简介:
AC多模式匹配算法产生于1975年的贝尔实验室,最早使用于图书馆的书目查询程序中。该算法以有限状态自动机(FSA),以及KMP前缀算法 为基础.(有说法: ac自动机是KMP的多串形式,是一个有限自动机)
AC定义:
AC有限自动机 M 是1个6元组:M =(Q,∑,g,f,qo,F)其中:
1、Q是有限状态集(模式树上的所有节点).
2、∑是有限的输入字符表(模式树所有边上的字符).
3、g是转移函数.
4、f是失效函数,不匹配时自动机的状态转移.
5、qo∈Q是初态(根节点);
6、F量Q是终态集(以模式为标签的节点集).
AC有限状态自动机实现:
首先假设模式集合{he,she his,hers}, 输入字符串"ushers":
AC自动机算法主要建立三个函数,转向函数goto,失效函数failure和输出函数output(output 构造间杂在goto 构造以及failure构造中);
1、AC有限状态自动机M 操作循环框架:
a> 如果g(s,a) = s', 则自动机M 继续调用goto函数,以新状态s',以及新字符x为输入;如果状态s',匹配了某个模式,则输出;
b> 如果f(s,a) = failure, 则自动机M 调用failure状态转移f(s) = s',并以状态s',字符a 调用步骤1;
构造M伪代码:
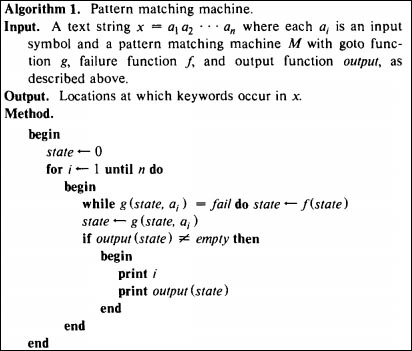
2、构造goto函数及输出函数output:
goto函数: 是一个状态在接受一个字符后转向另一个状态或者失败的函数(对应于FSA里的转移函数);
定义如下:
g(S,a) 其中S ∈ Q, a ∈ Σ :从当前状态S开始,沿着边上标签为a的路径所到的状态。假如状态节点(U,V)边上的标签为a,那么g(U,a)=V;如果根节点上出来的边上的标签没有a,则g(0,a)=O(失败),即如果没有匹配的字符出现,自动机停留在初态;如果不是根节点,且该节点出来的标签没有字符a,则g(U,a) = failure,称为失败;
下图(a)是用goto函数以{he,she his,hers}模式集构造的字符串模式匹配机:
状态0是初始状态,在状态0和状态1间的有向边标有字符'h',表示g(0,a) = 1;缺失的有向边表示失败,当任意字符σ != e或i,有g(1,σ) = failure;

注意: 所有字符有 g(0,σ) != failure, 状态0的这个属性确保 M 会处理输入的任意字符;任意字符σ不在以状态0开始有向边的字符,有g(0,σ) = 0;同时说明状态0的失效函数(failure) 没有意义,不用计算;
构造goto伪代码:

3、构造失效函数failure及输出函数output;
失效函数: 指的也是状态和状态之间一种转向关系,在goto失败(failure)的情况下使用的转换关系. 基本原理是KMP 算法的前缀函数;
下图(b)是各状态的失效函数值:

下图(c)是各状态i最终的output值:

首先,我们定义状态转移图(a)中状态s的深度为从状态0到状态s的最短路径。例如图(a)起始状态的深度是0,状态1和3的深度是1,状态2,4,和6的深度是2,等等。
计算思路:先计算所有深度是1的状态的失效函数值,然后计算所有深度为2的状态,以此类推,直到所有状态(除了状态0,因为它的失效函数没有定义)的失效函数值都被计算出。
计算方法:用于计算某个状态失效函数值的算法在概念上是非常简单的。首先,令所有深度为1的状态s的函数值为f(s) = 0。假设所有深度小于d的状态的f值都已经被算出了,那么深度为d的状态的失效函数值将根据深度小于d的状态的失效函数值来计算。
具体步骤:
为了计算深度为d 状态的失效函数值,假设深度为d-1的状态r,执行以下步骤:
Step1: 如果对所有字符a,有g(r, a) = fail,那么什么都不做;(好像是废话,这如果成立,说明状态r节点下面没有节点了,根本不需要计算)
Step2: 否则,对每个使g(r, a) = s成立的字符a,执行以下操作:
a) 记state = f(r);
b) 执行零次或者多次令state = f(state),直到出现一个state使得g(state, a) != fail; (注意到,因为对任意字符a,g(0, a) != fail,所以这种状态一定能够找到);
c) 记f(s) = g(state, a);
注意: 这里有点拗口,不好理解,一句话来说: 就是看当前状态节点前一个状态节点(父节点)的failure节点是否有当前字符的外向变,如果有,则当前状态failure状态就是对应外向变对应的节点;如果没有,则根据对应failure状态的failure状态;
举个例子:求图(a)中状态4 的failure 状态, 已知其前一个(父节点)的f(1)= 0,且状态0(根节点)有字符'h'的外向边,该外向边对应状态1,则有f(4) = 1;类似前缀规则:求已经匹配字串"sh" 最大后缀,同时是某个模式串的前缀;
failure 函数伪代码:

4、最后是遍历搜索:
状态机搜索过程中会有一种特殊情况:如果模式集中某个模式是另一个模式的子串,为了防止这种情况下漏掉子串模式,需要在这种子串的终态添加到长模式中;代码实现中就是某个状态的failure状态是某个终态,则当前状态也是终态,需要输出failure状态匹配的模式;
具体实现代码:
#include<iostream>
#include<string.h>
#include<malloc.h>
#include <queue>
using namespace std;
/* reallocation step for AC_NODE_t.outgoing array */
#define REALLOC_CHUNK_OUTGOING 2
struct ac_edge;
typedef struct node{
