20182320 2019-2020-1 《数据结构与面向对象程序设计》实验7报告
课程:《程序设计与数据结构》
班级: 1823
姓名: 郑力元
学号:20182320
实验教师:王志强
实验日期:2019年11月1日
必修/选修: 必修
1.实验内容
1.1
定义一个Searching和Sorting类,并在类中实现linearSearch,SelectionSort方法,最后完成测试。
要求不少于10个测试用例,提交测试用例设计情况(正常,异常,边界,正序,逆序),用例数据中要包含自己学号的后四位
提交运行结果图。
1.2
重构你的代码
把Sorting.java Searching.java放入 cn.edu.besti.cs1823.(姓名首字母+四位学号) 包中(例如:cn.edu.besti.cs1823.G2301)
把测试代码放test包中
重新编译,运行代码,提交编译,运行的截图(IDEA,命令行两种)
1.3
参考http://www.cnblogs.com/maybe2030/p/4715035.html ,学习各种查找算法并在Searching中补充查找算法并测试
提交运行结果截图
1.4
补充实现课上讲过的排序方法:希尔排序,堆排序,二叉树排序等(至少3个)
测试实现的算法(正常,异常,边界)
提交运行结果截图(如果编写多个排序算法,即使其中三个排序程序有瑕疵,也可以酌情得满分)
1.5
编写Android程序对实现各种查找与排序算法进行测试
提交运行结果截图
推送代码到码云(选做,加分)
2. 实验过程及结果
2.1
第一步:编写Searching和Sorting类
Searching类
public class Searching {
private int List[];
private int searchElement;
private int listSize;
private int locate;
public Searching(int[] list, int searchElement) {
List = list;
this.searchElement = searchElement;
listSize= List.length;
}
public boolean linearSearch(){
for (int i=listSize-1;;i--){
if (searchElement==List[i]){
locate=i;
return true;
}
else if (i==0){
return false;
}
}
}
}
