head == null) {
return;
}
Stack<ListNode> stack = new Stack();
while (head != null) {
stack.push(head);
head = head.next;
}
while (!stack.isEmpty()) {
System.out.print(stack.pop().key + " ");
}
}
public static void fromHeadtoTailPrintLinkedListByRecursion(ListNode head) {
if (head == null) {
return;
}
fromHeadtoTailPrintLinkedListByStack(head.next);
System.out.print(head.key + " ");
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
ListNode head = new ListNode(0);
head.next = new ListNode(1);
head.next.next = new ListNode(2);
head.next.next.next = new ListNode(3);
fromHeadtoTailPrintLinkedListByStack(head);
System.out.println();
fromHeadtoTailPrintLinkedListByRecursion(head);
}
}
7 重建二叉树

根据前序和中序遍历,可以确定每颗子树根节点所在的位置,然后根据根节点,划分左右子树,之后再分别在左右子树中重复之前的划分过程。(递归实现)
public static Node constructBinaryTreeByPreInOrder(int[] preOrder, int[] inOrder, int preOrder_start,
int inOrder_start, int length) {
if (length == 0) {
return null;
}
int rootInOrderIndex = 0;
for (int i = inOrder_start; i < inOrder_start + length; i++) {
if (preOrder[preOrder_start] == inOrder[i]) {
rootInOrderIndex = i;
break;
}
}
int left_length = rootInOrderIndex - inOrder_start;
int right_length = length - left_length - 1;
//根节点
Node root = new Node(preOrder[preOrder_start]);
//构建左子树
root.left = constructBinaryTreeByPreInOrder(preOrder, inOrder, preOrder_start + 1,
inOrder_start, left_length);
//构建右子树
root.right = constructBinaryTreeByPreInOrder(preOrder, inOrder, preOrder_start + left_length + 1,
rootInOrderIndex + 1, right_length);
return root;
}
8 二叉树的下一个节点

分三种情况:
- 当前节点有右子树,下一个节点是右子树中最左的节点
- 无右子树
- 父节点的左孩子是当前节点,下一个节点是父节点
- 遍历该节点的父节点,直到父节点的左孩子是当前节点,下一个节点是父节点
public class TreeNode {
public int value;
public TreeNode left;
public TreeNode right;
public TreeNode parent;
public TreeNode(int value) {
this.value = value;
}
}
public static TreeNode findNextNode(TreeNode treeNode) {
//当前节点有右子树,下一个节点是右子树中最左的节点
if (treeNode.right != null) {
TreeNode cur = treeNode.right;
while (cur.left != null) {
cur = cur.left;
}
return cur;
} else {
//无右子树
TreeNode par = treeNode.parent;
//父节点的左孩子是当前节点,下一个节点是父节点
if (par.left == treeNode) {
return par;
} else {
//遍历该节点的父节点,直到父节点的左孩子是当前节点,下一个节点是父节点
while (par.left != treeNode) {
par = par.parent;
treeNode = treeNode.parent;
}
return par;
}
}
}
9 用两个栈实现队列

delteHead和getHead操作:只有stackPop为空时,才能往里面压入数据
import java.util.Stack;
public class TwoStackToQueue<T> {
private Stack<T> stackPush;
private Stack<T> stackPop;
public TwoStackToQueue() {
stackPush = new Stack<T>();
stackPop = new Stack<T>();
}
public void appendTail(T node) {
stackPush.push(node);
}
public T deleteHead() {
if (stackPush.isEmpty() && stackPop.isEmpty()) {
throw new RuntimeException("Queue is empty!");
} else {
if (stackPop.isEmpty()) {
while (!stackPush.isEmpty()) {
stackPop.push((stackPush.pop()));
}
}
return stackPop.pop();
}
}
public T getHead(){
if (stackPush.isEmpty() && stackPop.isEmpty()) {
throw new RuntimeException("Queue is empty!");
} else {
if (stackPop.isEmpty()) {
while (!stackPush.isEmpty()) {
stackPop.push((stackPush.pop()));
}
}
return stackPop.peek();
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
TwoStackToQueue twoStackToQueue = new TwoStackToQueue();
twoStackToQueue.appendTail(1);
twoStackToQueue.appendTail(2);
twoStackToQueue.appendTail(3);
twoStackToQueue.appendTail(4);
System.out.println(twoStackToQueue.deleteHead());
System.out.println(twoStackToQueue.deleteHead());
System.out.println(twoStackToQueue.deleteHead());
twoStackToQueue.appendTail(5);
System.out.println(twoStackToQueue.deleteHead());
System.out.println(twoStackToQueue.getHead());
System.out.println(twoStackToQueue.deleteHead());
System.out.println(twoStackToQueue.deleteHead());
}
}
用两个队列实现栈
引入队列queue1和queue2,每次pop操作,就将queue1中的节点都放入queue2中,直至queue1中的节点个数为1,然后再将queue1的节点poll,之后,再交换queue1和queue2中的值。peek操作类似。
import java.util.LinkedList;
import java.util.Queue;
public class TwoQueueToStack<T> {
private Queue<T> queue1;
private Queue<T> queue2;
public TwoQueueToStack() {
queue1 = new LinkedList<T>();
queue2 = new LinkedList<T>();
}
public void push(T node) {
queue1.add(node);
}
public T pop() {
if (queue1.isEmpty() && queue2.isEmpty()) {
throw new RuntimeException("the stack is empty!");
}
while (queue1.size() != 1) {
queue2.add(queue1.poll());
}
T node = queue1.poll();
Queue<T> queue = queue1;
queue1 = queue2;
queue2 = queue;
return node;
}
public T peek() {
if (queue1.isEmpty() && queue2.isEmpty()) {
throw new RuntimeException("the stack is empty!");
}
T node = null;
while (!queue1.isEmpty()) {
node = queue1.poll();
queue2.add(node);
}
Queue<T> queue = queue1;
queue1 = queue2;
queue2 = queue;
return node;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
TwoQueueToStack twoQueueToStack = new TwoQueueToStack();
twoQueueToStack.push(1);
twoQueueToStack.push(2);
twoQueueToStack.push(3);
System.out.println(twoQueueToStack.pop());
twoQueueToStack.push(4);
System.out.println(twoQueueToStack.peek());
System.out.println(twoQueueToStack.pop());
System.out.println(twoQueueToStack.pop());
System.out.println(twoQueueToStack.pop());
System.out.println(twoQueueToStack.pop());
}
}
10 斐波那契数列

