Basically, an installation of Tomcat is running under the default JRE which can be found based on environment variables (
JAVA_HOME
), or registry entries (on Windows) or the JRE is specified during installation (Tomcat is installed as a service). Sometimes we need to change the default JRE for Tomcat, either for testing purposes or to run Tomcat under a targeted version of JRE. In this article, we summarize different ways to change JRE for a Tomcat installation.
To know which JRE version is used for Tomcat, go to the following URL:
 On Windows, create the
setenv.bat
file with the following content:
On Windows, create the
setenv.bat
file with the following content:
On *nix, create the
setenv.sh
file with the following content:
Note that this way only works with Tomcat installed from a zip distribution. It doesn’t apply for Tomcat installed as a service. Behind the scenes, the Tomcat’s start up script (
startup.bat
/
startup.sh
) will invoke the “setenv” script if it is present. One advantage of this way is that it doesn’t affect the system environment variables.
 This way is very simple to perform, and it does not depend on the system environment variables
JAVA_HOME
or
JRE_HOME
.
This way is very simple to perform, and it does not depend on the system environment variables
JAVA_HOME
or
JRE_HOME
.
 The
Edit Server Runtime Environment
dialog appears, select the targeted JRE version under the JRE list:
The
Edit Server Runtime Environment
dialog appears, select the targeted JRE version under the JRE list:
 Click
Finish
to close this dialog, and click
OK
to close the Preferences dialog. Now restart Tomcat to see the effect. Note that we can spot the JRE version by looking at the
Console
view as shown below:
Click
Finish
to close this dialog, and click
OK
to close the Preferences dialog. Now restart Tomcat to see the effect. Note that we can spot the JRE version by looking at the
Console
view as shown below:

localhost:8080/manager/status
And look at the JVM Version column: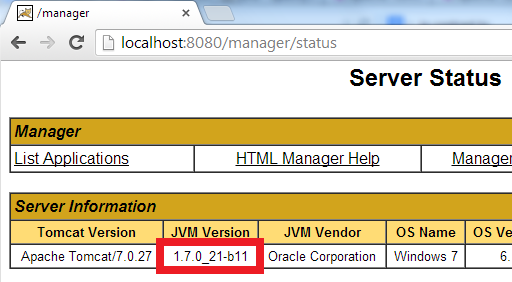
1. Changing JRE by updating JAVA_HOME or JRE_HOME
This way is very simple to implement but it works only for Tomcat installed from a zip distribution (in contrast to Tomcat installed as a service).-
- If only the JAVA_HOME environment variable is set, Tomcat will run under the JRE as part of the JDK specified by theJAVA_HOME variable. Therefore, we change JRE for Tomcat by updating this variable.
- If both the JAVA_HOME and JRE_HOME environment variables are set, the JRE_HOME is preferred. Here’s an example of a valid value for the JRE_HOME variable (path on Windows):
JRE_HOME=C:\Program Files\Java\jre7
Notice that updating the JAVA_HOME or JRE_HOME environment variables will affect all the applications that depend on them, so if you want to look for a more independent approach, see the second way as described below.2. Changing JRE by using “setenv” script
We can change the JRE for Tomcat by setting the JRE_HOME variable in a script file called setenv.bat (on Windows) or setenv.sh (on *nix). This file does not exist by default, so create such file and place it under CATALINA_BASE\bin directory ( CATALINA_BASE is the Tomcat installation directory).|
1
2
|
set "JRE_HOME=C:\Program Files\Java\jdk1.7.0_03\jre"
exit /b 0
|
|
1
2
|
JRE_HOME=/usr/java/jdk1.7.0_03/jre
CATALINA_PID="$CATALINA_BASE/tomcat.pid"
|
3. Changing JRE in Tomcat service manager
For a Tomcat installation which is installed as a service (on Windows), we can change the version of JRE that runs Tomcat by configuring the Java Virtual Machine setting in the Tomcat service manager program (e.g. Tomcat7w.exe), as shown in the following screenshot: This way is very simple to perform, and it does not depend on the system environment variables
JAVA_HOME
or
JRE_HOME
.
This way is very simple to perform, and it does not depend on the system environment variables
JAVA_HOME
or
JRE_HOME
.
4. Changing JRE in Eclipse IDE
If you are using Tomcat inside Eclipse IDE, changing the JRE version for Tomcat is also pretty easy. By default, Tomcat is running under the same JRE as Eclipse (Workbench default JRE). To change JRE version for a Tomcat runtime in Eclipse, go to the menu Window > Preferences . In the Preferences dialog, open the Server > Runtime Environments node, select a Tomcat version in the list, and then click the Edit button: The
Edit Server Runtime Environment
dialog appears, select the targeted JRE version under the JRE list:
The
Edit Server Runtime Environment
dialog appears, select the targeted JRE version under the JRE list:
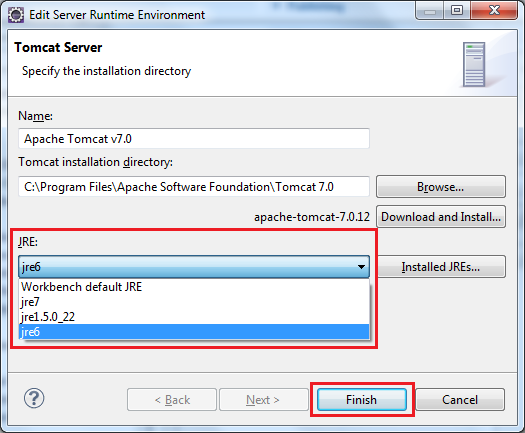 Click
Finish
to close this dialog, and click
OK
to close the Preferences dialog. Now restart Tomcat to see the effect. Note that we can spot the JRE version by looking at the
Console
view as shown below:
Click
Finish
to close this dialog, and click
OK
to close the Preferences dialog. Now restart Tomcat to see the effect. Note that we can spot the JRE version by looking at the
Console
view as shown below:
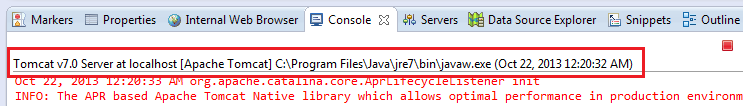
来源:oschina
链接:https://my.oschina.net/u/1433107/blog/544496