Sorting类
public class Sorting {
private int List[];
private int size;
public Sorting(int[] list) {
List = list;
size=List.length;
}
public void selectionSort(){
int temp,tempx;
for (int i=0;i<size-1;i++){
temp=i;
for (int j=i+1;j<size;j++){
if (List[temp]>List[j]){
temp=j;
}
}
if (temp == 0) {
continue;
}
else {
tempx=List[i];
List[i]=List[temp];
List[temp]=tempx;
}
}
}
}
我编写的上面两个类要运行的时候是要先自己创建一个数组并往里面放数,然后在这个数组里面实现运行,也就是说在使用Sorting类时它会修改原数组。
第二步:编写主函数代码调用运行两个类
运行代码:
public class SearchingTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int a1[]={1,2,3,4,5,6,7,2320};
int a2[]={9,8,7,6,5,4,3,2320};
System.out.println("线性查找:");
System.out.println(new Searching(a1,4).linearSearch());
System.out.println(new Searching(a1,6).linearSearch());
System.out.println(new Searching(a1,1).linearSearch());
System.out.println(new Searching(a1,2320).linearSearch());
System.out.println(new Searching(a1,999).linearSearch());
System.out.println(new Searching(a2,4).linearSearch());
System.out.println(new Searching(a2,6).linearSearch());
System.out.println(new Searching(a2,9).linearSearch());