1.递归,时间复杂度O(2^n^)
2.循环,时间复杂度O(n
public class Fibonacci_10 {
public static int calFibonacciRecursive(int n) {
if (n == 0) {
return 0;
}
if (n == 1) {
return 1;
}
return calFibonacciRecursive(n - 1) + calFibonacciRecursive(n - 2);
}
public static int calFibonacciNoRecursive(int n) {
int[] res={0,1};
if(n<2){
return res[n];
}
int f1=0;
int f2=1;
int f=0;
for (int i = 2; i <=n; i++) {
f=f1+f2;
f1=f2;
f2=f;
}
return f;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println(calFibonacciRecursive(10));
System.out.println(calFibonacciNoRecursive(20));
}
}
应用


11 旋转数组的最小数字

解法:
- 暴力,时间复杂度O(n)
- 二分查找,时间复杂度O(logn)。使用两个指针p1,p2,然后根据计算的mid值来移动p1,p2。
- 当arr[p1]== arr[mid] == arr[p2]时,无法判断p1和p2属于哪个递增子数组,直接调用getMin,进行顺序查找。
- 当arr[mid]>=arr[p1]时,mid属于p1所在的递增子数组,令p1=mid,继续二分。
- 当arr[mid]<=arr[p2]时,处理过程和2类似。
三种输入情况:
- 1,2,3,4,5
- 3,4,5,1,2
- 1,1,1,0,1
import org.jetbrains.annotations.NotNull;
public class FindMinNumberInRotateArray_11 {
public static int findByDichotomy(int[] arr) {
if (arr[0] < arr[arr.length - 1]) {
return arr[0];
}
int p1 = 0;
int p2 = arr.length - 1;
int mid = 0;
int min = arr[0];
while (arr[p1] >= arr[p2]) {
if (p1 + 1 == p2) {
min = arr[p2];
break;
}
mid = p1 + ((p2 - p1) >> 1);
if (arr[mid] == arr[p1] && arr[mid] == arr[p2]) {
return getMin(arr, p1, p2);
}
if (arr[mid] >= arr[p1]) {
p1 = mid;
} else if (arr[mid] <= arr[p2]) {
p2 = mid;
}
}
return min;
}
private static int getMin(int[] arr, int p1, int p2) {
int min = arr[p1];
for (int i = p1 + 1; i < p2; i++) {
if (min > arr[i]) {
min = arr[i];
}
}
return min;
}
public static int findByForce(int[] arr) {
int min = arr[0];
for (int i = 1; i < arr.length; i++) {
if (min > arr[i]) {
min = arr[i];
}
}
return min;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] arr = {3, 4, 5, 1, 2};
int[] arr1 = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5};
int[] arr2 = {1, 0, 1, 1, 1};
int[] arr3 = {1};
System.out.println(comparator(arr));
System.out.println(comparator(arr1));
System.out.println(comparator(arr2));
System.out.println(comparator(arr3));
}
@NotNull
public static String comparator(int[] arr) {
return findByDichotomy(arr) == findByForce(arr) ? "true" : "false";
}
}
12 矩阵中的路径

