准备工作
- Ubuntu安装mysql服务器:sudo apt-get install mysql-server
- Ubuntu安装mysql客户端:sudo apt-get install mysql-client;并记住登录密码。
- Python安装pymysql用于通过Python操作mysql数据库:pip3 install pymysql
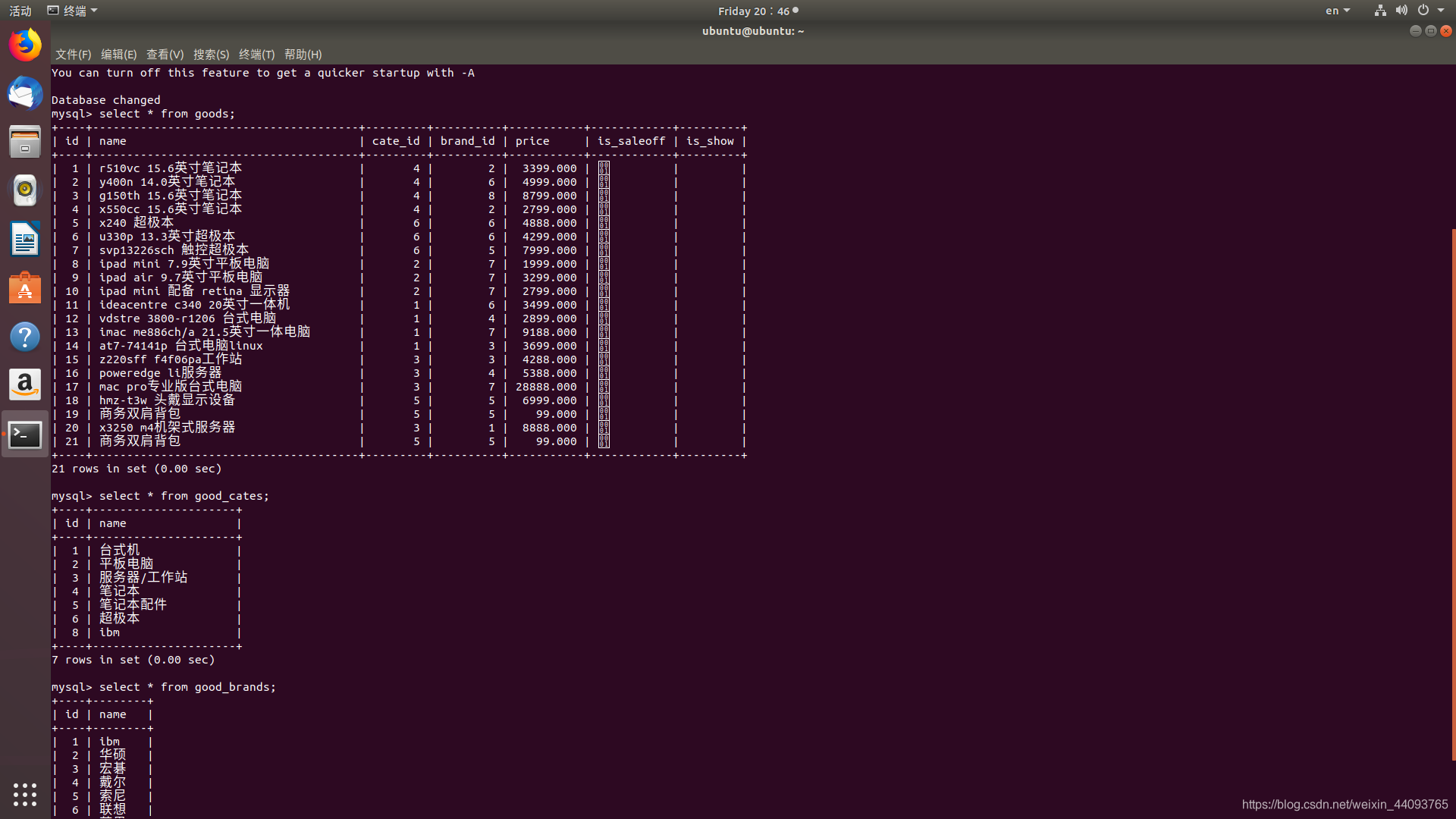
- 建立数据库,并建立相关联的三张表,博主建立的数据库名称为test,建立相关联表分别为:goods,good_cates,good_brands,效果如下图所示,且博主对数据库操作的例子均基于此。(数据基本操作请自行百度或参考其他博主)

基本函数简介
1.con = connect(host=“localhost(本机ip)”, port=3306(端口,mysql默认端口即为3306), user=‘root’(用户名root), password=‘12345678’(博主设置的登录密码为12345678),database=‘test’(使用test数据库,注:使用前需事先建立数据库),charset=‘utf8’(采用utf-8编码方式))
2. con.cursor() #获取游标对象
3. con.cursor.execute(sql) #执行sql语句
4. connect连接对象和cursor对象使用完最后需用close关闭。
实例
- 建立Test对象,为其定义属性并写相应的方法
class Test(object):
def __init__(self):
#获取连接对象
self.con = pymysql.connect(host="localhost", port=3306, user='root', password='12345678',database='test', charset='utf8')
#获取游标对象
self.cursor = self.con.cursor()
def __del__(self):
#关闭对象
self.cursor.close()
self.con.close()
def execute_sql(self, sql):
#执行sql语句
self.cursor.execute(sql)
for temp in self.cursor.fetchall():
print(temp)
@staticmethod
def show_menu():
print("----Test----")
print("1:所有商品")
print("2:所有商品分类")
print("3:所有品牌分类")
num = input("请输入功能对应的序号:")
return num
def run(self):
while True:
num = self.show_menu()
print(num)
if num == '1':
#查询所有商品
sql = "select * from goods;"
self.execute_sql(sql)
elif num == '2':
#查询分类
sql = "select name from good_cates;"
self.execute_sql(sql)
elif num == '3':
#查询品牌
sql = "select name from good_brands;"
self.execute_sql(sql)
else:
print("无效字符!")