System.out.println(new Searching(a2,2320).linearSearch());
System.out.println(new Searching(a2,999).linearSearch());
}
}
运行结果: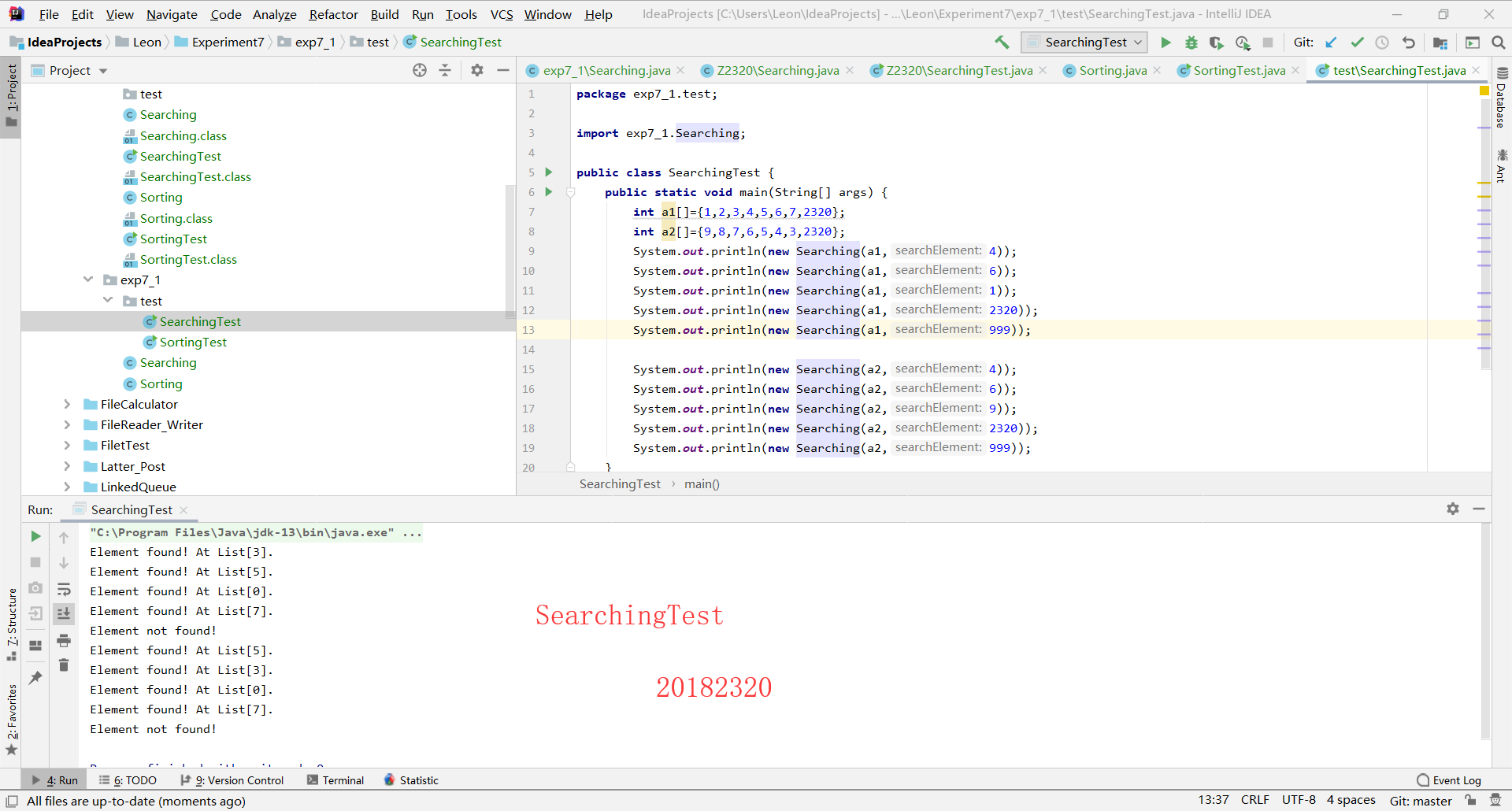
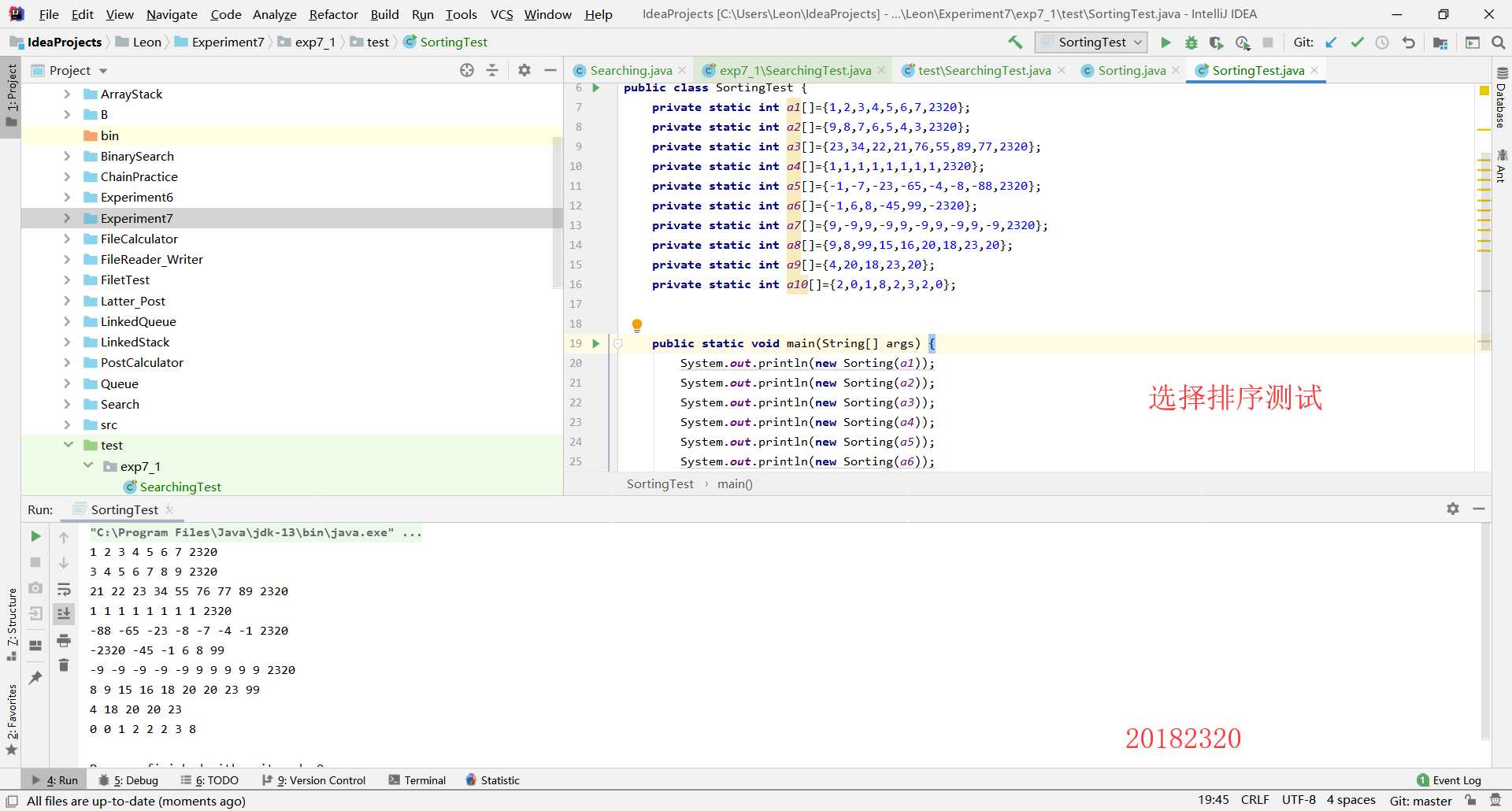
2.2
第一步:创建包cn.edu.besti.cs1823.Z2320,并把Searching和Sorting类和运行代码放入包中
第二步:打开Windows命令行,使用命令编译并运行三个.java文件,生成class,然后用命令行运行运行代码
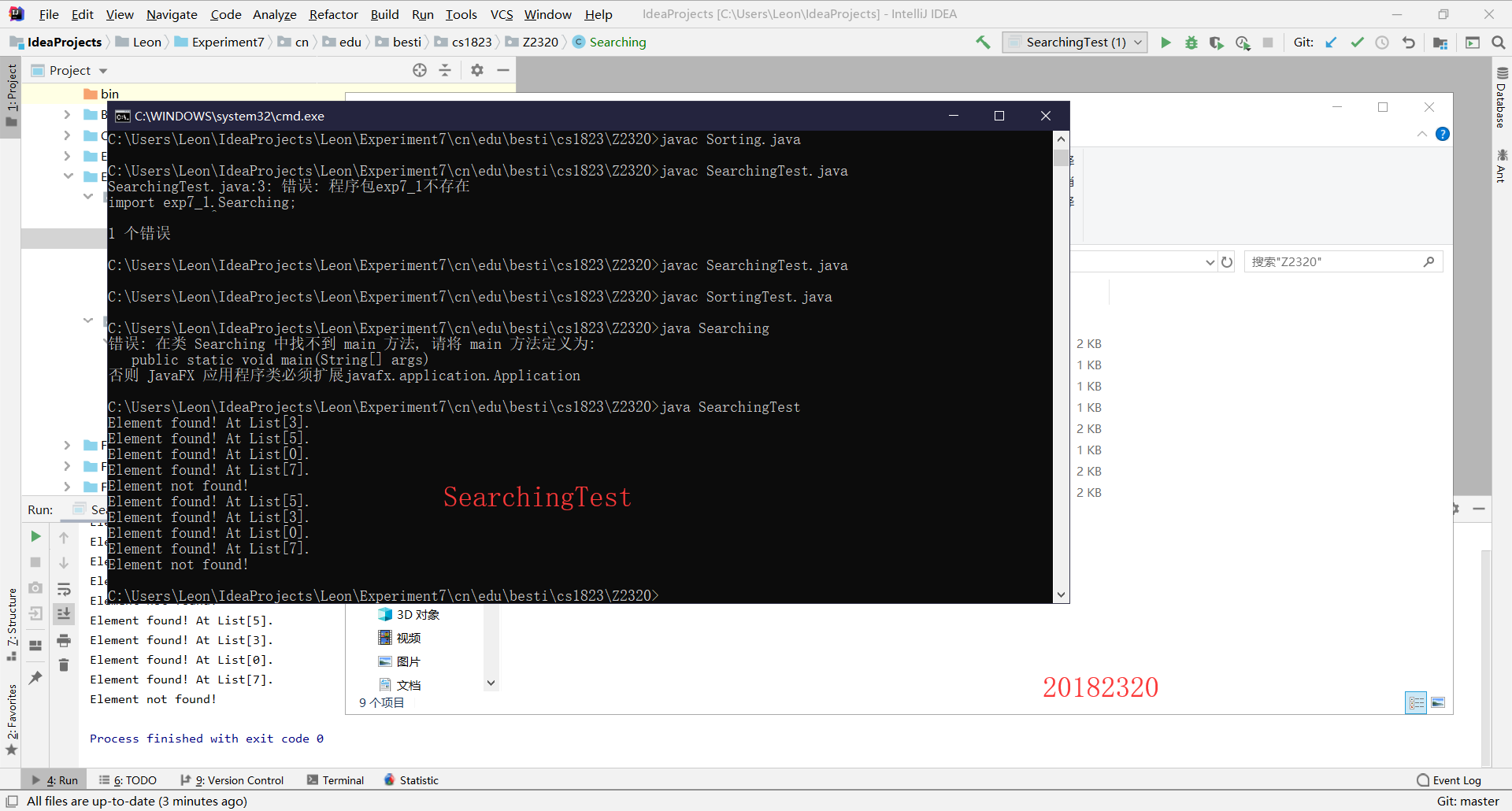
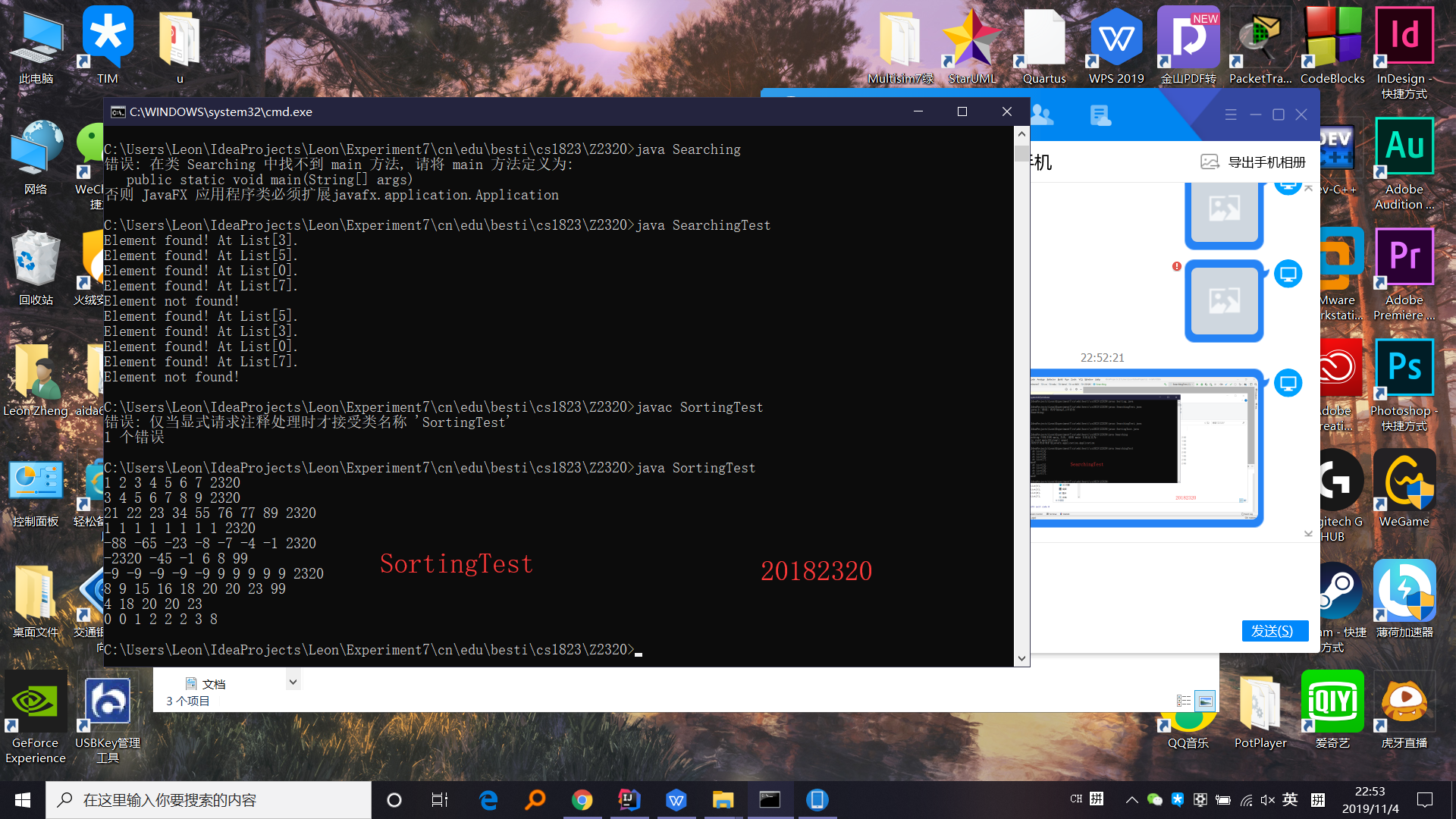
2.3
第一步:修改Searching类,添加二分查找、插入查找、斐波那契查找、二叉树查找和哈希查找的链地址实现,代码如下,各部分功能由注释解释
public class Searching {
private int List[];
private int searchElement;
private int listSize;
private int locate;
public Searching(int[] list, int searchElement) {
List = list;
this.searchElement = searchElement;
listSize= List.length;
}
//线性查找
public String linearSearch(){
for (int i=listSize-1;;i--){
if (searchElement==List[i]){
locate=i;
return "Element found! At List["+locate+"].";
}
else if (i==0){
return "Element not found!";
}
}
}
//二分法查找
public String binarySearch(){
int high=listSize-1;
int low=0;
int middle=(high+low)/2;
//调用Sorting方法排序
Sorting sorting=new Sorting(List);
while (low<=high){
if (List[middle]==searchElement){