思路:
回溯法,字符的遍历过程如下所示
public boolean hasPath(char[] matrix, int rows, int cols, char[] str) {
if (matrix == null || str == null || rows <= 0 || cols <= 0) {
return false;
}
//标记数组,用来记录该字符是否访问过
boolean[][] mark = new boolean[rows][cols];
char[][] chars = toArray(matrix, rows, cols);
for (int i = 0; i < rows; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < cols; j++) {
if (process(chars, str, 0, mark, i, j)) {
return true;
}
}
}
return false;
}
//将一维数组转换成二维数组
public char[][] toArray(char[] matrix, int rows, int cols) {
char[][] chars = new char[rows][cols];
for (int i = 0, index = 0; i < rows; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < cols; j++) {
chars[i][j] = matrix[index++];
}
}
return chars;
}
//递归函数
public boolean process(char[][] chars, char[] str, int pathLength, boolean[][] mark, int row, int column) {
//遍历的路径长度和字符串长度相等,说明,之前的字符都已经成功匹配,返回true
if (pathLength == str.length) {
return true;
}
//数组下标越界、字符不匹配、字符已经访问过,都返回false
if (row < 0 || column < 0 || row >= chars.length || column >= chars[0].length
|| chars[row][column] != str[pathLength] || mark[row][column]) {
return false;
}
//字符已访问,标记为true
mark[row][column] = true;
//递归遍历该字符傍边的字符,匹配成功,则路径长度加1
if (process(chars, str, pathLength + 1, mark, row - 1, column) ||
process(chars, str, pathLength + 1, mark, row + 1, column) ||
process(chars, str, pathLength + 1, mark, row, column - 1) ||
process(chars, str, pathLength + 1, mark, row, column + 1)) {
return true;
}
//该字符旁边的字符都不匹配,则说明这条路不符合,还原,将字符的遍历标记设置为false
mark[row][column] = false;
return false;
}
13 机器人的运动范围

思路:图的深度优先遍历
public int movingCount(int threshold, int rows, int cols) {
//标记数组
boolean[][] mark = new boolean[rows][cols];
//存储每个位置的数位和
int[][] matrix = new int[rows][cols];
for (int i = 0; i < rows; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < cols; j++) {
matrix[i][j] = getValue(i) + getValue(j);
}
}
return process(threshold, matrix, mark, 0, 0, rows, cols);
}
private int process(int threshold, int[][] matrix, boolean[][] mark, int i, int j, int rows, int cols) {
int count = 0;
//递归终止条件
if (i < 0 || j < 0 || i >= rows || j >= cols || matrix[i][j] > threshold || mark[i][j]) {
return 0;
}
//将访问过的位置标记为true
mark[i][j] = true;
//访问当前位置,加1,然后继续遍历该位置傍边的位置,累加起来,最终的返回值就是所能到达的格子数
count = 1 + process(threshold, matrix, mark, i - 1, j, rows, cols) + process(threshold, matrix, mark, i + 1, j, rows, cols) +
process(threshold, matrix, mark, i, j - 1, rows, cols) + process(threshold, matrix, mark, i, j + 1, rows, cols);
return count;
}
//计算一个整数的数位之和
public int getValue(int num) {
int res = 0;
int tmp = 0;
while (num / 10 > 0) {
tmp = num / 10;
res += num - tmp * 10;
num = tmp;
}
res += num;
return res;
}
14 剪绳子

public class cutRope_14 {
// 思路:
// f(n)=max(f(i)*f(n-i)),0<i<n
// f(n)表示把绳子剪成若干段后各段乘积的最大值
//1.递归
public int cutRope(int target) {
if (target < 2) {
return 0;
}
if (target == 2) {
return 1;
}
if (target == 3) {
return 2;
}
int max = 0;
for (int i = 1; i <= (target - 1) / 2; i++) {
max = Math.max(max, process(i) * process(target - i));
}
return max;
}
public int process(int target) {
//递归终止条件
if (target < 4) {
return target;
}
int max = 0;
for (int i = 1; i <= (target - 1) / 2; i++) {
max = Math.max(max, process(i) * process(target - i));
}
return max;
}
//2.动态规划,时间复杂度O(n^2),由递归转化而来
public int cutRopeDP(int target) {
if (target < 2) {
return 0;
}
if (target == 2) {
return 1;
}
if (target == 3) {
return 2;
}
int[] dp = new int[target + 1];
dp[1] = 1;
dp[2] = 2;
dp[3] = 3;
for (int i = 4; i <= target; i++) {
for (int j = 1; j <= i / 2; j++) {
dp[i] = Math.max(dp[i], dp[j] * dp[i - j]);
}
}
return dp[target];
}
// 3.贪心,时间复杂度O(1)
// n>4时,划分出尽可能多的3,因为3(n-3)>=2(n-2)
// n=4时,2*2 > 3*1,所以当划分出1和3时,要转变成2和2
// n<4时,特殊情况,单独处理
public int cutRopeGreedy(int target) {
if (target < 2) {
return 0;
}
if (target == 2) {
return 1;
}
if (target == 3) {
return 2;
}
int timeOf3 = target / 3;
if (target - timeOf3 * 3 == 1) {
timeOf3--;
}
int timeOf2 = (target - timeOf3 * 3) / 2;
int res = (int) (Math.pow(3, timeOf3) * Math.pow(2, timeOf2));
return res;
}
//测试
public static void main(String[] args) {
cutRope_14 cutRope_14 = new cutRope_14();
System.out.println(cutRope_14.cutRope(14));
System.out.println(cutRope_14.cutRopeDP(14));
System.out.println(cutRope_14.cutRopeGreedy(14));
}
}
15 二进制中1的个数

