问题
I need to know a way to have Gaussian Distribution of 50 numbers. I know of the Boost library which generates random numbers. In my case i don't need random, i need the normal distribution of 50 numbers. Any way to have that? thanks.
回答1:
I think the OP was asking for a random number generator, in which the random numbers are not uniformly distributed (as is typical e.g. rand() in C) but are Gaussian distributed.
This short routine adapted from "Numerical Recipes in C" (Press et al, 1992) may be of use:
double grand() {
double r,v1,v2,fac;
r=2;
while (r>=1) {
v1=(2*((double)rand()/(double)RAND_MAX)-1);
v2=(2*((double)rand()/(double)RAND_MAX)-1);
r=v1*v1+v2*v2;
}
fac=sqrt(-2*log(r)/r);
return(v2*fac);
}
...ensure the relevant #includes are present for the math functions and rand, and that srand(time(NULL)) or similar has been called to appropriately seed the C rand() RNG.
回答2:
As of C++11 there is a normal (gaussian) distribution available in the standard library:
http://www.cplusplus.com/reference/random/normal_distribution/
The mean value and standard deviation are passed as arguments when creating it. The link above provides a good example:
// normal_distribution
#include <iostream>
#include <random>
int main()
{
const int nrolls=10000; // number of experiments
const int nstars=100; // maximum number of stars to distribute
std::default_random_engine generator;
std::normal_distribution<double> distribution(5.0,2.0);
int p[10]={};
for (int i=0; i<nrolls; ++i) {
double number = distribution(generator);
if ((number>=0.0)&&(number<10.0)) ++p[int(number)];
}
std::cout << "normal_distribution (5.0,2.0):" << std::endl;
for (int i=0; i<10; ++i) {
std::cout << i << "-" << (i+1) << ": ";
std::cout << std::string(p[i]*nstars/nrolls,'*') << std::endl;
}
return 0;
}
回答3:
If I got your question right you looking for the estimated normal distribution, that is for the sample mean
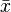 and the variance of the sample
and the variance of the sample  .
.
The former is calculated as:

and the latter as:

The sample mean can be used as expected value
 and the sample variance as
and the sample variance as  in the gaussian distribution:
in the gaussian distribution:

If you want more information check out:
- http://mathworld.wolfram.com/SampleVariance.html
- http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Sample_mean_and_sample_covariance
I hope that answered your question ;)
来源:https://stackoverflow.com/questions/17995894/normalgaussian-distribution-function-in-c