locate=middle;
return "Element found! At List["+locate+"].";
}
else {
if (searchElement<List[middle]){
high=middle-1;
}
else {
low=middle+1;
}
}
}
return "Element not found!";
}
//插入查找
public String insertionSearch(int low,int high){
//调用Sorting方法排序
Sorting sorting=new Sorting(List);
if (low>high){
return "Element not found!";
}
int mid=low+(searchElement-List[low])/(List[high]-List[low])*(high-low);
if (List[mid]==searchElement){
locate=mid;
return "Element found! At List["+locate+"].";
}
else if (searchElement>List[mid]){
low=mid+1;
}
else if (searchElement<List[mid]){
high=mid-1;
}
return insertionSearch(low,high);
}
//斐波那契查找
//先建立斐波那契数组
private int maxSize=20;
public void Fibonacci(int F[]){
F[0]=0;
F[1]=1;
for (int i=2;i<maxSize;i++){
F[i]=F[i-1]+F[i-2];
}
}
//斐波那契查找方法
public int fibonacciSearching(){
int low=0;
int high=listSize-1;
//创建斐波那契数组
int F[]=new int[maxSize];
Fibonacci(F);
//计算n位于斐波那契数列的位置
int k=0;
while (listSize>F[k]-1){
k++;
}
int temp[]= Arrays.copyOf(List,F[k]);
for(int i=listSize;i<F[k]-1;++i){
temp[i]=List[listSize-1];
}
while(low<=high) {
int mid = low + F[k - 1] - 1;