public class BinaryNumber_15 {
public int NumberOf1(int n) {
//数字在计算机中以二进制形式存储,负数在计算机中以补码存储,int类型的数据占4个字节
//为了防止负数右移出现死循环的情况,可以把1每次左移一位,然后和n比较
int res = 0;
int flag = 1;
while (flag != 0) {
if ((n & flag) != 0) {
res++;
}
flag = flag << 1;
}
return res;
}
public int NumberOf1Improve(int n) {
//(n-1)&n 每次运算的结果将n中二进制表示最右边的1变为0
int res = 0;
while (n != 0) {
n=(n-1)&n;
res++;
}
return res;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
BinaryNumber_15 binaryNumber_15 = new BinaryNumber_15();
int res = binaryNumber_15.NumberOf1(-8);
System.out.println(res);
}
}
16 数值的整数次方

base=0,exponent<0是非法输入,给用户提示输入错误
提高运算效率:
public class NumberExponent_16 {
public double Power(double base, int exponent) {
//非法输入
if (base == 0 && exponent < 0) {
throw new RuntimeException("input number error!");
}
double res = 1;
double tmp = exponent;
if (exponent < 0) {
exponent = -exponent;
}
//O(n)
for (int i = 1; i <= exponent; i++) {
res = res * base;
}
if (tmp < 0) {
res = 1 / res;
}
return res;
}
public double PowerImprove(double base, int exponent) {
//非法输入
if (base == 0 && exponent < 0) {
throw new RuntimeException("input number error!");
}
double res = 1;
double tmp = exponent;
if (exponent < 0) {
exponent = -exponent;
}
if (exponent % 2 == 0) {
//O(n/2)
for (int i = 1; i <= exponent / 2; i++) {
res = res * base;
}
res = res * res;
} else {
for (int i = 1; i <= (exponent - 1) / 2; i++) {
res = res * base;
}
res = res * res * base;
}
if (tmp < 0) {
res = 1 / res;
}
return res;
}
}
17 打印从1到最大的n位数

本质上是0-9的全排列顺序输出问题,用递归实现。
大数问题,一般使用字符串来表示数字。
public class PrintMaxNumber_17 {
//n没有限定范围,大数问题,需要用字符串来表示
public void print(int n) {
if (n <= 0) {
throw new RuntimeException("error input!");
}
char[] nums=new char[n];
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
//数字转字符,'0' + i 是 i 的ascii码
nums[0]=(char)('0'+i);
process(nums,0,n);
}
}
public void process(char[] nums,int index,int len){
if(index==len-1){
print(nums);
return;
}
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
nums[index+1]=(char)('0'+i);
process(nums,index+1,len);
}
}
private void print(char[] nums) {
//标记位,用来判断数字0之前是否有非零数字出现过
int flag=0;
String str="";
for (int i = 0; i < nums.length; i++) {
if(nums[i]!='0'){
flag=1;
str+=nums[i];
}
if(nums[i]=='0'&&flag==1){
str+=nums[i];
}
}
System.out.print(str+" ");
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
PrintMaxNumber_17 printMaxNumber_17=new PrintMaxNumber_17();
printMaxNumber_17.print(3);
}
}
18 删除链表中的节点

链表中删除节点的两种方法:
public class DeleteNode_18 {
static class Node {
int value;
Node next;
public Node(int value) {
this.value = value;
}
}
//O(1)
public static Node deleteNode(Node head, Node deleteNode) {
//要删除节点的下一个节点不为空时,用下一个节点的值替代当前节点,然后将当前节点指向下一个节点的节点,O(1)
if (deleteNode.next != null) {
deleteNode.value = deleteNode.next.value;
deleteNode.next = deleteNode.next.next;
} else {
//链表中只有一个节点
if (head == deleteNode) {
head = null;
} else {
//要删除节点的下一个节点为空,即链表中最后一个节点,O(n)
Node cur = head;
while (cur.next != deleteNode) {
cur = cur.next;
}
cur.next = null;
}
}
return head;
}
public static void printNode(Node head) {
while (head != null) {
System.out.print(head.value + " ");
head = head.next;
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Node node1 = new Node(1);
Node node2 = new Node(2);
Node node3 = new Node(3);
node1.next = node2;
node2.next = node3;
Node head = deleteNode(node1, node3);
printNode(head);
}
}
19 正则表达式匹配