unsigned int id; /* Node ID : just for debugging purpose */
unsigned short depth; /* depth: distance between this node and the root */
struct node *parent; /*parent node, for compute failure function*/
struct node *failure_node; /* The failure node of this node */
short int final; /* 0: no ; 1: yes, it is a final node */
int patternNo; /*Accept pattern index: just for debugging purpose */
/* Outgoing Edges */
struct ac_edge* outgoing_edge;/* Array of outgoing character edges */
unsigned short outgoing_num; /* Number of outgoing character edges */
unsigned short outgoing_max; /* Max capacity of allocated memory for outgoing character edges */
}AC_NODE_t;
/* The Ougoing Edge of the Node */
struct ac_edge
{
char alpha; /* Edge alpha */
AC_NODE_t * next; /* Target of the edge */
};
static void node_assign_id (AC_NODE_t * thiz);
static AC_NODE_t * node_find_next(AC_NODE_t * pAc_node, char ch);
/******************************************************************************
* Create node
******************************************************************************/
AC_NODE_t *node_create()
{
AC_NODE_t* pNode = (AC_NODE_t*)malloc(sizeof(AC_NODE_t));
memset(pNode, 0, sizeof(AC_NODE_t));
pNode->failure_node = NULL;
pNode->parent = NULL;
pNode->final = 0;
/*init outgoing character edges*/
pNode->outgoing_max = REALLOC_CHUNK_OUTGOING;
pNode->outgoing_edge = (struct ac_edge *) malloc (pNode->outgoing_max*sizeof(struct ac_edge));
node_assign_id(pNode);
return pNode;
}
/******************************************************************************
* assign a unique ID to the node (used for debugging purpose).
******************************************************************************/
static void node_assign_id (AC_NODE_t * thiz)
{
static int unique_id = 0;
thiz->id = unique_id ++;
}
/******************************************************************************
* Establish an new edge between two nodes
******************************************************************************/
void node_add_outgoing (AC_NODE_t * thiz, AC_NODE_t * next, char alpha)
{
if(thiz->outgoing_num >= thiz->outgoing_max)
{
thiz->outgoing_max += REALLOC_CHUNK_OUTGOING;
thiz->outgoing_edge = (struct ac_edge *)realloc(thiz->outgoing_edge, thiz->outgoing_max*sizeof(struct ac_edge));
}
thiz->outgoing_edge[thiz->outgoing_num].alpha = alpha;
thiz->outgoing_edge[thiz->outgoing_num++].next = next;
}
/******************************************************************************
* Create a next node with the given alpha.