if (searchElement < temp[mid]) {
high = mid - 1;
k -= 1;
} else if (searchElement > temp[mid]) {
low = mid + 1;
k -= 2;
} else {
if (mid < listSize)
return mid; //若相等则说明mid即为查找到的位置
else
return listSize - 1; //若mid>=n则说明是扩展的数值,返回n-1
}
}
return -1;
}
//二叉树查找
public boolean BinaryTreeSearching(){
//建立二叉树
BSTNode root=new BSTNode(List[0]);
BSTree bsTree=new BSTree(root);
locate=0;
for (int i=0;i<List.length;i++){
bsTree.add(List[i],root);
}
//开始查找
return bsTree.search(searchElement,root);
}
public void BlockSearch(){
int[] index = new int[]{10, 20, 30,2321};
BlockSearch blockSearch=new BlockSearch(index);
for (int i=0;i<List.length;i++){
blockSearch.insert(List[i]);
}
blockSearch.search(searchElement);
}
//哈希查找
public void hash_Chain(){
int defaultCapacity=100;
LinearNode<Integer>[] temp;
temp=new LinearNode[defaultCapacity];
//把数组用链地址法放入另一个数组中
for (int i=0;i<List.length;i++){
int locate=List[i]%11;
//检测扩容
if (locate>=defaultCapacity){
defaultCapacity=defaultCapacity*2;
LinearNode<Integer>[] larger=new LinearNode[defaultCapacity];
for (int j=0;i<temp.length;i++){
larger[j]=temp[j];
}
temp=larger;
}