当模式中的第二个字符不是 “*” 时:
1、如果字符串第一个字符和模式中的第一个字符相匹配,那么字符串和模式都后移一个字符,然后匹配剩余的。
2、如果 字符串第一个字符和模式中的第一个字符相不匹配,直接返回 false。
而当模式中的第二个字符是 “*” 时:
如果字符串第一个字符跟模式第一个字符不匹配,则模式后移 2 个字符,继续匹配。如果字符串第一个字符跟模式第一个字符匹配,可以有 3 种匹配方式:
1、模式后移 2 字符,相当于 x * 被忽略;
2、字符串后移 1 字符,模式后移 2 字符;
3、字符串后移 1 字符,模式不变,即继续匹配字符下一位,因为 * 可以匹配多位;
这里需要注意的是:Java 里,要时刻检验数组是否越界。
public class RegularExpressionMatch_19 {
public boolean match(char[] str, char[] pattern) {
if (str == null || pattern == null) {
return false;
}
int strIndex = 0;
int patternIndex = 0;
return matchCore(str, strIndex, pattern, patternIndex);
}
public boolean matchCore(char[] str, int strIndex, char[] pattern, int patternIndex) {
//有效性检验:str到尾,pattern到尾,匹配成功
if (strIndex == str.length && patternIndex == pattern.length) {
return true;
}
//pattern先到尾,匹配失败
if (strIndex != str.length && patternIndex == pattern.length) {
return false;
}
//模式第2个是*,且字符串第1个跟模式第1个匹配,分3种匹配模式;如不匹配,模式后移2位
if (patternIndex + 1 < pattern.length && pattern[patternIndex + 1] == '*') {
if ((strIndex != str.length && pattern[patternIndex] == str[strIndex])
|| strIndex != str.length && (pattern[patternIndex] == '.')) {
return matchCore(str, strIndex, pattern, patternIndex + 2)// 模式后移2,视为x*匹配0个字符
|| matchCore(str, strIndex + 1, pattern, patternIndex + 2)// 视为模式匹配1个字符
|| matchCore(str, strIndex + 1, pattern, patternIndex);// *匹配1个,再匹配str中的下一个
} else {
return matchCore(str, strIndex, pattern, patternIndex + 2);
}
}
//模式第2个不是*,且字符串第1个跟模式第1个匹配,则都后移1位,否则直接返回false
if ((strIndex != str.length && pattern[patternIndex] == str[strIndex])
|| (strIndex != str.length && pattern[patternIndex] == '.')) {
return matchCore(str, strIndex + 1, pattern, patternIndex + 1);
}
return false;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
RegularExpressionMatch_19 regularExpressionMatch_19 = new RegularExpressionMatch_19();
boolean res = regularExpressionMatch_19.match("".toCharArray(), ".*".toCharArray());
System.out.println(res);
}
}
20 表示数值的字符串

使用正则表达式进行匹配
[] : 字符集合
() : 分组
? : 重复 0 ~ 1 次+ : 重复 1 ~ n 次
* : 重复 0 ~ n 次
. : 任意字符
\\. : 转义后的 .
\\d : 数字
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
public class JudgeNumber_20 {
public boolean judge(String str) {
if (str == null || str.length() == 0)
return false;
return str.matches("[+-]?\\d*(\\.\\d+)?([eE][+-]?\\d+)?");
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
JudgeNumber_20 judgeNumber_20 = new JudgeNumber_20();
String[] strings = {"+100", "5e2", "-123", "3.1416", "-1E-16",
"12e", "1a3.14", "1.2.3", "+-5", "12e+4.3" };
for (String str : strings) {
System.out.println(str + " " + judgeNumber_20.judge(str));
}
}
}
21 调整数组顺序使奇数位于偶数前面