******************************************************************************/
AC_NODE_t * node_create_next (AC_NODE_t * pCur_node, char alpha)
{
AC_NODE_t * pNext_node = NULL;
pNext_node = node_find_next (pCur_node, alpha);
if (pNext_node)
{
/* The (labeled alpha) edge already exists */
return NULL;
}
/* Otherwise add new edge (node) */
pNext_node = node_create ();
node_add_outgoing(pCur_node, pNext_node, alpha);
return pNext_node;
}
/******************************************************************************
* Find out the next node for a given Alpha to move. this function is used in
* the pre-processing stage in which edge array is not sorted. so it uses linear search.
******************************************************************************/
static AC_NODE_t * node_find_next(AC_NODE_t * pAc_node, char ch)
{
int i = 0;
if(NULL == pAc_node)
{
return NULL;
}
for (i=0; i < pAc_node->outgoing_num; i++)
{
if(pAc_node->outgoing_edge[i].alpha == ch)
return (pAc_node->outgoing_edge[i].next);
}
return NULL;
}
/******************************************************************************
* add parent node's all leaf node(outgoing node) into queue
******************************************************************************/
int queue_add_leaf_node(AC_NODE_t *parent, queue<AC_NODE_t*> &myqueue)
{
int i;
for (i = 0; i < parent->outgoing_num; i++)
{
myqueue.push (parent->outgoing_edge[i].next);
}
return 0;
}
/******************************************************************************
* Initialize automata; allocate memories and add patterns into automata
******************************************************************************/
AC_NODE_t * ac_automata_create(char pattern[][255], int patterns_num)
{
int iPattern_index, iChar_index;
AC_NODE_t *root = node_create();
AC_NODE_t *pCur_node = NULL, *pNext_node = NULL;
char alpha;
for(iPattern_index=0; iPattern_index<patterns_num; iPattern_index++)
{
pCur_node = root;
for(iChar_index=0; iChar_index<strlen(pattern[iPattern_index]); iChar_index++) ///对每个模式进行处理
{
alpha = pattern[iPattern_index][iChar_index];
pNext_node = node_find_next(pCur_node, alpha);
if(NULL != pNext_node)
{
pCur_node = pNext_node;
}
else
{
pNext_node = node_create_next(pCur_node, alpha);
if(NULL != pNext_node)
{
pNext_node->parent = pCur_node;
pNext_node->depth = pCur_node->depth + 1;
pCur_node = pNext_node;
}
}
}
pCur_node->final = 1;
pCur_node->patternNo = iPattern_index;
}
return root;
}
/******************************************************************************
* find failure node for all node, actually failure function maps a state into a new state.
* the failure function is consulted whenever the goto function reports fail;
* specificialy compute the failue node, we use it's parent node's failure node
******************************************************************************/
int ac_automata_setfailure(AC_NODE_t * root)
{
int i =0;
queue<AC_NODE_t*> myqueue;
char edge_ch = '\0';
AC_NODE_t *pCur_node = NULL, *parent = NULL, *pNext_Node = NULL;
for(i= 0; i< root->outgoing_num; i++) //f(s) = 0 for all states s of depth 1
{
root->outgoing_edge[i].next->failure_node = root;
}
queue_add_leaf_node(root, myqueue);
while(!myqueue.empty())
{
parent = myqueue.front();
myqueue.pop();
queue_add_leaf_node(parent, myqueue);
for(i = 0; i < parent->outgoing_num; i++)
{
edge_ch = parent->outgoing_edge[i].alpha;
pCur_node = parent->outgoing_edge[i].next;
pNext_Node = node_find_next(parent->failure_node, edge_ch);
if(NULL == pNext_Node)
{
if(parent->failure_node == root)
{
pCur_node->failure_node = root;
}
else
{
parent = parent->failure_node->parent;
}
}
else
{
pCur_node->failure_node = pNext_Node;
}
}
}
return 0;
}
/******************************************************************************
* Search in the input text using the given automata.
******************************************************************************/
int ac_automata_search(AC_NODE_t * root, char* text, int txt_len, char pattern[][255])
{
AC_NODE_t *pCur_node = root;
AC_NODE_t *pNext_node = NULL;
int position = 0;
while(position < txt_len)
{
pNext_node = node_find_next(pCur_node, text[position]);
if (NULL == pNext_node)
{
if(pCur_node == root)
{
position++;
}
else
{
pCur_node = pCur_node->failure_node;
}
}
else
{
pCur_node = pNext_node;
position++;
}
if(pCur_node->final == 1) ///some pattern matched
{
cout<<position-strlen(pattern[pCur_node->patternNo])<< '\t' << '\t' <<pCur_node->patternNo<< '\t' << '\t' <<pattern[pCur_node->patternNo]<<endl;
}
}
return 0;
}
/******************************************************************************
* Prints the automata to output in human readable form.
