BFS 广搜算法
讲一下图的遍历,广搜。
广搜是图的遍历的一种,它能够在图中的两的点之间找到一条最短的一条路径。但是如果仅使用广搜,搜索的规模会与点的数量以及边的数量有关。当规模很大的时候,广搜不是一种很好的解决方案。
举个例子,这是图的形式
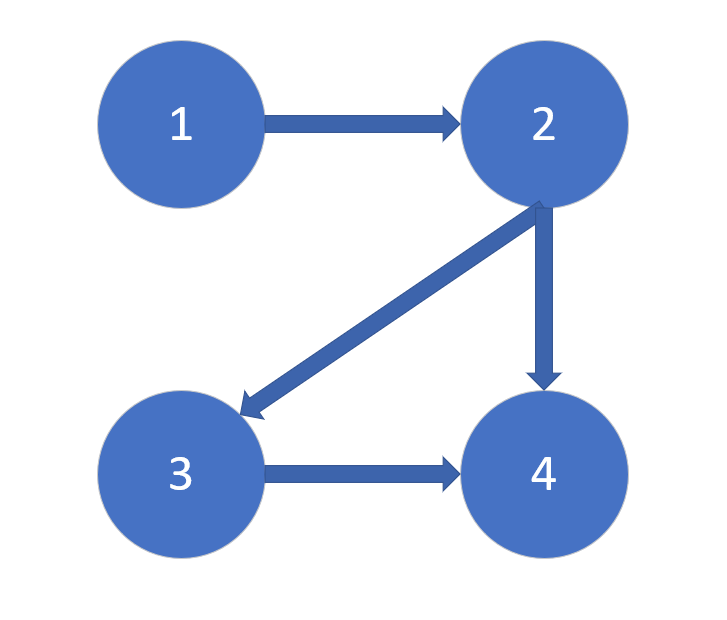
然后便是其邻接矩阵的形式:
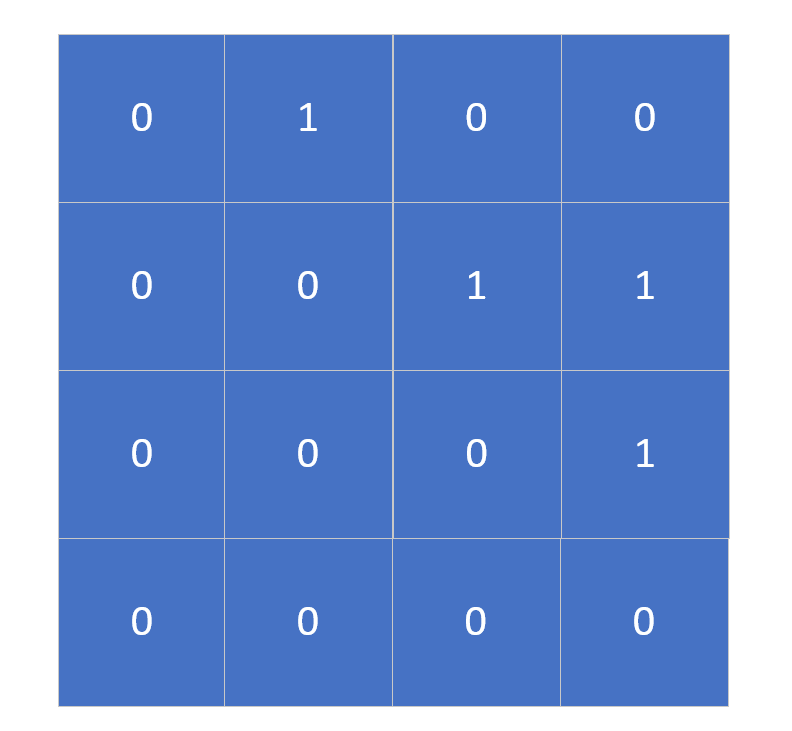
再者是其邻接表的形式:
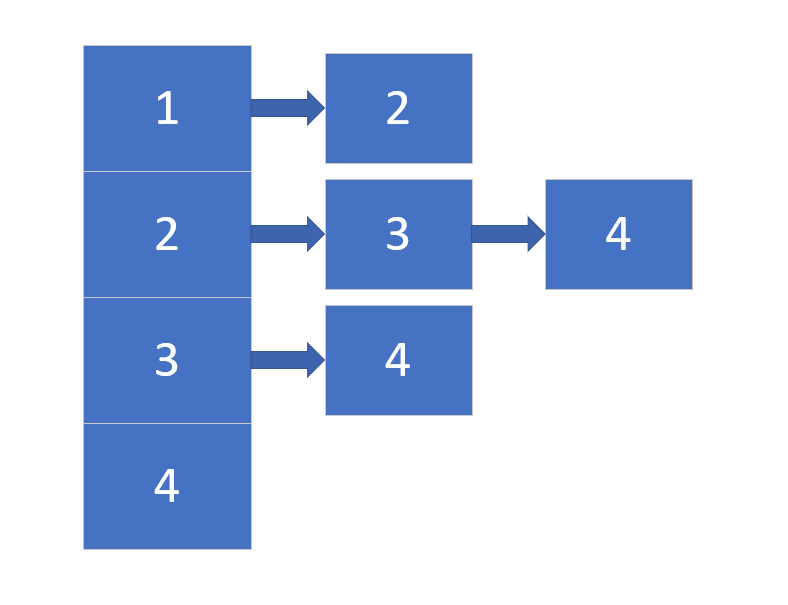
如若没有了解该算法的大体思想,可以参考我的另一篇文章
以下便是代码,改代码使用的是链式结构,即邻接表实现,输入格式在main.cpp中注释部分
main.cpp
#include"GraphBFS.h"
int main()
{
GraphBFS g1;
g1.Init();
g1.Display();
return 0;
}
/*
5
5
1 5 2
1 2 4
2 3 5
3 4 1
4 5 6
*/
GraphBFS.h
#pragma once
#ifndef _GRAPHBFS_H_
#define _GRAPHBFS_H_
#include<iostream>
#include<cstdlib>
#include<queue>
#include<vector>
using namespace std;
const int MAX = 0xffffff;
struct nPoint
{
int arrive;
int d;
nPoint* next = nullptr;
};
class GraphBFS//使用邻接表访问
{
private:
int nodeNumber;
int begin, end;
vector<nPoint>Graph;//连续性,相当于头指针
vector<bool>visited;//判断是否经历过
vector<int>distance;//距离
vector<int>parent;//父母
queue<int>q1;//队列
void BFS(int s);//进行广搜
void PrintPath(int b, int e);//打印路线
void LinkNode(int locate,nPoint *p);//链接nPoint结点
public:
GraphBFS();//构造函数
void Init();//初始化
void Display();
~GraphBFS();
};
#endif // !_GRAPHBFS_H_
GraphBFS.cpp
#include "GraphBFS.h"
GraphBFS::GraphBFS()
{
nodeNumber = 0;
begin = end = 0;
Graph.clear();
visited.clear();
distance.clear();
while (!q1.empty())
q1.pop();
}
void GraphBFS::Init()
{
cout << "请输入点的个数" << endl;