使用双指针begin和end
begin=0,end=arr.length-1
public class OddEvenNumber_21 {
public void adjust(int[] arr) {
int begin = 0;
int end = arr.length - 1;
while (begin < end) {
while (judgeOddEven(arr[begin]) && begin < end) {
begin++;
}
while (!judgeOddEven(arr[begin]) && begin < end) {
end--;
}
swap(arr, begin, end);
}
}
public boolean judgeOddEven(int i) {
return i % 2 == 0;
}
public void swap(int[] arr, int begin, int end) {
int tmp = arr[begin];
arr[begin] = arr[end];
arr[end] = tmp;
}
public void printArray(int[] arr) {
for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
System.out.print(arr[i] + " ");
}
System.out.println();
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
OddEvenNumber_21 oddEvenNumber_21 = new OddEvenNumber_21();
int[] arr = new int[10];
for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
arr[i] = (int) (Math.random() * 20);
}
oddEvenNumber_21.printArray(arr);
oddEvenNumber_21.adjust(arr);
oddEvenNumber_21.printArray(arr);
}
}
22 链表中倒数第k个节点

设置两个指针p1、p2,p1=p2=head
让p1先走k-1步,然后p1和p2同时走,p1走到链表尾结点,则p2正好走到倒数第k个节点
代码鲁棒性:
- 输入的链表头指针为null
- k=0
- 链表中节点个数小于k
public class TheLastKthNode_22 {
static class ListNode {
int value;
ListNode next;
ListNode(int value) {
this.value = value;
}
}
public static ListNode theLastKthNode(ListNode head, int k) {
if(head==null){
throw new RuntimeException("Error,head is null!");
}
if(k==0){
throw new RuntimeException("Error,the value of k is 0!");
}
ListNode p1 = head;
ListNode p2 = head;
int i=0;
while (i != (k - 1)) {
if(p1.next==null){
throw new RuntimeException("Error,the number of ListNode is less than k!");
}
p1 = p1.next;
i++;
}
while (p1.next != null) {
p1 = p1.next;
p2 = p2.next;
}
return p2;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
ListNode listNode1 = new ListNode(1);
ListNode listNode2 = new ListNode(2);
ListNode listNode3 = new ListNode(3);
ListNode listNode4 = new ListNode(4);
ListNode listNode5 = new ListNode(5);
ListNode listNode6 = new ListNode(6);
listNode1.next = listNode2;
listNode2.next = listNode3;
listNode3.next = listNode4;
listNode4.next = listNode5;
listNode5.next = listNode6;
ListNode listNode=theLastKthNode(listNode1,8);
System.out.println(listNode.value);
}
}
23 链表中环的入口节点

思路:
- 先判断链表是否存在环,使用快慢指针,快指针一次走两步,慢指针一次走一步,两个指针相遇,则说明链表有环,记录下相遇时候的节点LoopNode
- 计算环中的节点个数,从LoopNode节点出发,再次回到LoopNode,就得到了环中节点的个数k
- 设置两个指针p1和p2,让p1先走k步,然后p1和p2同时走,相遇时候的节点EntryNode即为环的入口节点
public class LoopOfLinkedList_23 {
static class LinkedList {
int value;
LinkedList next;
LinkedList(int value) {
this.value = value;
}
}
public static LinkedList findLoopNode(LinkedList head) {
if (head == null) {
throw new RuntimeException("head is null!");
}
LinkedList p1 = head.next;
LinkedList p2 = head;
LinkedList loopNode = null;
while (p1.next != null) {
p1 = p1.next;
if (p1.next != null) {
p1 = p1.next;
}
p2 = p2.next;
// System.out.println(p1.value + " " + p2.value);
if (p1 == p2) {
loopNode = p1;
break;
}
}
if (loopNode == null) {
return null;
}
int count = 1;
LinkedList tmpList=loopNode;
while (loopNode.next != tmpList) {
count++;
// System.out.println(count);
loopNode = loopNode.next;
}
p1 = p2 = head;
while (count-- > 0) {
p1 = p1.next;
}
while (p1 != p2) {
p1 = p1.next;
p2 = p2.next;
}
return p1;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
LinkedList linkedList1 = new LinkedList(1);
LinkedList linkedList2 = new LinkedList(2);
LinkedList linkedList3 = new LinkedList(3);
LinkedList linkedList4 = new LinkedList(4);
LinkedList linkedList5 = new LinkedList(5);
LinkedList linkedList6 = new LinkedList(6);
linkedList1.next = linkedList2;
linkedList2.next = linkedList3;
linkedList3.next = linkedList4;
linkedList4.next = linkedList5;
linkedList5.next = linkedList6;
linkedList6.next = linkedList3;
LinkedList linkedList = findLoopNode(linkedList1);
System.out.println(linkedList.value);
}
}
24 反转链表
- 非递归:使用一个newList节点来记录逆向之后的头结点
- 递归:每次递归,head.next要设置为null
public class ReverseLinkedList {
static class LinkedList {
int value;
LinkedList next;
LinkedList(int value) {
this.value = value;
}
}
//非递归
public static LinkedList reverse(LinkedList head) {
LinkedList newList = new LinkedList(-1);
while (head != null) {
LinkedList next = head.next;
head.next = newList.next;
newList.next = head;
head = next;
}
return newList.next;
}
//递归
public static LinkedList reverseByRecursive(LinkedList head){
if(head==null||head.next==null){
return head;
}
LinkedList next=head.next;
head.next=null;
LinkedList newHead=reverseByRecursive(next);
next.next=head;
return newHead;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
LinkedList linkedList1 = new LinkedList(1);
LinkedList linkedList2 = new LinkedList(2);
LinkedList linkedList3 = new LinkedList(3);
LinkedList linkedList4 = new LinkedList(4);
LinkedList linkedList5 = new LinkedList(5);
LinkedList linkedList6 = new LinkedList(6);
linkedList1.next = linkedList2;
linkedList2.next = linkedList3;
linkedList3.next = linkedList4;
linkedList4.next = linkedList5;
linkedList5.next = linkedList6;
LinkedList reverseHead = reverse(linkedList1);
while (reverseHead!=null){
System.out.println(reverseHead.value);
reverseHead=reverseHead.next;
}
}
}
25 合并两个排序的链表