LinearNode<Integer> b;
b=temp[locate];
if (b==null){
LinearNode<Integer> tempx=new LinearNode(List[i]);
temp[locate]=tempx;
}
else {
while (b!=null){
if (b.getNext()==null){
break;
}
b=b.getNext();
}
b.setNext(new LinearNode(List[i]));
}
}
//开始查找
int locate2=searchElement%11;
LinearNode<Integer>[] temp3=temp;
while (temp3[locate2]!=null){
if (temp3[locate2].getElement()==searchElement){
System.out.println("哈希链式查找:true");
break;
}
temp3[locate2]=temp3[locate2].getNext();
}
if (temp[locate2]==null){
System.out.println("哈希链式查找:false");
}
}
}
第二步:补充测试代码并运行
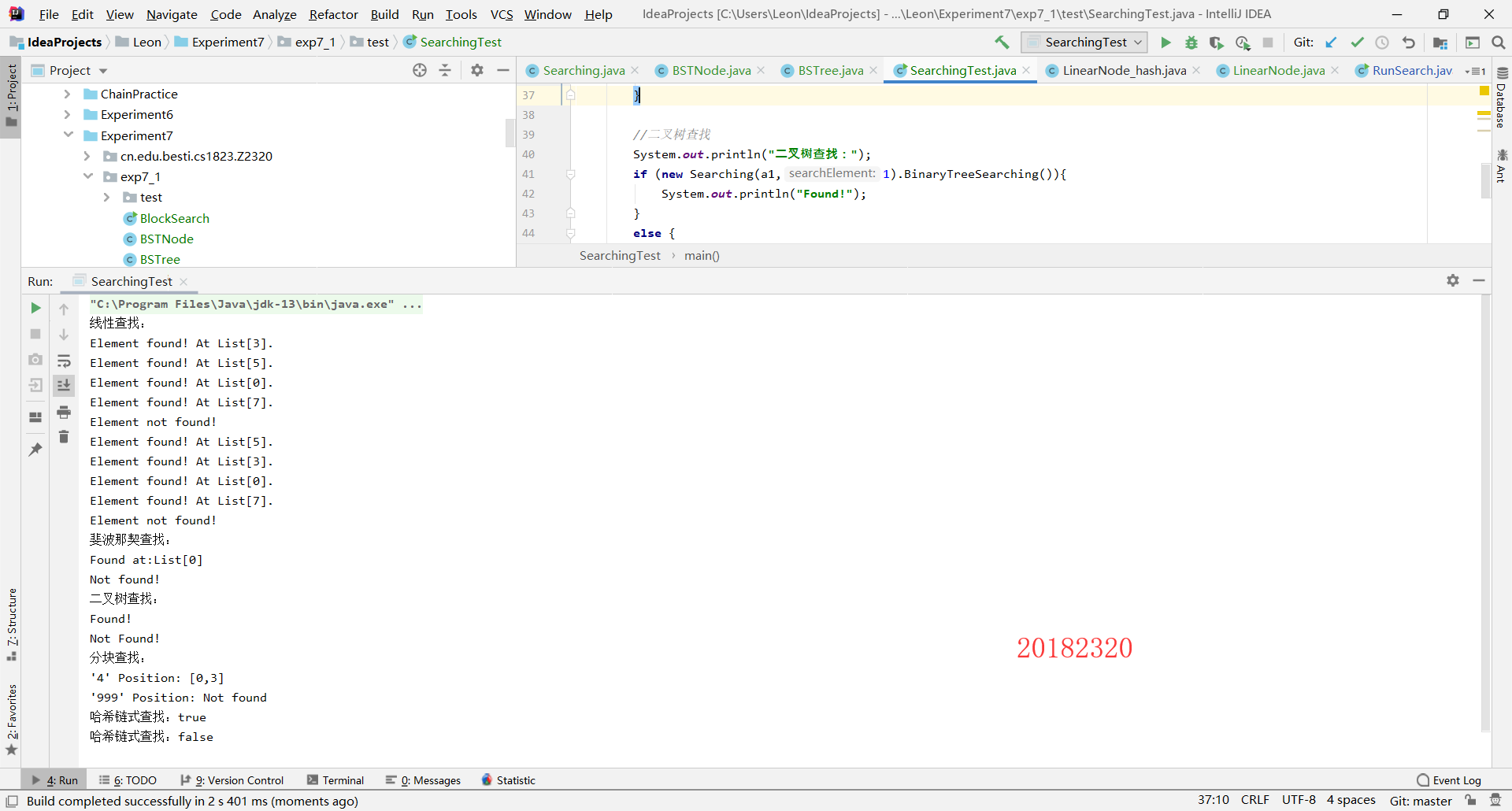
2.4
第一步:修改Sorting类,补充希尔排序、二分法排序、堆排序,代码如下
public class Sorting {
private static int List[];
private static int size;
private static String list="";
public Sorting(int[] list) {
List = list;
size=List.length;
}
//选择排序
public String selectionSort(){
int temp,tempx;
for (int i=0;i<size-1;i++){
temp=i;
for (int j=i+1;j<size;j++){
if (List[temp]>List[j]){
temp=j;
}
}
if (temp == 0) {
continue;
}
else {
tempx=List[i];
List[i]=List[temp];
List[temp]=tempx;
}
}
String string="";
for (int i=0;i<size;i++){
string=string+List[i]+" ";