cin >> nodeNumber;
Graph.resize(nodeNumber + 1);//链表申请
visited.resize(nodeNumber + 1, false);
distance.resize(nodeNumber + 1, MAX);
parent.resize(nodeNumber + 1, -1);
cout << "请输入有几个关系" << endl;
int a,b,c;
cin >> a;
cout << "请输入各边的关系以及距离" << endl;
while (a--)
{
nPoint* p = new nPoint;
cin >> b >> c >> p->d;
p->arrive = c;
LinkNode(b, p);//利用头插法插入链表中,b是定位到那个链表
}
cout << "请输入开始点和结束点" << endl;
cin >> begin >> end;
}
void GraphBFS::BFS(int s)
{
visited[s] = true;
distance[s] = 0;
q1.push(s);
while (!q1.empty())
{
int u = q1.front();
nPoint* op1 = Graph[u].next;
while (op1)
{
if (!visited[op1->arrive])
{
q1.push(op1->arrive);
parent[op1->arrive] = u;
distance[op1->arrive] = distance[u] + op1->d;
visited[op1->arrive] = true;
}
op1 = op1->next;
}
q1.pop();
}
}
void GraphBFS::LinkNode(int locate, nPoint *p)
{
nPoint* op1 = nullptr;
op1 = Graph[locate].next;
Graph[locate].next = p;
p->next = op1;
op1 = nullptr;
}
void GraphBFS::Display()
{
BFS(begin);
cout << "路径是: ";
PrintPath(begin, end);
cout << endl << "距离是: " << distance[end] << endl;
}
void GraphBFS::PrintPath(int b, int e)
{
if (b == e)
cout << b << " ";
else if (parent[e] == -1)
return;
else {
PrintPath(b, parent[e]);
cout << e << " ";
}
}
GraphBFS::~GraphBFS()
{
Graph.clear();
visited.clear();
while (!q1.empty())
q1.pop();
begin = end = 0;
nodeNumber = 0;
}