public class MergeSortedLinkedList_25 {
public static LinkedList mergeSortedLinkedList(LinkedList head1, LinkedList head2) {
LinkedList head = new LinkedList(-1);
LinkedList cur = head;
while (head1 != null && head2 != null) {
if (head1.value <= head2.value) {
cur.next = head1;
head1 = head1.next;
} else {
cur.next = head2;
head2 = head2.next;
}
cur = cur.next;
}
if (head1 != null) {
cur.next = head1;
}
if (head2 != null) {
cur.next = head2;
}
return head.next;
}
public static LinkedList mergeSortedLinkedListByRecursive(LinkedList head1, LinkedList head2) {
if (head1 == null) {
return head2;
}
if (head2 == null) {
return head1;
}
if (head1.value <= head2.value) {
head1.next = mergeSortedLinkedListByRecursive(head1.next, head2);
return head1;
} else {
head2.next = mergeSortedLinkedListByRecursive(head1, head2.next);
return head2;
}
}
}
26 树的子结构

public class SubTree_26 {
static class BinaryTreeNode {
double value;
BinaryTreeNode left;
BinaryTreeNode right;
BinaryTreeNode(int value) {
this.value = value;
}
}
//遍历所有根节点值相同的子树
public static boolean hasSubTree(BinaryTreeNode binaryTreeNode1, BinaryTreeNode binaryTreeNode2) {
boolean result = false;
if (binaryTreeNode1 != null && binaryTreeNode2 != null) {
if (binaryTreeNode1.value == binaryTreeNode2.value) {
result = judge(binaryTreeNode1, binaryTreeNode2);
}
if (!result) {
result = hasSubTree(binaryTreeNode1.left, binaryTreeNode2);
}
if (!result) {
result = hasSubTree(binaryTreeNode1.right, binaryTreeNode2);
}
}
return result;
}
//判断根节点相同的子树是否完全一样
public static boolean judge(BinaryTreeNode binaryTreeNode1, BinaryTreeNode binaryTreeNode2) {
if (binaryTreeNode2 == null) {
return true;
}
if (binaryTreeNode1 == null) {
return false;
}
if (!Equals(binaryTreeNode1.value, binaryTreeNode2.value)) {
return false;
} else {
return judge(binaryTreeNode1.left, binaryTreeNode2.left) && judge(binaryTreeNode1.right, binaryTreeNode2.right);
}
}
//计算机表示小数(float、double)存在误差,不能直接用等号判断两个小数是否相等。如果两个小数的差的绝对值很小,
// 小于0.0000001,则认为相等
public static boolean Equals(double a, double b) {
if (Math.abs(a - b) < 0.0000001) {
return true;
} else {
return false;
}
}
}
27 二叉树的镜像

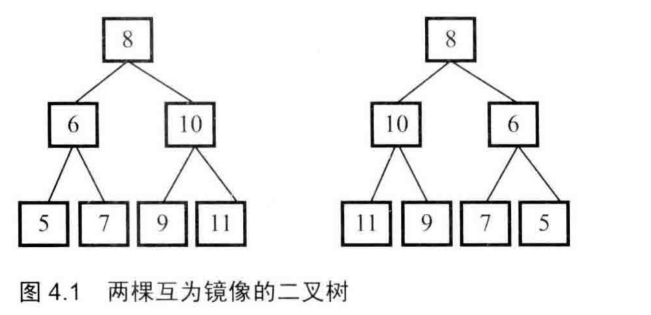
前序遍历,递归依次交换左右节点
public class BinaryTreeMirror_27 {
class BinaryTreeNode {
int value;
BinaryTreeNode left;
BinaryTreeNode right;
}
public void mirrorRecursive(BinaryTreeNode root) {
if (root == null) {
return;
}
if (root.left == null && root.right == null) {
return;
}
BinaryTreeNode tmp = root.left;
root.left = root.right;
root.right = tmp;
if (root.left != null) {
mirrorRecursive(root.left);
}
if (root.right != null) {
mirrorRecursive(root.right);
}
}
}
28 对称的二叉树