}
return string;
}
//希尔排序
public String shellSort(){
int temp=List.length/2;
int first,last;
while (temp>0){
for (int i=0;i+temp<List.length-1;i++){
first=i;
last=i+temp;
if (List[first]>List[last]){
int temp2=List[first];
List[first]=List[last];
List[last]=temp2;
}
}
temp=temp/2;
}
String result="";
for (int i=0;i<List.length;i++){
result=result+List[i]+" ";
}
return result;
}
//二叉树排序
public void binarySort() throws Exception {
BSTNode roots = new BSTNode();
for (int number : List) {
roots.add(number);
}
System.out.println(roots.values());
}
//堆排序
public static void heapify(int[] arrays, int currentRootNode, int size) {
if (currentRootNode < size) {
//左子树和右字数的位置
int left = 2 * currentRootNode + 1;
int right = 2 * currentRootNode + 2;
//把当前父节点位置看成是最大的
int max = currentRootNode;
if (left < size) {
//如果比当前根元素要大,记录它的位置
if (arrays[max] < arrays[left]) {
max = left;
}
}
if (right < size) {
//如果比当前根元素要大,记录它的位置
if (arrays[max] < arrays[right]) {
max = right;
}
}
//如果最大的不是根元素位置,那么就交换
if (max != currentRootNode) {
int temp = arrays[max];
arrays[max] = arrays[currentRootNode];
arrays[currentRootNode] = temp;