******************************************************************************/
void ac_automata_display (AC_NODE_t * root)
{
unsigned int i;
AC_NODE_t * pCur_node = root;
struct ac_edge * pEdge = NULL;
if(root == NULL)
{
return;
}
printf("---------------------------------\n");
queue<AC_NODE_t*> myqueue;
myqueue.push( pCur_node );
while(!myqueue.empty())
{
pCur_node = myqueue.front();
myqueue.pop();
printf("NODE(%3d)/----fail----> NODE(%3d)\n", pCur_node->id, (pCur_node->failure_node)?pCur_node->failure_node->id:0);
for (i = 0; i < pCur_node->outgoing_num; i++)
{
myqueue.push (pCur_node->outgoing_edge[i].next);
pEdge = &pCur_node->outgoing_edge[i];
printf(" |----(");
if(isgraph(pEdge->alpha))
printf("%c)---", pEdge->alpha);
else
printf("0x%x)", pEdge->alpha);
printf("--> NODE(%3d)\n", pEdge->next->id);
}
printf("---------------------------------\n");
}
}
/******************************************************************************
* Release all allocated memories to the automata
******************************************************************************/
int ac_automata_release(AC_NODE_t * root)
{
if(root == NULL)
{
return 0;
}
queue<AC_NODE_t*> myqueue;
AC_NODE_t *pCur_node = NULL;
myqueue.push( root );
root = NULL;
while(!myqueue.empty())
{
pCur_node = myqueue.front();
myqueue.pop();
for (int i = 0; i < pCur_node->outgoing_num; i++)
{
myqueue.push (pCur_node->outgoing_edge[i].next);
}
free(pCur_node);
}
return 0;
}
int main()
{
unsigned int i = 0;
char haystack[] = "ushers";
char needle[4][255]={"he","she", "his","hers"};
/* 1. create ac finite state automata match machine, compute goto and output func*/
AC_NODE_t *root = ac_automata_create(needle, sizeof(needle)/sizeof(needle[0]));
/* 2. compute failure function*/
ac_automata_setfailure( root );
/* 3. Display automata (if you are interested)*/
ac_automata_display( root );
cout << endl << "haystack : " << haystack << endl;
cout << "needles : ";
for(i = 0; i<sizeof(needle)/sizeof(needle[0]); i++)
{
cout << needle[i] << " ";
}
cout << endl << endl;
cout << "match result : " << endl << "position\t" << "node_id\t\t" << "pattern" << endl;
/* 3. seaching multi patterns use automata*/
ac_automata_search(root, haystack, strlen(haystack), needle);
/* 4. Release the automata */
ac_automata_release ( root );
return 0;
}后记:
根据不同的AC_NODE结构设计,实现会有些不同,但原理一样;
可以改进的地方:
1、可以把同深度节点排序,后面查找某状态的指定字符外向边状态,可以使用二分查找,加快速度;
2、这里的AC_NODE 里面每个节点只对应一个匹配模式(patternNo),理论上是有多个的匹配模式的,有待完善;
3、已知g(4,e) = 5; 假设M 当前状态为4, 且下一个字符不是'e',这时候M 会调用f(4)=1,其实这时候我们已经不需要去查找状态1以'e'为外向边的状态了,因为下一个字符确定不是'e';如果没有"his"模式,我们可以直接从状态1跳到状态0;而现在代码是会去做这个多余查找动作的。这个可以用确定有限自动机来避免,下篇文章我会详细和大家讨论下.
有任何问题,还请不吝赐教~
references:
<1>、Efficient String Matching: An Aid to Bibliographic Search.pdf(june 1975)
<2>、http://blog.csdn.net/sunnianzhong/article/details/8832496
<3>、http://blog.csdn.net/sealyao/article/details/4560427
<4>、http://www.it165.net/pro/html/201311/7860.html
<5>、http://sourceforge.net/projects/multifast/
<6>、多模式匹配算法的研究.pdf
<7>、模式匹配算法在网络入侵系统中的应用研究.pdf
来源:oschina
链接:https://my.oschina.net/u/227203/blog/196426