思路:比较二叉树的根左右和根右左遍历的序列,来进行判断
public class BinaryTreeSymmetry_28 {
class BinaryTreeNode {
int value;
BinaryTreeNode left;
BinaryTreeNode right;
}
public boolean isSymmetry(BinaryTreeNode root) {
return process(root, root);
}
public boolean process(BinaryTreeNode root1, BinaryTreeNode root2) {
if (root1 == null && root2 == null) {
return true;
}
if (root1 == null || root2 == null) {
return false;
}
if (root1.value != root2.value) {
return false;
}
return process(root1.left, root2.right) && process(root1.right, root2.left);
}
}
29 顺时针打印矩阵

每次打印一个圈,可以用递归或者循环实现
public class ClockwisePrintMatrix_29 {
public static void clockwisePrintMatrix(int[][] arr) {
if (arr == null) {
return;
}
print(arr, 0, 0, arr.length - 1, arr[0].length - 1);
}
public static void print(int[][] arr, int leftX, int leftY, int rightX, int rightY) {
//递归终止条件
if (leftX > rightX || leftY > rightY) {
return;
}
//单行和单列需要单独处理,否则会输出重复的序列
if (leftX == rightX) {
for (int i = leftY; i <= rightY; i++) {
System.out.print(arr[leftX][i] + " ");
}
} else if (leftY == rightY) {
for (int i = leftX; i <= rightX; i++) {
System.out.print(arr[i][leftY] + " ");
}
//其他情况,顺时针转圈打印,注意边界的处理
} else {
for (int i = leftY; i < rightY; i++) {
System.out.print(arr[leftX][i] + " ");
}
for (int i = leftX; i <= rightX; i++) {
System.out.print(arr[i][rightY] + " ");
}
for (int i = rightY - 1; i >= leftY; i--) {
System.out.print(arr[rightX][i] + " ");
}
for (int i = rightX - 1; i > leftX; i--) {
System.out.print(arr[i][leftY] + " ");
}
print(arr, ++leftX, ++leftY, --rightX, --rightY);
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[][] arr = {
{1, 2, 3, 4},
{5, 6, 7, 8},
{9, 10, 11, 12},
{13, 14, 15, 16}
};
int[][] arr1 = {
{1, 2, 3, 4},
};
int[][] arr2 = {
{1}, {2},{3}, {4},
};
clockwisePrintMatrix(arr);
System.out.println();
clockwisePrintMatrix(arr1);
System.out.println();
clockwisePrintMatrix(arr2);
/* result:
* 1 2 3 4 8 12 16 15 14 13 9 5 6 7 11 10
* 1 2 3 4
* 1 2 3 4
* */
}
}
30 包含min函数的栈

使用两个栈:dataStack和minStack。
dataStack存储实际的数据
minStack存储当前栈内元素最小的数据
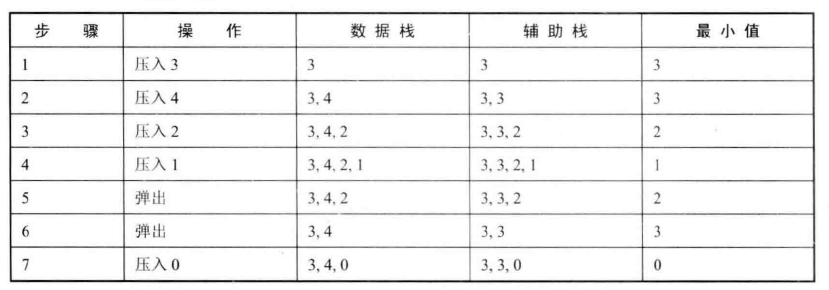
import java.util.Stack;
public class MinStack {
Stack<Integer> dataStack;
Stack<Integer> minStack;
public MinStack() {
dataStack = new Stack<>();
minStack = new Stack<>();
}
public void push(int data) {
dataStack.push(data);
if (minStack.isEmpty()) {
minStack.push(data);
} else {
int min = minStack.peek();
if (data < min) {
min = data;
}
minStack.push(min);
}
}
public int pop() {
int data = dataStack.pop();
minStack.pop();
return data;
}
public int min() {
return minStack.peek();
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
MinStack minStack = new MinStack();
minStack.push(3);
System.out.println(minStack.min());
minStack.push(4);
System.out.println(minStack.min());
minStack.push(2);
System.out.println(minStack.min());
minStack.push(1);
System.out.println(minStack.min());
minStack.pop();
System.out.println(minStack.min());
}
}