性质
基本性质:二叉树_百度百科
关于二叉树的深度(高度)涉及到结点的层数,有的教材规定根结点在第\(0\)层,有的则规定根结点在第\(1\)层。
这里全部以《数据结构-C语言版》(严蔚敏,吴伟民版)为准:高度和深度为同一个概念,根节点在第1层,树的高度是看一共有几层。 高度为\(h\)的完全二叉树,最多有\(2^{n}-1\)个节点,第\(k\)层最多有\(2^{k-1}\)个节点。 含有\(n\)个节点的完全二叉树,高度为\(log(n)+ 1\)下取整。
完全二叉树:
如果第一个元素下标为\(1\),则第\(k\)个元素的左孩子为\(2*k\),右孩子为\(2*k+1\),父节点为 \(k / 2\) 下取整,最后一个父节点为 \(length / 2\) 下取整。
如果第一个元素下标为\(0\),则第\(k\)个元素的左孩子为\(2*k+1\),右孩子为\(2*k+2\),父节点为 \((k - 1)/ 2\) 下取整,最后一个父节点为 \(length / 2\) 下取整后减一。
二叉树的前驱后继节点,表示中序遍历时,一个节点的前一个和后一个。
高度为\(h\)的完全二叉树,最多有\(2^{h}-1\)个节点。
节点为\(n\)的完全二叉树,高度为\(log(n)\)。
二叉树的遍历
二叉树的有三种遍历方式,先中后序遍历,“先、中、后”表示根节点的遍历次序。
先序:先遍历分支的根节点,再遍历左子树,最后遍历右子树。
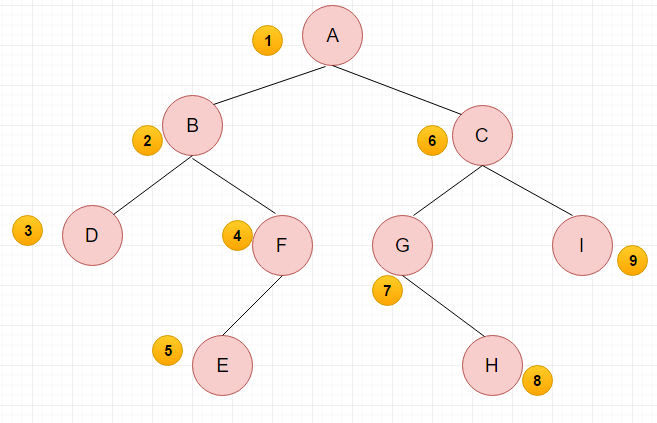
先序序列:\(ABDFECGHI\)
中序:先遍历分支的左子树,再遍历根节点,最后遍历右子树。
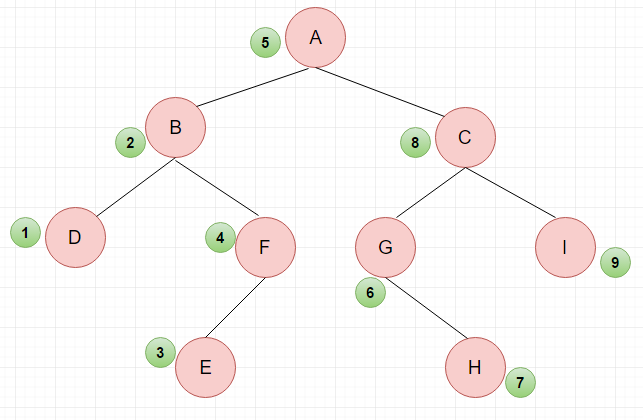
中序序列:\(DBEFAGHCI\)
后序:先遍历分支的左子树,再遍历右子树,最后遍历根节点。
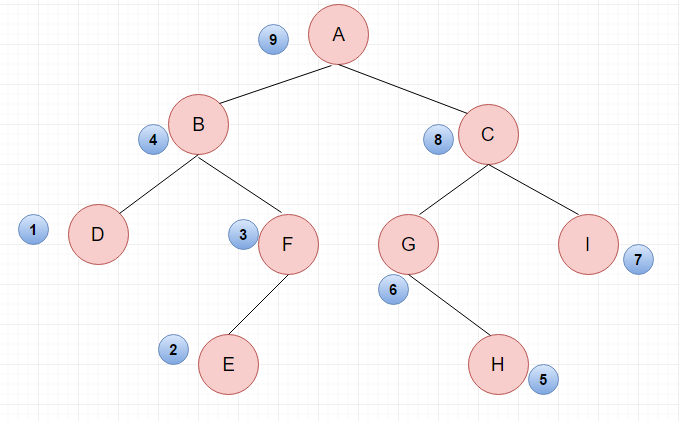
后序序列:\(DEFBHGICA\)
二叉树遍历的实现
后序遍历非递归,是借用两个栈A,B,用A栈访问,压栈顺序为中左右(先序为中右左),把这些节点再存到B栈里,最后一起出栈。
//先序
void preorderUnRecur(BTree T) {
stack<BTree>s;
s.push(T);
while (!s.empty()) {
T = s.top();
s.pop();
cout << T->data << " ";
if (T->Right)
s.push(T->Right);
if (T->Left)
s.push(T->Left);
}
cout << endl;
}
//中序
void inorderUnRecur(BTree T) {
if (!T)return;
stack<BTree>s;
while (!s.empty() || T) {
if (T) {
s.push(T);
T = T->Left;
}
else {
T = s.top(); s.pop();
cout << T->data << " ";
T = T->Right;
}
}
cout << endl;
}
//后序
void postorderUnRecur(BTree T) {
if (!T)return;
stack<BTree>s1,s2;
s1.push(T);
while (!s1.empty()) {
T = s1.top(); s1.pop();
s2.push(T);
if (T->Left)s1.push(T->Left);
if (T->Right)s1.push(T->Right);
}
while (!s2.empty()) {
cout << s2.top()->data << " ";
s2.pop();
}
cout << endl;
}
递归实现,相比来说就比较简单了:
void Inorder(BTree t) {
if (!t)return;
Inorder(t->Left);
cout << t->data << " ";
Inorder(t->Right);
}
void Preorder(BTree t) {
if (!t)return;
cout << t->data << " ";
Preorder(t->Left);
Preorder(t->Right);
}
void Postorder(BTree t) {
if (!t)return;
Postorder(t->Left);
Postorder(t->Right);
cout << t->data << " ";
}
二叉树的构建
二叉树的建立一般有两种方法:
(1)用数组的方式,或者一个个输入,按照节点的顺序,用一个特殊值(比如0,# )表示当前位置没有节点。但这样总归是会出现冲突的,比如某个节点的值就是0, # 的ASCII值。就不做写了。
(2)给定包含中序序列的两个序列。以下为 给定前序、中序序列时,创建二叉树。
通过包含中序序列(只有前后序列创建出的二叉树不唯一)的两个序列可以推出唯一的二叉树。
typedef struct BTNode
{
int data;
struct BTNode* Left;
struct BTNode* Right;
}*BTree;
void PreAndInToPost(int* pre, int* in, int length) {
if (length == 0) return;
int rootIndex;
BTree BT = new BTNode;
BT->data = *pre;