- 主函数调用
def main():
#实例化对象
test = Test()
#调用对象run方法
test.run()
if __name__ == "__main__":
main()
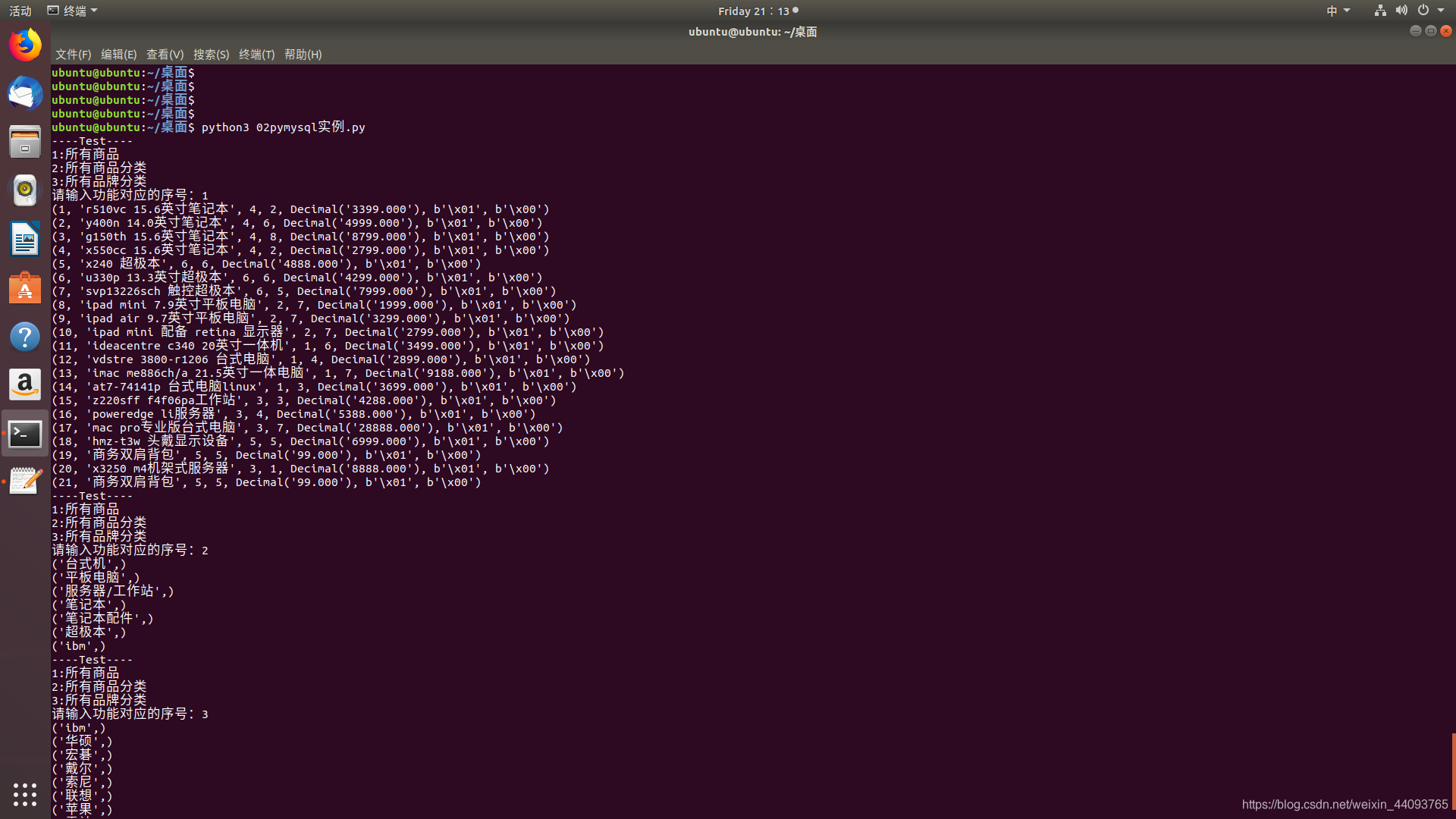
- 效果演示

来源:CSDN
作者:Big-one
链接:https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_44093765/article/details/86357096