//继续比较,直到完成一次建堆
heapify(arrays, max, size);
}
}
}
public static void maxHeapify(int[] arrays, int size) {
// 从数组的尾部开始,直到第一个元素(角标为0)
for (int i = size - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
heapify(arrays, i, size);
}
}
public static String dui(int[] arrays) {
for (int i = 0; i < arrays.length; i++) {
//每次建堆就可以排除一个元素了
maxHeapify(arrays, arrays.length - i);
//交换
int temp = arrays[0];
arrays[0] = arrays[(arrays.length - 1) - i];
arrays[(arrays.length - 1) - i] = temp;
}
String result="";
for(int i=0;i<arrays.length;i++)
{
result =result+ " "+arrays[i];
}
return result;
}
}
第二步:修改并运行测试代码
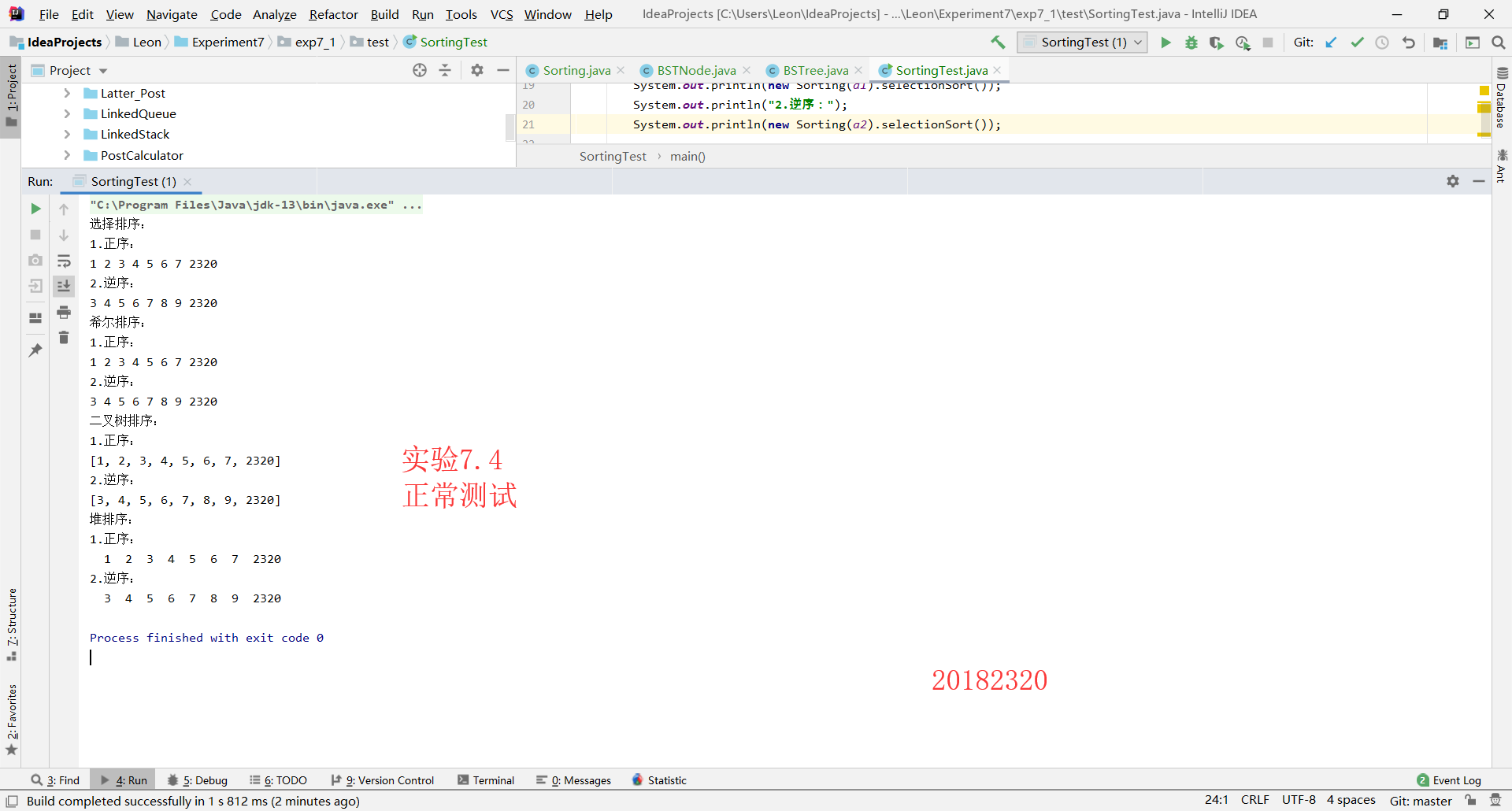
2.5
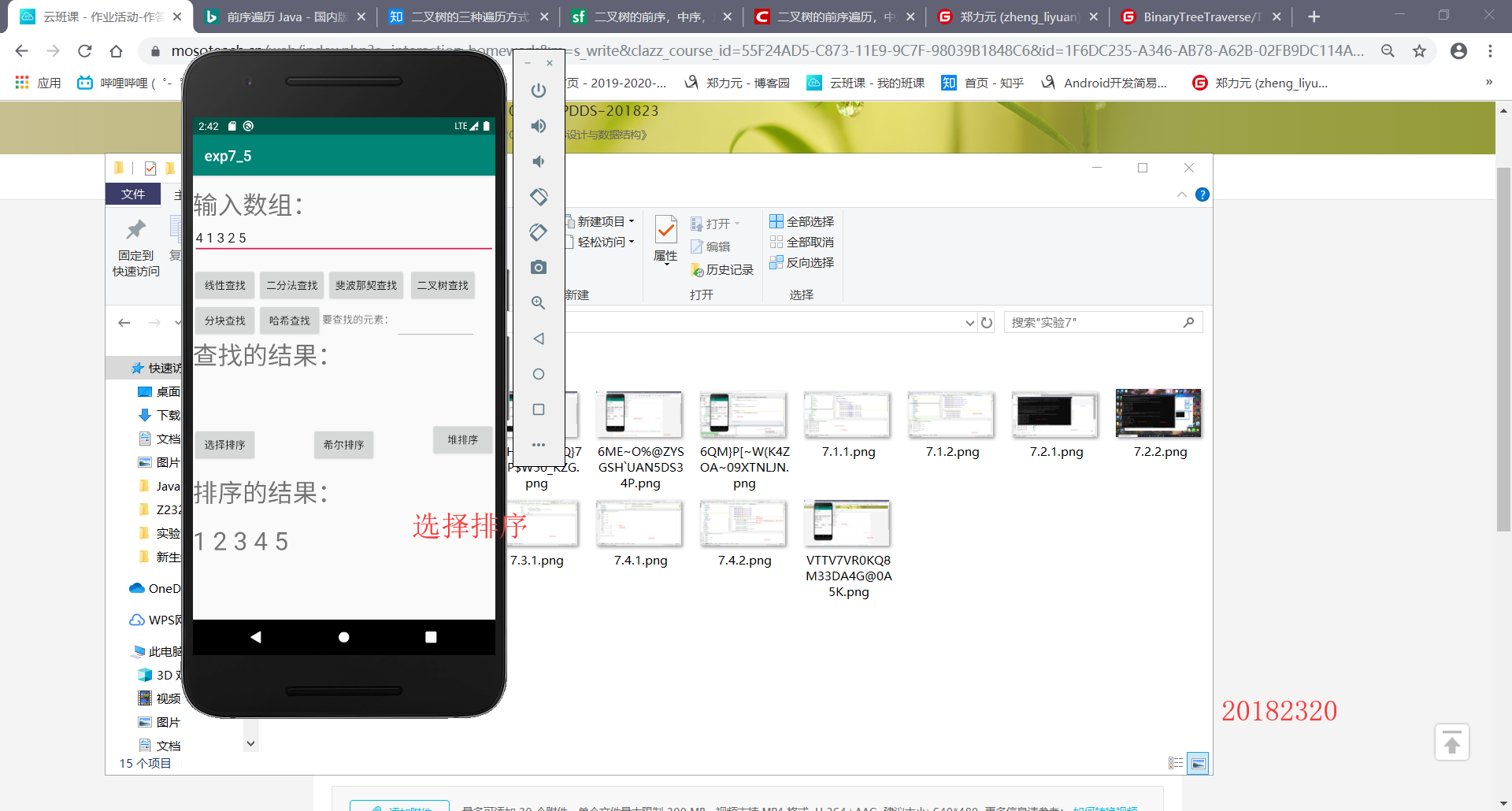
第一步:制作布局

第二步:将idea的代码除测试代码之外转移至AndroidStudio中
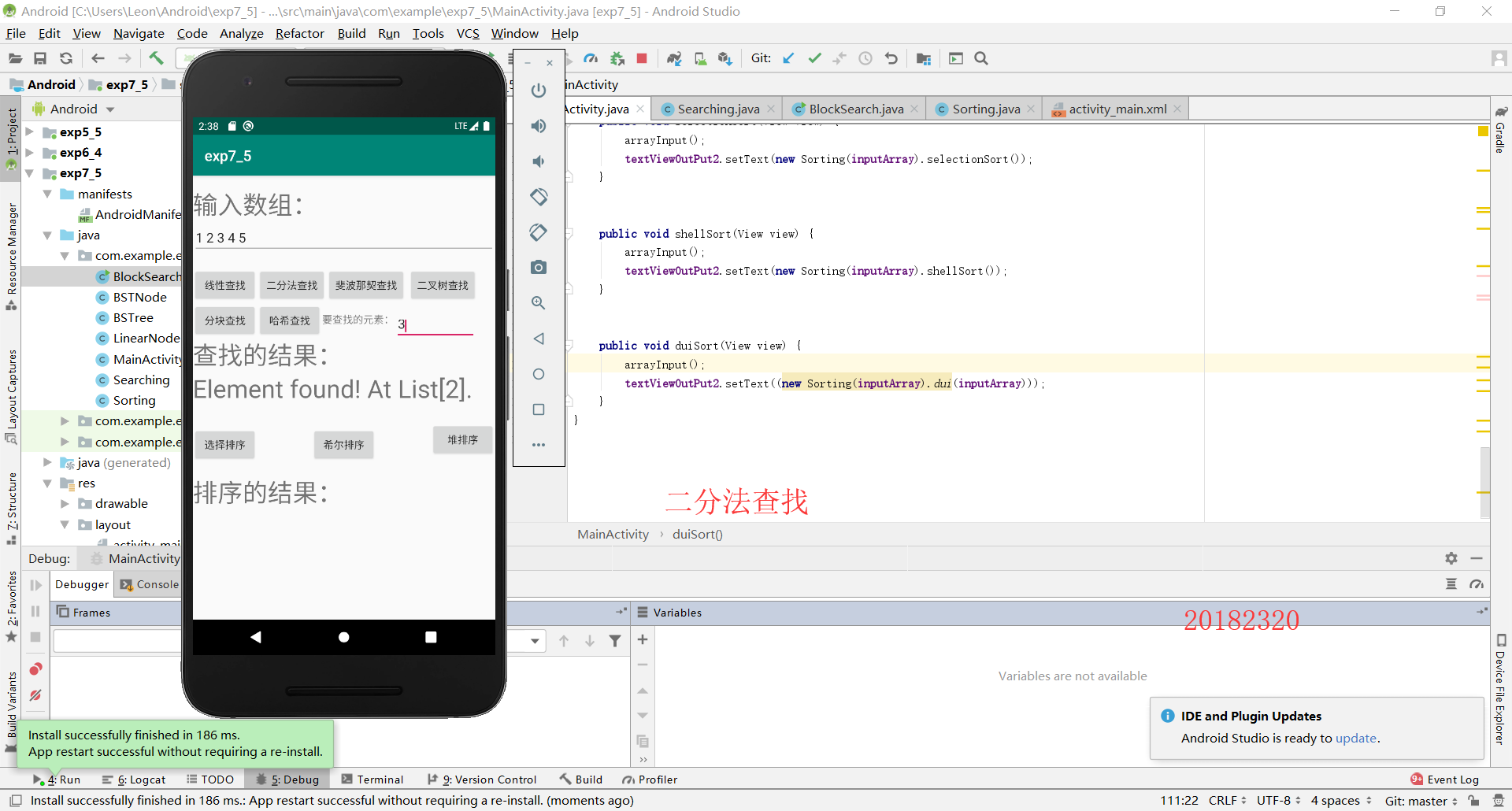
第三步:在MainActivity中实现布局的监听器的实现,和测试结果的输入输出,并运行
3. 实验过程中遇到的问题和解决过程
问题1:
在做实验7.2的时候,将idea的完整代码贴到系统中去运行,会出现编译不通过的现象。
问题1解决:
通过询问老师,发现是因为代码中含有import和package语句,出现了的打包调包的问题。删除代码中的全部import和package语句,才能正常运行。
其他(感悟、思考等)
这次的实验涉及到多种查找和排序的方法,不同的方法有不同的逻辑和效率,一般来说,越简单、越好理解的方法,效率不怎么高,所以当我们需要进行更高层次的编程工作的时候,就需要锻炼逻辑思维能力,掌握较为复杂但是能够提高程序性能的算法。