for (rootIndex = 0; in[rootIndex] != *pre; rootIndex++);
PreAndInToPost(pre + 1, in, rootIndex);
PreAndInToPost(pre + rootIndex + 1, in + rootIndex + 1, length - (rootIndex + 1));
cout << BT->data << " ";
}
void PostAndInToPre(int* in, int* post, int length) {
if (length == 0) return;
int rootIndex;
BTree BT = new BTNode;
BT->data = *(post + length - 1);
for (rootIndex = length - 1; in[rootIndex] != *(post + length - 1); rootIndex--);
cout << BT->data << " ";
PostAndInToPre(in, post, rootIndex);
PostAndInToPre(in + rootIndex + 1, post + rootIndex, length - (rootIndex + 1));
}
完整测试代码如下:
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
typedef char ElemType;
typedef struct BTNode
{
ElemType data;
struct BTNode* Left;
struct BTNode* Right;
}*BTree;
BTree creat_tree_from_pre_inorder(ElemType* pre, ElemType* in, int length) {
if (length == 0) return NULL;
int rootIndex;
BTree BT = new BTNode;
//将当前根节点入树
BT->data = *pre;
for (rootIndex = 0; in[rootIndex] != *pre; rootIndex++);
BT->Left = creat_tree_from_pre_inorder(pre + 1, in, rootIndex);
BT->Right = creat_tree_from_pre_inorder(pre + rootIndex + 1, in + rootIndex + 1, length - (rootIndex + 1));
return BT;
}
BTree creat_tree_from_post_inorder(ElemType* in, ElemType* post, int length) {
if (length == 0) return NULL;
int rootIndex;
BTree BT = new BTNode;
//将当前根节点入树
BT->data = *(post + length - 1);
for (rootIndex = length - 1; in[rootIndex] != *(post + length - 1); rootIndex--);
BT->Left = creat_tree_from_post_inorder(in, post, rootIndex);
BT->Right = creat_tree_from_post_inorder(in + rootIndex + 1, post + rootIndex/*删掉post的最后一个*/, length - (rootIndex + 1));
return BT;
}
void Inorder(BTree BT) {
if (!BT)return;
Inorder(BT->Left);
cout << BT->data << " ";
Inorder(BT->Right);
}
void Preorder(BTree BT) {
if (!BT)return;
cout << BT->data << " ";
Preorder(BT->Left);
Preorder(BT->Right);
}
void Postorder(BTree BT) {
if (!BT)return;
Postorder(BT->Left);
Postorder(BT->Right);
cout << BT->data << " ";
}
int main() {
char pre[] = "ABDGHCEIF";
char in[] = "GDHBAEICF";
char post[] = "GHDBIEFCA";
BTree T1 = creat_tree_from_pre_inorder(pre, in, strlen(in));
BTree T2 = creat_tree_from_post_inorder(in, post, strlen(in));
Postorder(T1);
cout << endl;
Preorder(T1);
cout << endl;
return 0;
}
相关小算法
获取二叉树的深度
int height(BTree T) {
if (T == NULL)
return 0;
int left = height(T->Left);
int right = height(T->Right);
return left >= right ? left + 1 : right + 1;
}